Detection method of potassium ion in water
There are many methods for daily detection of potassium ions in water. Among them, the more convenient method is atomic absorption spectrometry. The principle is to directly inhale the sample into an atomizer for atomization. Under the high temperature of the flame, the atoms are pyrolyzed into the ground state. This ground state atom absorbs the energy of the characteristic wavelength light emitted by the light source lamp made of the element, and the energy of the characteristic wavelength light absorbed in the flame and the concentration of the element in the sample In direct proportion, the detector transfers the absorption value to the signal system, and calculates the metal content in the sample according to the absorption value. This method is suitable for industrial water, raw water and domestic water with a potassium content of 0.3-50mg/L.

Instruments and reagents used for testing
1. Flame atomic absorption spectrophotometer
2. Light source
3. Oil-free air compressor
4. Gas
5. Acetylene pressure reducer
6.Glassware
7. Hydrochloric acid
8. Nitric acid
9. Cesium chloride solution
Weigh 25g of cesium chloride into a 200mL beaker, add 500mL of tertiary reagent water containing 50mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid, dissolve and transfer to a 1L volumetric flask, and then dilute to the mark with tertiary reagent water.
10. Potassium chloride standard solution
a. Potassium stock solution
Weigh 1.9070g of high-purity potassium chloride baked to constant weight at 140℃, put it into a 100mL beaker, add 20mL of tertiary reagent water, dissolve it and transfer to a 1L volumetric flask, dilute to the mark with tertiary reagent water, shake Store evenly in a polyethylene bottle for later use.
b. Potassium standard working solution
Pipette 5.0mL of the potassium stock solution, put it into a 500mL volumetric flask, and dilute to the mark with tertiary reagent water.
Potassium ion detection steps in water
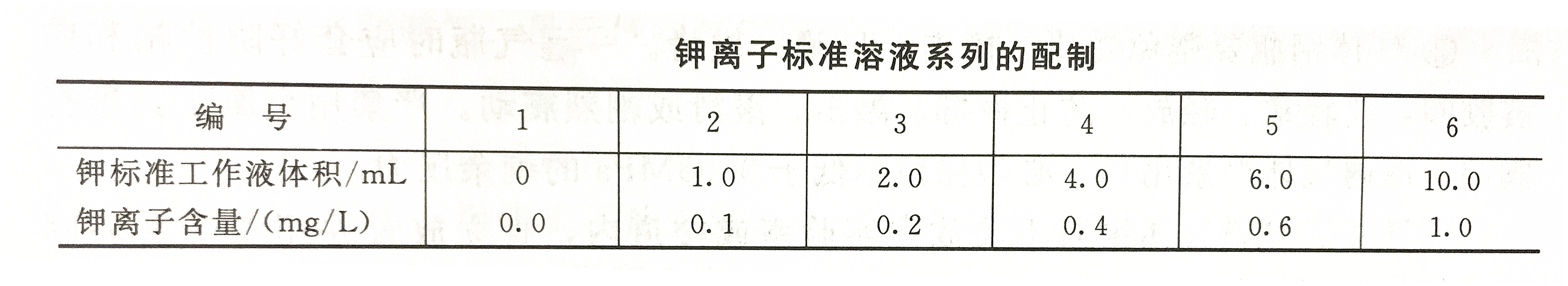
Draw a standard curve
According to the potassium ion standard solution preparation table, accurately draw the potassium standard working solution into a 100mL volumetric flask, add 10mL cesium chloride solution to each, dilute to the mark with tertiary reagent water, and shake it well.
Under the best working conditions of the instrument, at the wavelength of 766.5nm, adjust the reagent blank to zero, and measure the absorbance according to the concentration from low to high. The measured absorbance is the ordinate and the corresponding potassium content is the abscissa. standard curve line.
Water sample preparation
Take about 500 mL of a water sample, add concentrated hydrochloric acid to acidify it to a pH of about 1 (add 8.0 mL of hydrochloric acid per liter of water sample). When there are more suspended solids in the water sample, it can be filtered with a 0.45um filter, and the filtrate is stored in a polyethylene plastic bottle.
Determination of water samples
In a 100mL volumetric flask, add 10.0mL cesium chloride solution, pipette 10.0mL water sample, and dilute to the mark. Measure the absorbance according to the same instrument conditions in the standard curve drawing, and do a blank test at the same time. If the potassium content in the water sample is not in the range of 0.1~1.0mg/L, the volume of the water sample can be adjusted appropriately. Finally, calculate the potassium ion content in the water according to the corresponding formula.





