
Instruments and reagents used in phenol photometry
1. Spectrophotometer wavelength range 400-800nm2. Water bath temperature control accuracy ±2℃
3. Volumetric flasks 50mL, 100mL, 1000mL
4. Pipette 5mL, 10mL
5. Preparation of ammonia-free reagent water
a. Ion exchange method Pass the secondary reagent water through the hydrogen type strong acid cation exchange resin.
b. Distillation method Add 0.10 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid to every 1000 mL of reagent water, re-distill in a glass instrument, discard the first 50 mL of distilled water, collect the remaining water in a stoppered glass bottle, and add about 10 g of strong acid cation exchange per liter of collected water Resin (Type H).
6.EDTA solution (50g/L)
Weigh 5.0g disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and dissolve in 60mL sodium hydroxide solution (weigh 1g sodium hydroxide and dissolve in 60mL ammonia-free reagent water), cool to room temperature, add ammonia-free reagent water to 100mL.
7. Phenol solution (630g/L)
Weigh 31.5g of phenol and dissolve it in 5mL of isopropanol and 10mL of acetone. After dissolving, add isopropanol to 50mL. This solution should be prepared before use.
8. Sodium hydroxide solution (270g/L)
Weigh 27g of sodium hydroxide dissolved in a small amount of ammonia-free reagent water, dilute to 100mL, and store in a plastic bottle.
9. Sodium phenate solution
Pipette 20mL phenol solution and 20mL sodium hydroxide solution in a 100mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark with ammonia-free reagent water, shake well, and put into a brown bottle. This solution should be prepared before use.
10. Acetic acid solution (1+1).
11. Starch solution (10g/L).
12. Sodium hypochlorite solution (available chlorine about 10g/L)
The commercial sodium hypochlorite solution is very unstable, and its available chlorine content needs to be determined quantitatively. After the concentration is determined, it is diluted to a 10g/L solution. This solution should be prepared before use.
The available chlorine determination method is as follows:
Take 5mL sodium hypochlorite solution in a 100mL volumetric flask and dilute to the mark with ammonia-free reagent water. Take 10mL of this solution in a 300mL iodine flask, add about 100mL of water, add 1~2g of potassium iodide, add 6mL of acetic acid solution, and shake well. Seal, place in a dark place for 5 minutes, titrate with 0.1mol/L sodium thiosulfate standard solution, add 2mL starch solution after the solution turns light yellow, continue titration until the blue color disappears, record the volume of sodium thiosulfate standard solution consumed, and at the same time Carry out a blank test, and then obtain the available chlorine content of the sodium hypochlorite solution.
13. Preparation of ammonia standard solution
a. Ammonia stock solution (1mL contains 1mg NH3)
Weigh 3.1409g of premium grade pure ammonium chloride baked to constant weight at 110°C, dissolve it with a small amount of reagent water, transfer to a 1000mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark, shake well, and store in the reagent bottle.
b. Ammonia working solution I (1mL contains 0.01mg NH3)
Take 10.00mL of the above ammonia stock solution in a 1000mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark, and shake well. Prepare when this solution is used
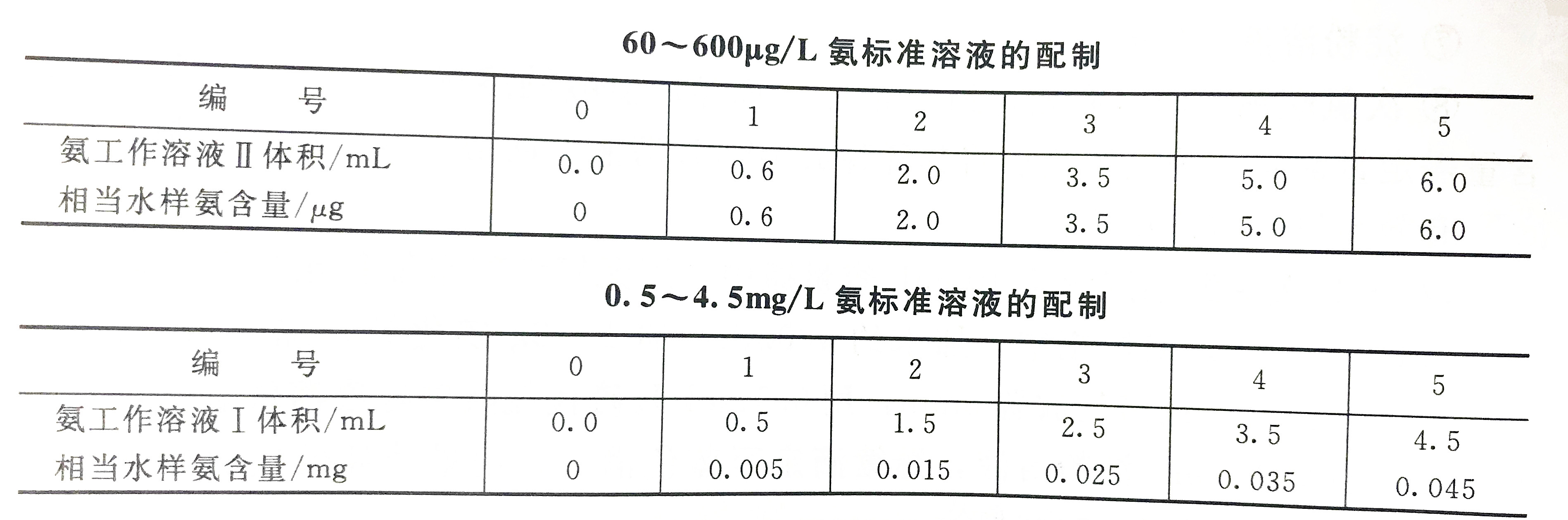
c. Ammonia working solution Ⅱ (1mL contains 1ugNH3)
Take 10.00mL ammonia working solution I into a 100mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark with reagent water and shake well, prepare this solution when using it.
Operation of phenol spectrophotometric method for detecting ammonia content in water
1. Water sample collection
Generally, it can be directly sampled. When the water sample is turbid, use a 0.45um filter membrane to filter, and discard the 50mL that is filtered out; if it cannot be measured immediately after sampling, use hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH value of the sample to 2~3.Store in a dark place at 0~10℃, and determine as soon as possible.
2. Drawing of working curve
a. According to the relevant operating regulations, take the ammonia working solution and inject it into a set of 50mL volumetric flasks, add 1.0mLEDTA solution and 4.0mL sodium phenate solution, and shake well.
b. Add 3.0mL sodium hypochlorite solution, dilute to 50mL with ammonia-free reagent water, and shake up. Place in a water bath at a temperature of 20-25℃ for 30 minutes.
c. When the ammonia concentration is 60~600g/L, use a 50mm cuvette; when the ammonia concentration is 0.5~4.5mg/L, use a 10mm cuvette, and use the reagent blank as a reference to determine the absorbance at a wavelength of 625nm.
d. Use the measured absorbance to draw a working curve against the corresponding ammonia content.
3. Water sample determination
a. Pipette 10mL water sample into a 50mL volumetric flaskb. Operate according to the drawing steps of the working curve.
c. According to the measured absorbance value, find out from the working curve or calculate the ammonia content from the regression equation.
The above is the detailed steps of phenol photometric method to detect ammonia content in water



