Nitrate is a common nitrogen compound, and it is also very common in nature. Nitrate substances are easily soluble in water, so they also contain some in water. Under normal circumstances, the nitrate content in the water is very low, and the impact on the human body, animals and plants is very limited. However, when water quality is polluted, nitrates may exceed the standard, especially industrial wastewater and urban sewage treatment tail waters contain high concentrations of nitrates. If they are not treated, they will have a great impact on surface water and groundwater. Today we will explain how to detect nitrate in water by UV spectrophotometry.

The Principle of Ultraviolet Photometric Method for Detecting Nitrate in Water
Nitrate and nitrite in water absorb ultraviolet light at a wavelength of 219.0nm, so we can get the parameters of nitrate based on the absorbance of ultraviolet light, but the measurement range is 0-40mg/L. For the interference of nitrite, you can use sulfamic acid to remove the interference. If there is interference from other organic substances in the water sample, you can take two water samples and add zinc-copper particle reducing agent to the first one to remove all the nitric acid. Root ions and nitrite ions were used as blank control solutions. Add sulfamic acid to destroy the nitrite ion in the second part, and then check the absorbance of the nitrate ion.
Instruments and reagents used for testing
equipment
1. Ultraviolet visible spectrophotometer.
2. Quartz cuvette 1cm.
3. 25mL colorimetric tube with stopper.
4.0.45μm filter membrane.
Reagent drugs
1. Sulfamic acid solution (10g/L)
Weigh 5g of sulfamic acid, dissolve it in 500mL of tertiary reagent water, shake well, and store in a reagent bottle (freshly prepared).
2. Copper sulfate solution (50g/L)
Weigh 25g of copper sulfate (CuSO4·5H2O), dissolve it in 500mL reagent water, shake it well, and store it in a reagent bottle.
3.2mol/L hydrochloric acid solution
Mix 17mL concentrated hydrochloric acid with 83mL tertiary reagent water.
4. Zinc-copper reducing agent
Take 5g of zinc particles with a particle size of 2~3mm and wash them twice with tertiary reagent water, then wash with 2mol/L hydrochloric acid solution, and finally wash twice with tertiary reagent water, put them into a 100mL beaker, and add 100mL copper sulfate solution. When a black film appears on the surface of the zinc particles, discard the solution, wash twice with tertiary reagent water, air-dry the processed zinc-copper particles, and bottle them for later use.
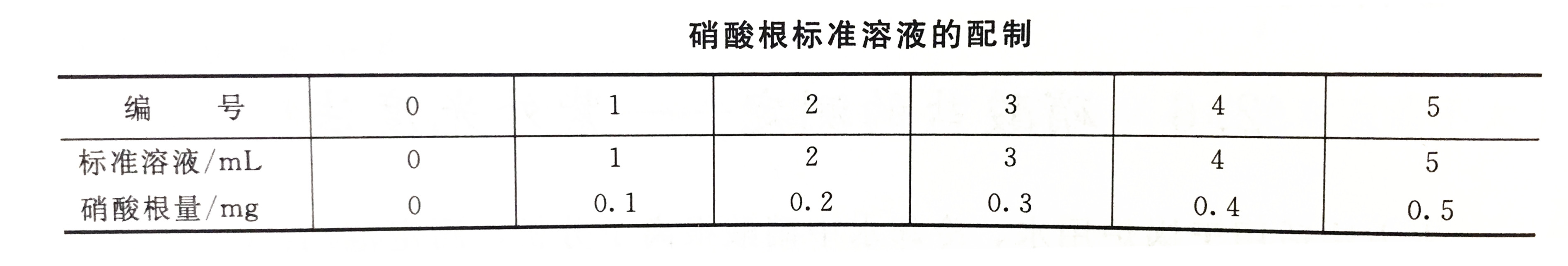
5. Potassium nitrate standard solution (1mL contains 0.1mgNO3)
a. Potassium nitrate stock solution (1mL containing 0.4mgNO3): accurately weigh 0.6523g potassium nitrate dried at 105℃ for 2h, dissolve it in 20mL tertiary reagent water, transfer it into a 1L volumetric flask, and dilute to the mark with tertiary reagent water , Shake well.
b. Potassium nitrate standard solution (1mL contains 0.1mgNO3): accurately draw 25mL of potassium nitrate stock solution in a 100mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark with tertiary reagent water, and shake well.
Nitrate detection procedure
1. Draw a standard curve
Accurately absorb the standard solution according to the corresponding steps and dilute it to the mark with tertiary reagent water in a 25mL colorimetric tube. After shaking it, measure its corresponding absorbance at 219nm with a 1cm quartz cuvette. And draw a standard curve with absorbance as the ordinate and nitrate ion content as the abscissa.
2. Determination of water samples
a. Prepare to take two 10mL water samples filtered by 0.45um filter membrane and put them into 25mL colorimetric tubes respectively. Add 0.8g (about 3-4 grains) zinc-copper reducing agent and 1mL hydrochloric acid solution to one water sample ( 2mol/L), placed for 5h and filtered in a 25mL colorimetric tube, washed with tertiary reagent water and diluted to the mark. Shake evenly as a blank control.
b. Add 1 mL of sulfamic acid solution to another water sample, dilute to the mark with tertiary reagent water, and shake it evenly. Then detect its absorbance, and find out the content of nitrate ions from the standard curve. Finally, the nitrate parameters in water are obtained by the formula p=(m/V)x1000.



