
Instruments and reagents used in zinc reagent spectrophotometry
1. Spectrophotometer2. Electric heater or electric stove
3. Medicine refrigerator
4. Hydrochloric acid solution (1+4)
5. Nitric acid solution (1+2)
6. Sulfuric acid solution (1+2)
7. Concentrated hydrochloric acid (excellent grade pure)
8. Zinc reagent solution
Accurately weigh 0.075g of zinc reagent, add 50mL of methanol (or ethanol) and warm it at 50°C. After it is completely dissolved, dilute to 100mL with first-grade reagent water and pour it into a brown bottle. This solution should be stored in the medicine refrigerator.
9. Ammonium acetate solution
Weigh 500g of ammonium acetate dissolved in the first-grade reagent water, transfer it into a 1L volumetric flask and dilute to the mark.
10. Tartaric acid solution
Weigh 15g of tartaric acid in the first-grade reagent water, transfer it to a 100mL volumetric flask and dilute to the mark.
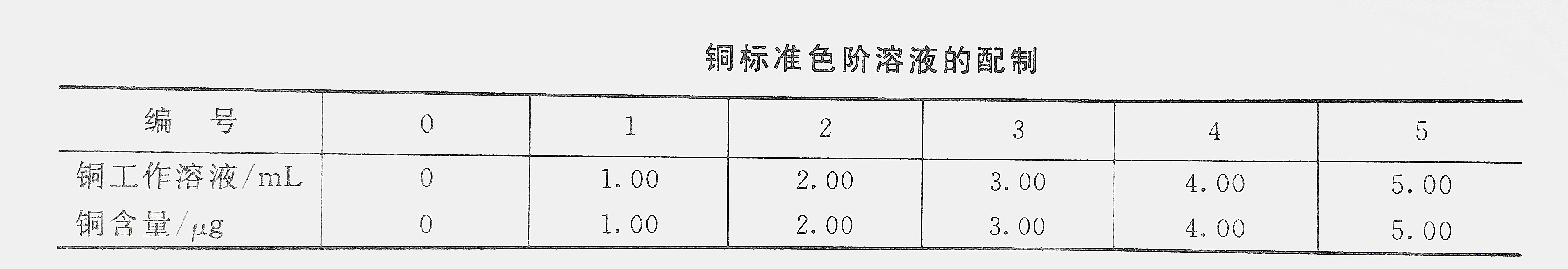
11. Copper standard solution
Prepare copper stock solution, weigh 0.1000g metallic copper in 20mL nitric acid and 5mL sulfuric acid, slowly heat to dissolve, continue heating to evaporate to dryness, add first-grade reagent water to dissolve after cooling, transfer to a 1L volumetric flask and dilute to the mark.
Prepare the copper working solution, draw 10mL of the copper stock solution into a 1L volumetric flask and dilute to the mark.
Operation steps of zinc reagent spectrophotometry
(1) Draw working curveAccording to the copper standard color gradation solution table, take the copper working solution and inject it into a set of 100mL volumetric flasks (you can also make a smaller range of working curves according to the copper content in the water sample), each add 8mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid, and add a reagent water to make the volume Become about 50mL, shake well. Add 25mL of ammonium acetate solution and 2mL of tartaric acid solution in sequence to make the pH between 3.5-4.8, and accurately add 0.2mL of zinc reagent solution to develop color, dilute to the mark with first-grade reagent water, and measure with a 100mm long cuvette at a wavelength of 600nm Absorbance, plot the relationship between copper content and absorbance.
(2) Determination of copper ion in water
1. Wash the sampling bottle with warm concentrated hydrochloric acid, and then fully wash it with first-grade reagent water, and then add concentrated hydrochloric acid (add 2mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid for every 500mL water sample) to the sampling bottle, take the water sample directly, and remove the water after sampling. Shake well.
2. Take a 200mL water sample (when the copper content is above 50ug/L, appropriately reduce the sampling volume, dilute with first-class reagent water to about 200mL), pour it into a 300mL conical flask, add 8mL concentrated hydrochloric acid, and carefully boil and concentrate to 20- 40mL.
3. After cooling, transfer all to a 100mL volumetric flask, add 25mL ammonium acetate solution and 2mL tartaric acid solution to make the pH between 3.5-4.8.
4. Accurately add 0.2mL zinc reagent solution to develop color, and dilute to the mark with first-grade reagent water. Perform the same operation reference with the first-level reagent water, use a 100mm long cuvette to measure the absorbance at a wavelength of 600nm, and check the copper amount m(ug) from the working curve. The allowable error of the final measured average value is not more than 0.5ug/L.
Precautions for zinc reagent spectrophotometry
1. In the range of pH=3.5-4.8, the interference of nickel and zinc is negligible. In addition, the possible presence of hydrazine, trivalent chromium, trivalent iron, aluminum, calcium, magnesium, silicate, etc. in the water sample has no effect on the determination. Interference, the interference caused by the coexistence of divalent iron can be eliminated by adding tartaric acid.2. The quality of zinc reagent will vary with different manufacturers and different batch numbers. The storage period of a good quality solution is 5 days, while the poor one should be prepared every time it is used.
3. The utensils used in this method can be soaked in hydrochloric acid solution (1+4) overnight, and then thoroughly washed with first-grade reagent water.
4. Method for removing copper from ammonium acetate solution: inject 100 mL of ammonium acetate solution into the separatory funnel, add 20 mL of zinc reagent-isoamyl alcohol solution (2 mL of zinc reagent solution is dissolved in 100 mL of isoamyl alcohol), shake well, stand for 5 minutes, and separate , Discard the colored alcohol layer.
5. After each preparation of the zinc reagent solution, the working curve should be redrawn.



