
Method of measuring BOD5
①Dilution method
For some domestic sewage, industrial waste water, and seriously polluted surface water, because it contains more organic matter, it needs to be diluted and then cultured for determination to reduce its concentration and ensure sufficient dissolved oxygen.During the measurement, two equal aliquots of the diluted water sample were taken, one to determine the dissolved oxygen value of the day, and the other to determine the dissolved oxygen value after incubating in an incubator at 20 degrees Celsius for 5 days. Calculate the value of BOD5 according to the difference between the two parameters before and after. The calculation formula of BOD5 is as follows:
(D1-D2)-(B1-B2)f1/f2
In the formula, D1 and D2 refer to the dissolved oxygen mass concentration of the water sample before and after the culture after dilution.
B1, B2 refer to the mass concentration of dissolved oxygen in pure diluted water before and after incubation.
f1 and f2 refer to the proportion of dilution water and water sample in the culture flask.
For clean surface water with high dissolved oxygen content and low organic content, if the BOD5 is not greater than 6mg/L, it can be directly measured without dilution. For water samples with a large BOD5 value, it needs to be diluted. After 5 days of incubation, the dissolved oxygen is greater than 2mg/L, and the remaining dissolved oxygen is above 1mg/L to be determined. In the case of a relatively fixed degree of contamination of the water sample, such as routine analysis in a factory laboratory, some skilled water quality testers can use experience to determine the dilution factor. Under such operating conditions, it is necessary to take water samples of three dilution multiples during testing. After comparing the final analysis results of the three water samples, take one of the appropriate dilution multiples to calculate the BOD5 value.
In order to ensure that the water sample has enough dissolved oxygen after dilution, the diluted water sample is usually aerated with air to make the dissolved oxygen in the diluted water close to saturation. Inorganic nutrients and buffer substances, such as phosphate, calcium, magnesium, and iron salts, should also be added to the dilution water to ensure the growth of microorganisms.
For industrial wastewater containing no or less microorganisms, such as acidic wastewater, alkaline wastewater, high-temperature wastewater, and chlorine-treated wastewater, it is necessary to introduce microorganisms that can decompose organics in the wastewater during BOD5 detection.
②Determination method of water quality detector
The dilution method has always been regarded as the standard detection method for BOD5, but this method requires at least 5 days for measurement, and for some water pollution, the data after 5 days may have lost the significance of further pollution control measures. For example, some industrial wastewater has a large fluctuation range, sometimes even several times the difference. Often the same water sample uses different dilution multiples, and the results obtained are different. Therefore, the use of a water quality detector can overcome this repeatability error caused by the difference in the initial oxygen content.At present, the barometer coulometric BOD tester is more commonly used. The pretreated water sample is placed in a culture flask and stirred with an electromagnetic stirrer. When the biological oxidation reaction is carried out, the dissolved oxygen in the water sample is consumed, and the oxygen in the upper space of the culture flask is dissolved in the water sample. The CO2 produced by the reaction escapes from the water sample and enters the space of the culture flask. When CO2 is absorbed by the CO2 absorbent soda lime placed in the culture flask, the partial pressure of oxygen in the flask and the total pressure drop. The pressure drop is detected by an electrode pressure gauge and converted into an electrical signal, which is amplified by an amplifier and the relay is closed to drive the synchronous motor to work. At the same time, the electrolysis device performs CuSO4, constant current electrolysis of the solution, and the oxygen produced by the electrolysis is continuously supplied to the culture bottle, so that the air pressure in the culture bottle gradually rises. When the pressure in the culture bottle returns to the original state, the relay is disconnected and the electrolysis Stop working with the synchronous motor. Through this repeated process, the space above the culture bottle is always maintained at a constant pressure state, so as to promote the activities of microorganisms and the normal progress of biochemical reactions. During the BOD measurement time, the amount of oxygen produced by electrolysis is equivalent to the BOD value of the water sample. According to Coulomb's law, the amount of oxygen consumed is proportional to the amount of electricity required during electrolysis, and the amount of oxygen produced by electrolysis can be obtained.
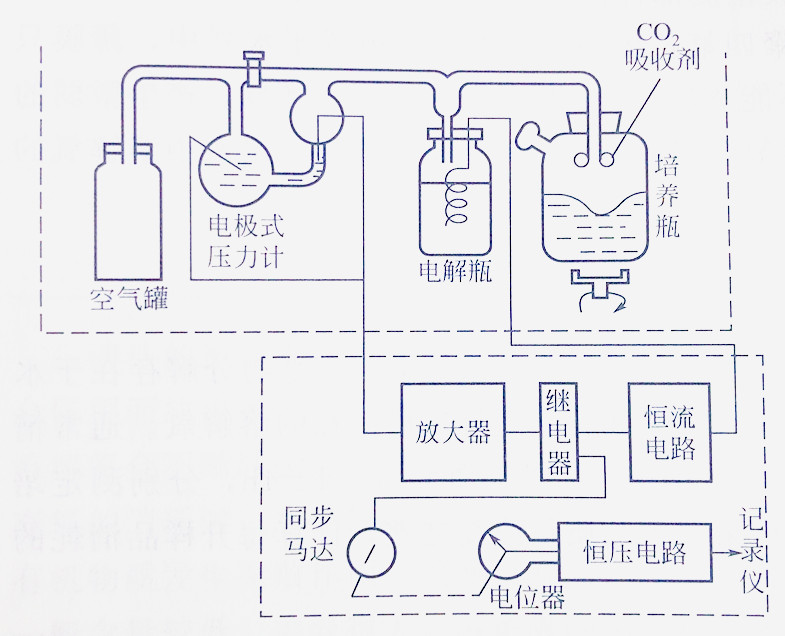
During the operation of the instrument, a synchronous motor starts with electrolysis, and the motor converts its working condition into an electric potential through a potentiometer connected to it. The electric potential is proportional to the amount of oxygen produced by electrolysis. Therefore, a millivoltmeter can be used to automatically record the oxygen consumption curve of the BOD value over time. This barometer coulometric BOD tester can not only measure the five-day biochemical oxygen demand BOD3, but also measure the BOD value of any culture days.
The dilution method needs to prepare several water samples with different dilution times to measure the BOD value, while the instrument method only needs one water sample to perform the measurement. Since the recorder made automatic and continuous records during the measurement process, the oxygen consumption curve obtained can reflect the whole process of the biochemical reaction of the water sample. The result of this measurement method is higher than that of the dilution method. This situation may be caused by the difference between the continuous stirring and the dilution method.



