Classification of chemical reagents for water quality testing
1. General chemical reagents
According to national standards, chemical reagents can be divided into two categories according to their purpose. General chemical reagents are one of them. According to their purity, specifications and scope of application, they can be divided into four categories. For example, commonly used indicators belong to general chemical reagents with specific specifications. And the scope of application is detailed in the table below.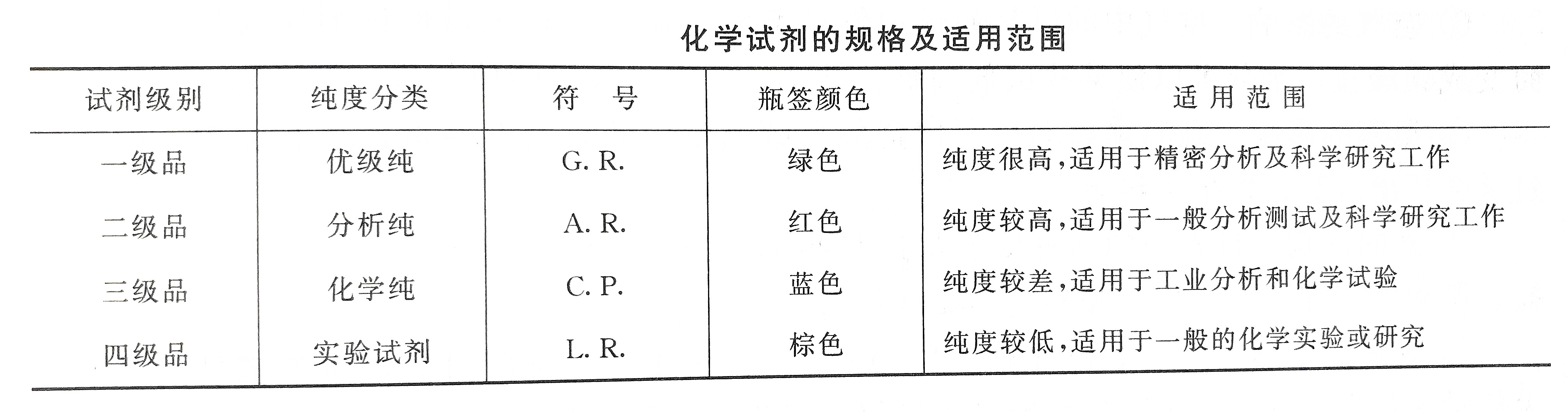
2. Special chemical reagents
a. Reference reagentIts purity is equivalent to (or higher than) the first grade, and the main component content is generally 99.5%-100.00%, which can be used as a reference substance in titration analysis, or it can be directly formulated into a standard titration solution of known concentration.
b. High purity reagent
The main component content of this type of reagent can reach more than four nines (99.99%), and it is mainly used as a standard substance in extremely precise analysis or a matrix for preparing a standard sample. Among them, the impurity content of "spectrally pure" reagents cannot be detected by spectroscopic analysis or is below a certain limit; "spectrophotometrically pure" reagents require no or very few interfering substances within a certain wavelength range; "chromatographically pure" reagents or The impurity content of "chromatographic reference material" cannot be detected by chromatographic analysis or is below a certain limit.
c. Biochemical reagents
Used in various biochemical tests.

Selection method of water quality detection chemical reagent
The purity of chemical reagents has a greater impact on the accuracy of the test results, but the higher the purity of the reagent, the more expensive its price. Therefore, reagents of different specifications should be selected according to the detection tasks, detection methods and requirements for the accuracy of the detection results.The principle of the selection of chemical reagents is to choose the reagent grade as low as possible on the premise of meeting the testing requirements, neither over-grade and causing waste, nor arbitrarily lowering the reagent grade to reduce the accuracy of the test results. The choice of reagent usually considers the following points.
1. For trace detection, reagents with high purity specifications should be selected to reduce the blank value. For arbitration detection, superior grade and detection reagents are generally used.
2. In the titration test, the standard titration solution prepared by the indirect method should be prepared with the test pure reagent, and then calibrated with the reference substance. For experiments that do not require very high test results, you can also use superior grade or test pure instead of reference reagents for calibration. Other reagents used in titration testing are generally pure reagents for testing.
3. In instrument testing, superior grade or special reagents are generally selected, and high-purity reagents should be used for the determination of trace components.
4. Chemical pure reagents should be used when preparing common test solutions and cleaning solutions in quantitative or qualitative testing. It should be noted that the level of reagents is high, and there are special requirements for the purity of test water and the cleanliness of containers and instruments. They must be used in conjunction to meet the requirements. In addition, due to the specifications and signs of imported chemical reagents and the current level of chemical reagents in my country The standards are not the same, you can refer to the relevant chemistry manuals to distinguish when using them.
The above is the classification and selection method of water quality testing chemical reagents



