At present, there are many methods to detect the aluminum content in water. Among them, the aluminum reagent spectrophotometric method is more commonly used. Under the condition of pH 3.8-4.5, the aluminum in the water sample will react with the aluminum reagent (rose red carboxylic acid). The stable red complex is then measured by a spectrophotometer. This method is suitable for water bodies such as high-purity water and tap water.

Instruments and reagents used for testing
1. A 50mL colorimetric tube with a ground plug.2. Spectrophotometer
3. 0.1% aluminum reagent
Weigh 0.1g aluminum reagent, dissolve it in 100mL first-grade reagent water, and store it in a brown bottle.
4.1% ascorbic acid solution
Weigh 1.0 g of ascorbic acid, dissolve it in 100 mL of first-grade reagent water, and store it in a brown bottle.
5. Concentrated hydrochloric acid
6. Concentrated ammonia
7. Hydrochloric acid solution (1+1)
8. Congo red test paper
9. Preparation of aluminum standard solution
a. Stock solution
Weigh 0.5000g of pure aluminum foil, place it in a beaker, add 10mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid, slowly heat it, dissolve it and transfer it to a 500mL volumetric flask, and then dilute it to the mark with first-grade reagent water.
b. Intermediate solution
Take 10mL of the stock solution and pour it into a 1L volumetric flask, add 1mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid, and then dilute to the mark with first-grade reagent water.
c. Working solution
It is made by acidifying with intermediate solution and diluting 10 times with first grade reagent water.
10. Acetic acid-ammonium acetate buffer solution
Weigh 38.5g of ammonium acetate and dissolve it in about 500mL of first-grade reagent water, slowly add 104mL of glacial acetic acid, then transfer to a 1L volumetric flask, and dilute to the mark with first-grade reagent water.
Detection steps of aluminum in water
1. Draw a working curve
a. The measuring range is 0~100g/L working curve. Take the aluminum working solution in a set of colorimetric tubes, dilute it to 50mL with first-grade reagent water, then add 2mL ascorbic acid, and shake well; put in a small piece of Congo red test paper, and carefully add concentrated ammonia or hydrochloric acid (1+1) solution Adjust the pH of the solution. Make the Congo red test paper a purple-blue color (pH≈3~5), add 2mL acetic acid-ammonium acetate buffer solution, and shake well. Then add 2mL aluminum reagent, shake well; 15min later, under the spectrophotometer wavelength of 530nm, use a 30mm (or 100mm) cuvette, use the reagent blank as a reference, measure the absorbance, and draw a working curve based on the absorbance and the corresponding aluminum content .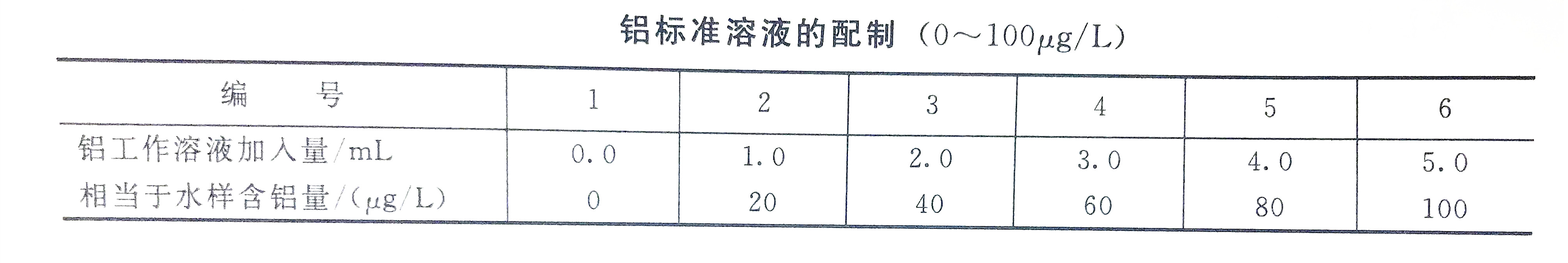
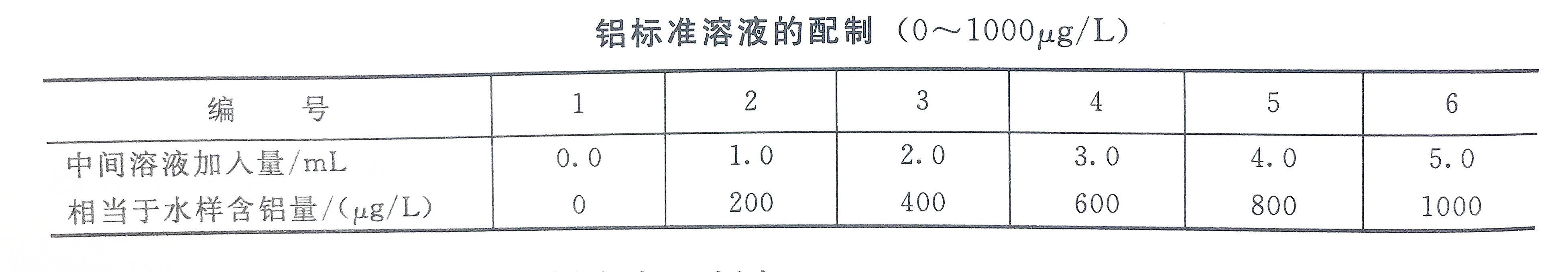
b. Measuring the working curve of the range of 0-1000ug/L, take the aluminum intermediate solution and inject it into a set of colorimetric tubes, and dilute to 50mL with first-grade reagent water. Then add the reagents according to the above method, shake well, after 15 minutes, use a 30mm cuvette with a spectrophotometer wavelength of 530nm to measure the absorbance with the blank reagent as a reference, and then draw a working curve based on the measured absorbance and the corresponding aluminum content.
2. Determination of water samples
a. The sampling bottle is cleaned with concentrated hydrochloric acid, and then washed with first-grade reagent water, and then concentrated hydrochloric acid is added to the sampling bottle (2mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid for every 500mL water sample). After draining the water in the sampling tube, take a sample directly. After sampling, the water sample should be shaken immediately.b. Take 50mL of water sample and inject it into the colorimetric tube, and determine the absorbance according to the working curve drawing method. Find out the aluminum content of the water sample from the working curve.



