The direct potentiometric method used in water quality detection is a quantitative analysis method by measuring the electromotive force in the galvanic cell. In the potentiometric method, the galvanic cell consists of two electrodes. An indicator electrode, its potential will change with the concentration of the measured ion, it can indicate the concentration of the measured ion. The other is the reference electrode, whose potential is not affected by changes in the composition of the test solution and has a relatively constant value. When the indicator electrode and the reference electrode are immersed in the galvanic cell composed of the test sample, the concentration of the measured ion can be obtained by measuring the electromotive force of the galvanic cell and using the basic formula of the electrode potential.
1. Classification of indicator electrodes used in water quality testing
1) The first type of electrode consists of metal immersed in a solution of the same metal ion. This type of electrode can reflect the change of cation concentration. For example, silver wire is inserted into the silver wire solution to form a silver electrode. The electrode reaction and potential are
Ag+ + e=Ag E= E0 +0.0591[Ag+]
This silver electrode can be used not only to measure the concentration of silver ions, but also to potentiometric titration of changes in the concentration of silver ions caused by reactions such as precipitation or coordination.
2) The second type of electrode consists of an anion solution of metal and its insoluble salt. This type of electrode can indirectly reflect the concentration of anions that form insoluble salts with metal ions, such as Ag-AgCl electrodes can be used to determine the concentration of C. The electrode reaction and potential reaction are as follows
AgCl + e-= Ag+Cl- E=E0AgCl/Ag-00591[CI]
3) The inert metal electrode consists of a stable inert metal, such as platinum electrode. In the solution, the electrode itself does not participate in the reaction, only as a conductor, is the place where the oxidized state and the reduced state of the substance exchange electrons. It can show the equilibrium potential of the redox system in the solution. For example, a platinum wire is inserted into a solution containing Fe3+ and Fe2+ to form an inert platinum electrode, and its electrode reaction and electrode potential are: Fe3+ + e- = Fe2+
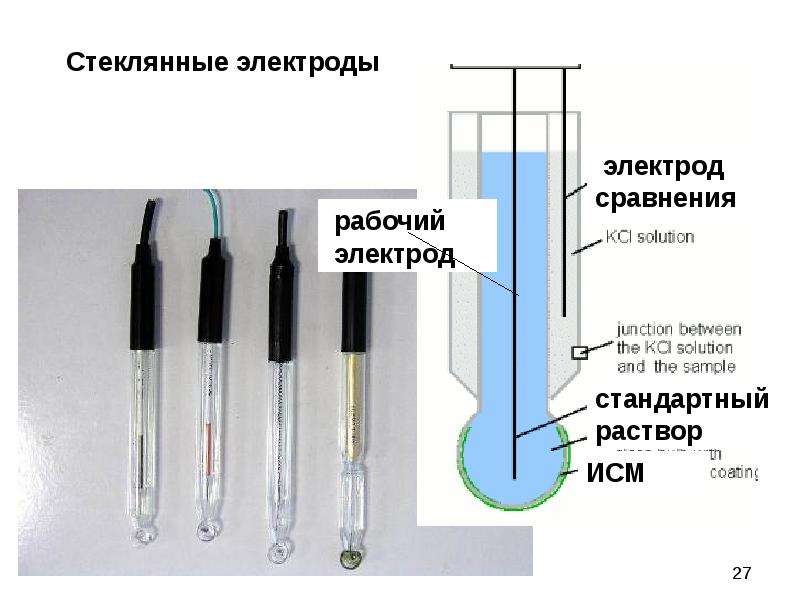
4) Membrane electrode This type of electrode uses a solid or liquid membrane as a sensor, which can indicate the concentration of a certain ion in the solution. The membrane potential and ion concentration conform to the Nernst equation. However, the generation mechanism of membrane electrodes is different from the above-mentioned various types of electrodes. There is no electron transfer on the electrodes, and the generation of electrode potential is the result of ion exchange and diffusion. Various ion selective electrodes belong to this type of indicator electrodes, such as glass electrodes.
2. The reference electrode used in water quality testing
The reference electrode is a relative standard for measuring the electrode potential. Therefore, the electrode potential of the reference electrode is required to be constant and reproducible. The standard hydrogen electrode is usually used as the primary standard of the reference electrode. However, due to the inconvenience of preparation and use, it has rarely been used as a reference electrode. The porous material is replaced by calomel electrode and silver-silver chloride electrode, which are easy to prepare, and convenient to use.
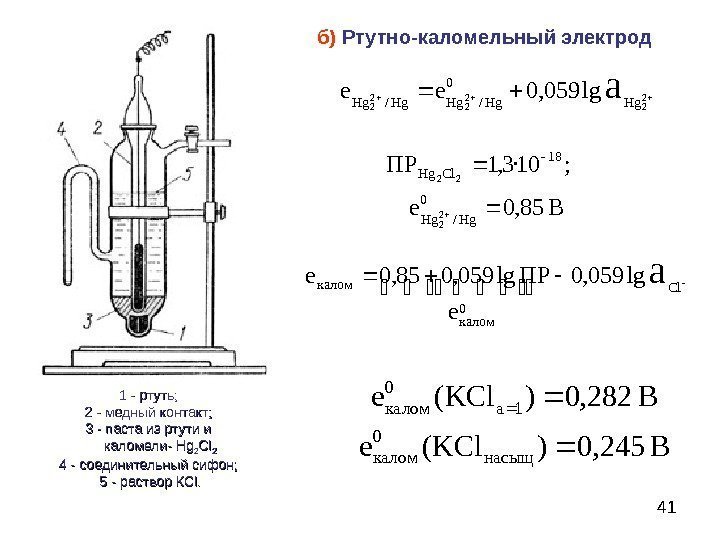
The calomel electrode is most commonly used in actual work, which is composed of metallic mercury, calomel Hg2Cl2 and KCl solution. The electrode consists of two glass sleeves made of glass porous material. A platinum wire is sealed in the inner glass tube, inserted into pure mercury, and a layer of calomel and mercury mixed paste is placed underneath. The outer glass tube is filled with KCl solution. The contact part between the lower end of the electrode and the solution to be tested is a microporous material such as a biscuit ceramic core or a glass sand core, which forms a path connecting the solutions to each other
Calomel electrode electrode reaction is: Hg2 Cl2+2eF 2Hg+2CI
The electrode potential is: E=E-0.0591[C1] or E=E0+0.0591CcL-



