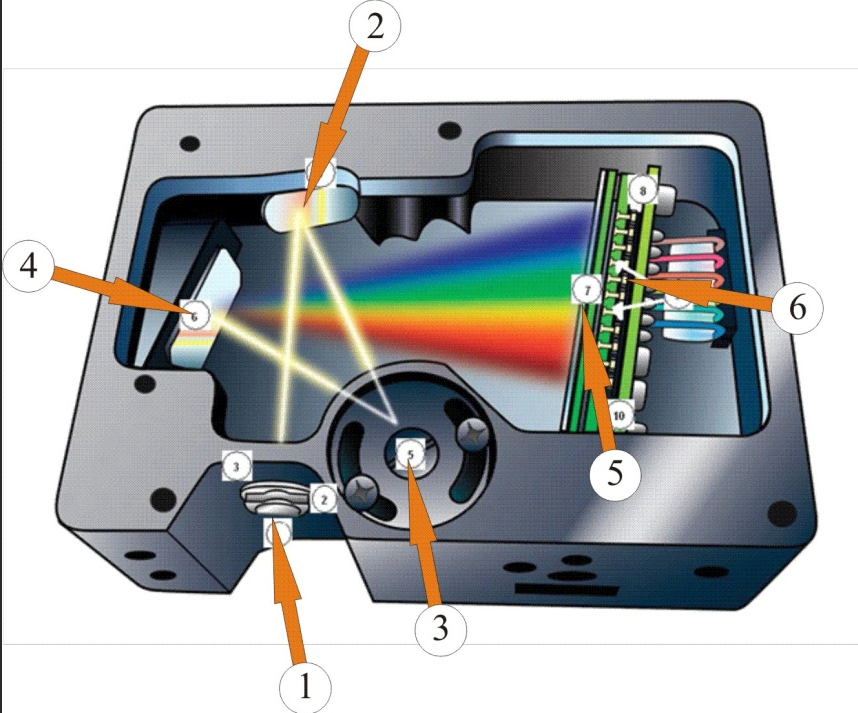
Working principle of spectrophotometer
Spectrophotometers can be divided into single-beam spectrophotometers and dual-beam spectrophotometers according to the optical path; according to the number of wavelengths provided during the measurement, they can be divided into single-wavelength spectrophotometers and dual-wavelength spectrophotometers.
1. Single beam spectrophotometer
Single beam refers to the light emitted from the light source, after passing through a series of optical elements such as the monochromator and the absorption cell, it is always a beam of light when it is finally irradiated on the detector. Commonly used single-beam visible spectrophotometers are 721, 722, etc.; single-beam visible-ultraviolet spectrophotometers are 751G, 752, 754, and 756MC.
Shanguangdong spectrophotometer is characterized by simple structure and low price, which is mainly suitable for quantitative analysis. But the disadvantage is that the measurement result is greatly affected by the fluctuation of the light source intensity, which brings a large error to the quantitative analysis result.
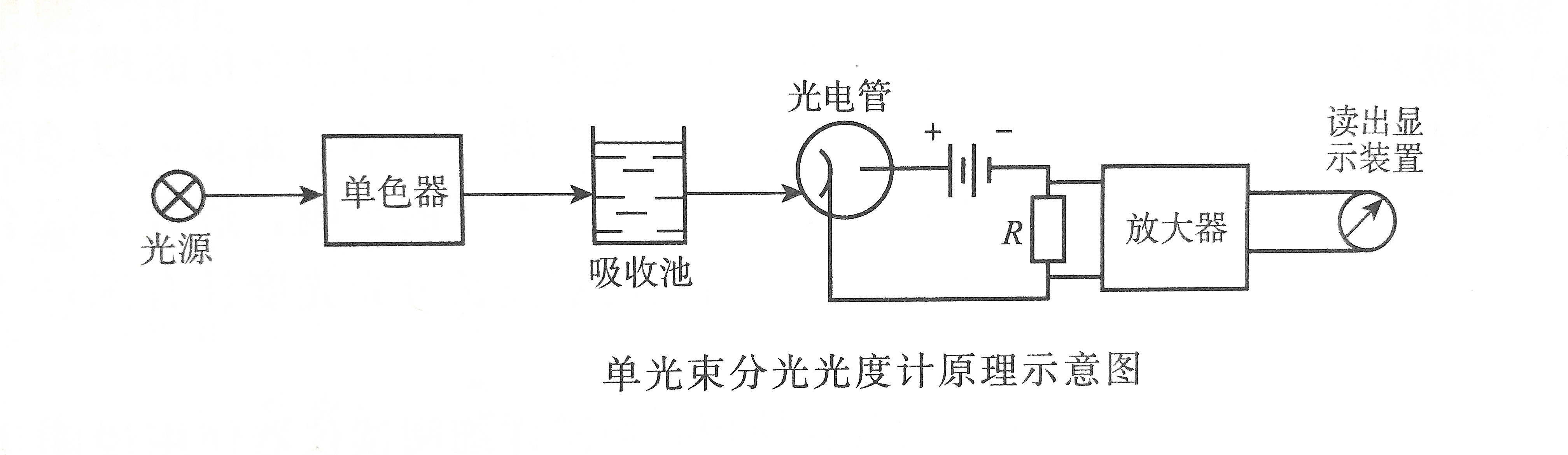
2. Double beam spectrophotometer
The light emitted from the light source passes through the monochromator and is divided into two beams of equal intensity by a rotating fan-shaped mirror (ie, light cutter), and passes through the reference solution and the sample solution respectively. Using another light cutter that is synchronized with the previous one, the two beams of light are alternately irradiated on the same detector at different times, and the signals from the two beams are compared through a synchronization signal generator, and the The ratio of the two signals is converted to the corresponding absorbance value after logarithmic transformation.
Its characteristic is that it can continuously change the wavelength, automatically compare the transmittance intensity of the sample and the reference solution, and automatically eliminate the error caused by the change in the intensity of the light source. This type of photometer is more suitable for analysis that must obtain a complex absorption spectrum curve in a wide wavelength range.
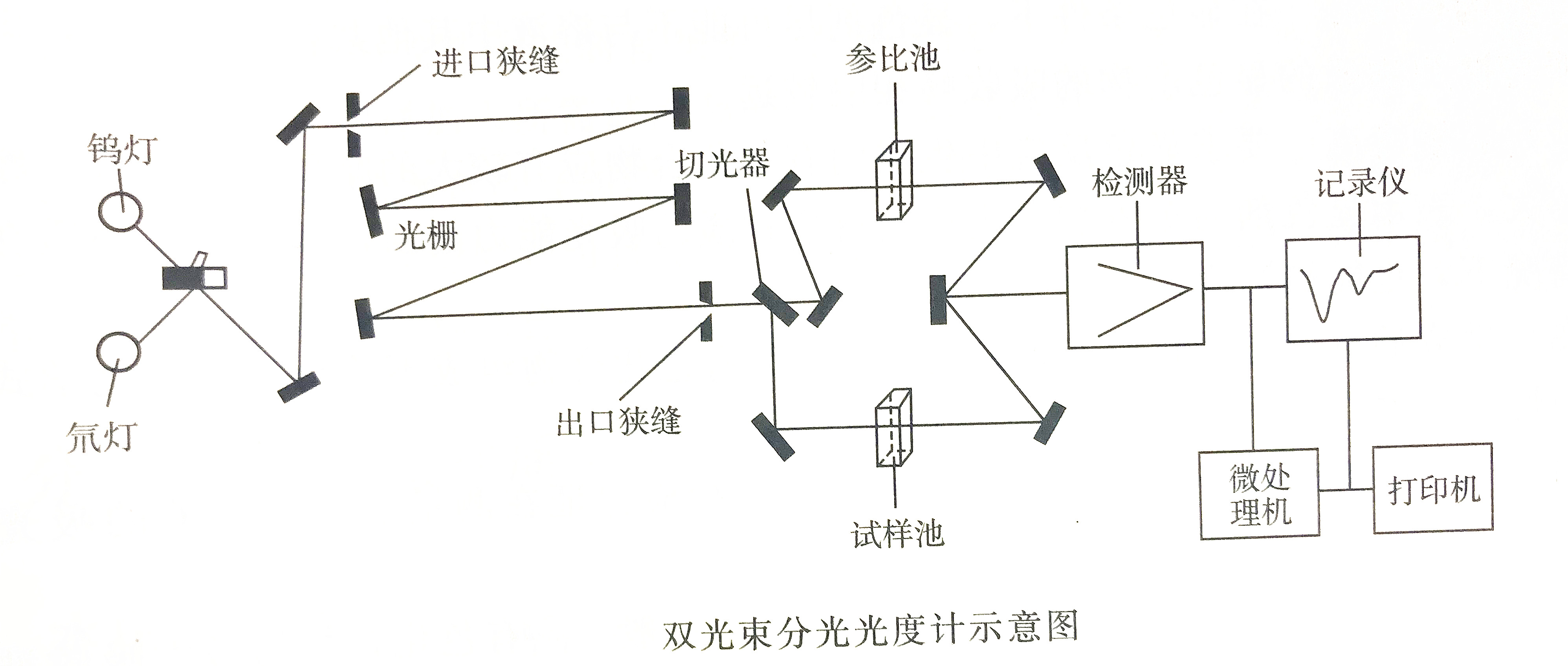
3. Dual-wavelength spectrophotometer
The main difference between a dual-wavelength spectrophotometer and a single-wavelength spectrophotometer is the use of a dual monochromator, which can simultaneously obtain two monochromatic lights with different wavelengths.
The light emitted by the light source is divided into two beams, and two beams of monochromatic light with different wavelengths A1 and A2 are obtained through two freely rotatable grating monochromators. Then with the help of a light cutter, the two beams of light are alternately irradiated to the absorption cell containing the test solution at a certain time interval, and the detector shows the difference in transmittance or absorbance of the test solution at wavelengths A1 and A2.
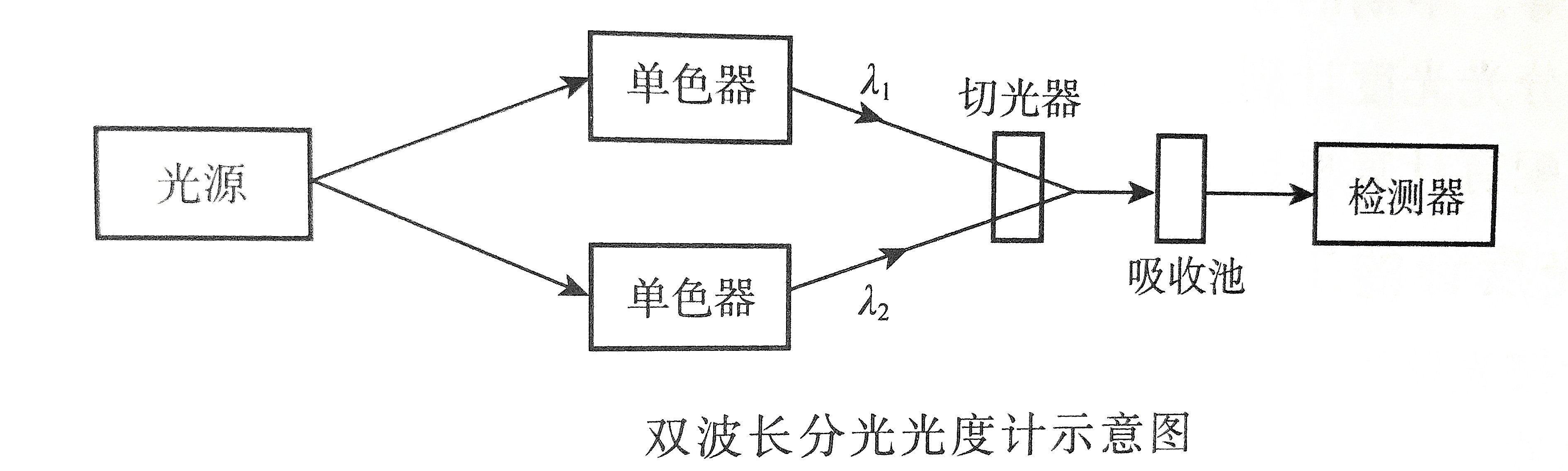
The feature of the dual-wavelength spectrophotometer is that it does not use a reference solution, but only uses one solution to be tested, so it can eliminate background absorption interference, including the difference in the composition of the solution to be tested and the reference solution and the influence of the thickness of the absorption solution. It is suitable for mixtures and Quantitative analysis of turbid samples. But its shortcoming is also obvious that it is more expensive.
The above is the working principle of the water quality detection spectrophotometer, but in actual operation, you must read the instructions for use of the instrument in detail, and operate according to the introduction of the manual.



