In the "Urban Water Supply Quality Standard", one of the toxicological indicators clearly stipulates that the arsenic content in drinking water should not exceed 0.01mg/L. It can be seen that the excessive arsenic content in water is a very serious problem; there are many detection methods for arsenic in water. We will introduce how to use the new silver salt spectrophotometric method to detect arsenic in water.
This method is suitable for the determination of trace arsenic in surface water and groundwater. The principle is that potassium borohydride (or sodium borohydride) generates new ecological hydrogen in an acid solution, reducing inorganic arsenic in water to
Arsenic hydrogen gas, with nitric acid-silver nitrate-polyvinyl alcohol-ethanol solution as the absorption liquid. Arsenide reduces the silver ions in the absorption solution to elemental colloidal silver, making the solution yellow, and the color intensity is proportional to the amount of hydride. The yellow solution has the maximum absorption at 400nm and the peak shape is symmetrical. The color has no obvious change within 2h (below 20°C).

Instruments and reagents used to detect arsenic in water
1. Spectrophotometer
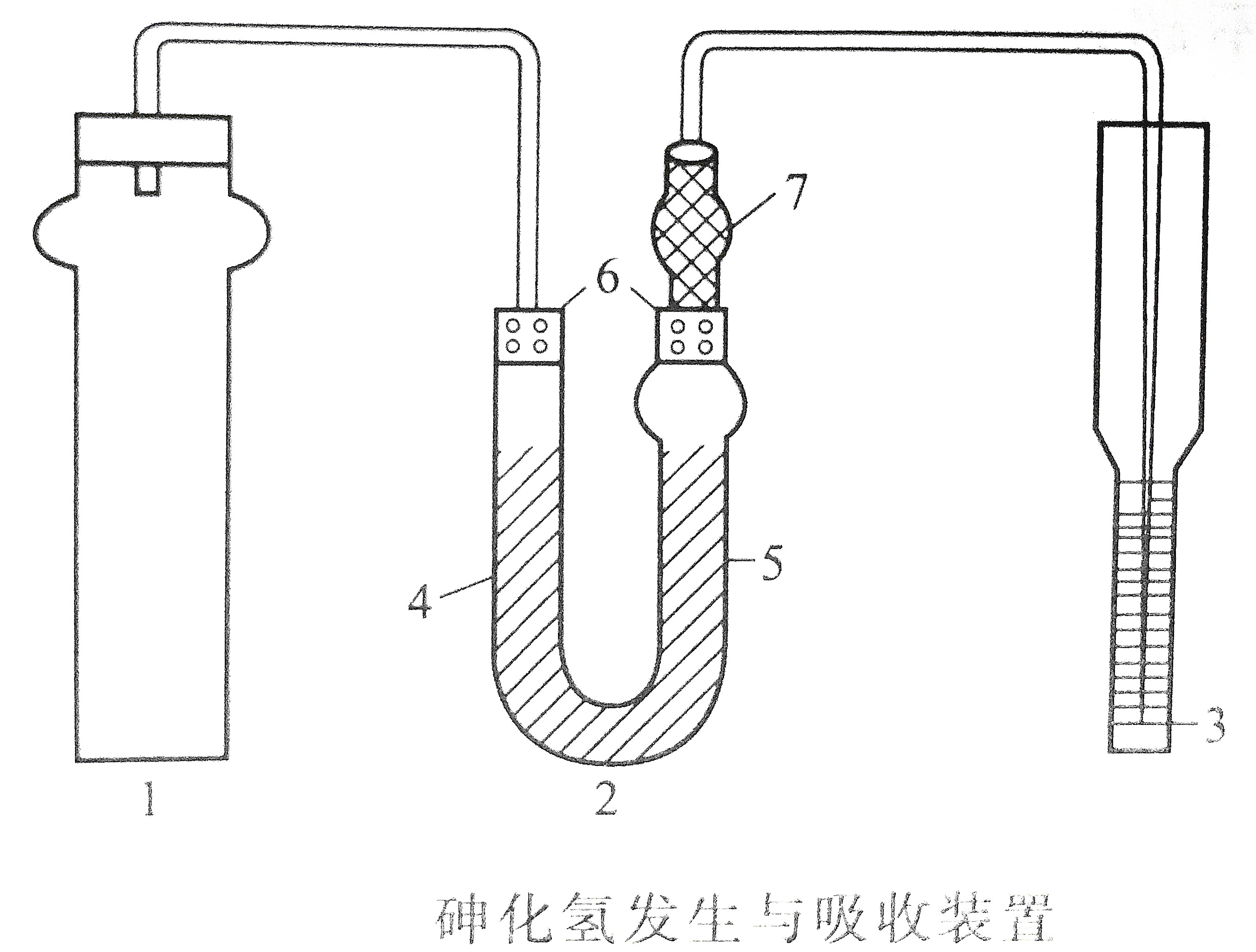
2. Arsenic hydrogen generation and absorption device
3. Sulfuric acid
4. Nitric acid
5. Perchloric acid
6.Ethanol
7. Potassium borohydride tablets
8. Aqueous solution of polyvinyl alcohol (0.2%)
Weigh 0.4g polyvinyl alcohol (average degree of polymerization of 1750±50) and place it in a 250mL beaker, add 200mL of tertiary reagent water, and dissolve under constant stirring by heating. After it is fully dissolved, cover with a watch glass and boil slightly for 10min. After cooling, store in a glass bottle, this solution can be stable for one week.
9. Potassium iodide-thiourea solution (15%)
1 g of thiourea is contained in 100 mL of 15% potassium iodide aqueous solution.
10. Silver Nitrate Nitrate Solution
Weigh 2.040g silver nitrate into a 100mL beaker, add about 50mL tertiary reagent water, stir to dissolve, add 5mL nitric acid, dilute with tertiary reagent water to 250mL, shake well, and store in a brown bottle.
11. Sulfuric acid tartaric acid solution
In 400mL of 0.5moL/L sulfuric acid, add 60g of tartaric acid (first grade) to dissolve.
12. Dimethylformamide mixed solution (referred to as DMF mixed solution)
Mix dimethylformamide and ethanolamine in a volume ratio (9+1). This solution can be stored for 30 days in a brown bottle.
13. Lead acetate cotton
Soak 10 g of absorbent cotton in 100 mL of 10% lead acetate solution. After 0.5h, take it out and twist off the excess water, let it dry naturally at room temperature, and put it into a ground bottle for later use.
14. Absorption liquid
Mix silver nitrate, polyvinyl alcohol, and ethanol in a volume ratio (1+1+2), and prepare them immediately before use.
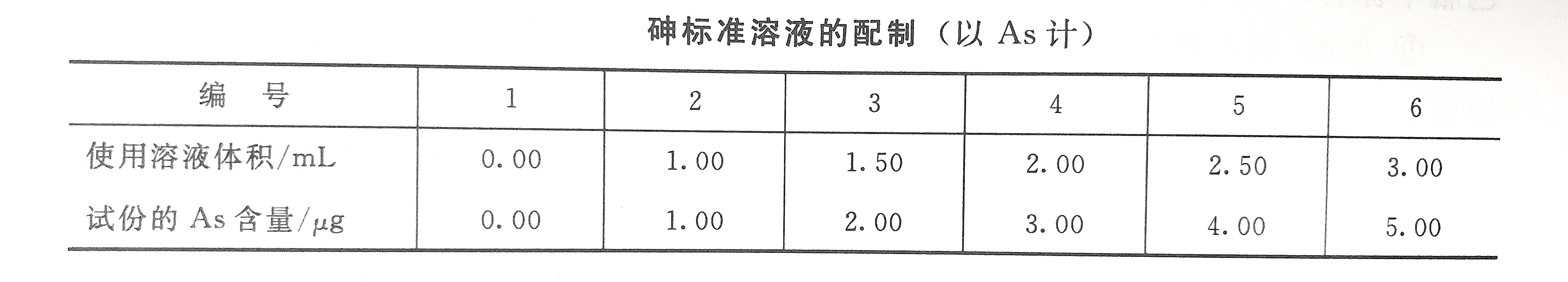
15. Arsenic standard solution
Weigh 0.1320g of arsenic trioxide and bake at 110°C for 2h, put it in a 50mL beaker, add 2mL of 20% sodium hydroxide solution, stir to dissolve, then add 10mL of 1mol/L sulfuric acid, transfer it to a 100mL volumetric flask, and dilute with tertiary reagent water to Mark and mix well. Take 1.00mL of the above solution and dilute it to 1000mL to prepare a standard solution of 1.0mg/L of arsenic. Now equipped before use.
Arsenic detection steps in water
1 Water sample treatment
Generally speaking, clean groundwater and surface water can be sampled and measured directly, but if the water quality is relatively complicated, it needs to be pre-treated and then tested. Specific steps are as follows:
(1) Take an appropriate amount of sample (no more than 3ug arsenic) and place it in a 250mL beaker, add 6.0mL hydrochloric acid, 2.0mL nitric acid and 2.0mL perchloric acid, heat it on a hot plate until white smoke is emitted, and steam until nearly dry. After cooling, use 0.5mol/L hydrochloric acid 1.5mL to dissolve, and then heat to boiling. Remove and cool, add 20-30mg ascorbic acid, 15% potassium iodide thiourea solution 2.0mL, leave it for 15min, then heat and boil slightly for 1min.
(2) After removing and cooling, rinse the watch glass and the cup wall with a small amount of tertiary reagent water, add 2 drops of methyl orange indicator, use (1+1) ammonia to adjust to yellow, and then use 0.5mol/L hydrochloric acid to adjust to The solution is just reddish, add 5mL of sulfuric acid-tartaric acid solution (or 20% tartaric acid solution), transfer this solution into a 50mL reaction tube, and dilute with tertiary reagent water to the mark to be tested.
2. Detection steps
(1) Water sample reaction
Take 250mL of clean water sample (when the arsenic concentration is high, you can take a small amount of sample diluted to 250mL with tertiary reagent water, the arsenic content is not more than 3ug), put it in a 250mL reaction tube, add 20mL of sulfuric acid-tartaric acid solution, and mix. Add 3.0mL absorption solution to each dry absorption tube, and connect the airway tube according to the operation steps. Put two pieces of potassium borohydride (or sodium borohydride) into the vesicles of the reaction tube, cover the plugs, pour one piece of the potassium borohydride tablets in the vesicles into the solution, and wait until the reaction is completed (about 5min), Then pour another piece into the solution, react for 5 minutes, and the color-developing solution is to be tested. If the volume of the test solution is less than 50mL, a 50mL reaction tube can be used to add 1 piece of potassium borohydride to react. Both the sample and the calibration curve were performed with a 50mL reaction tube.
(2) Detection operation
Using a 10mm cuvette, with a blank absorber as a reference, measure the absorbance of the above absorber at 400nm. Take a set of arsenic standard solution according to the arsenic standard solution preparation table, and inject it into a 250mL reaction tube, the following operations are the same for the same product, and the corresponding calibration curve is drawn. Then calculate the arsenic content in the water sample.



