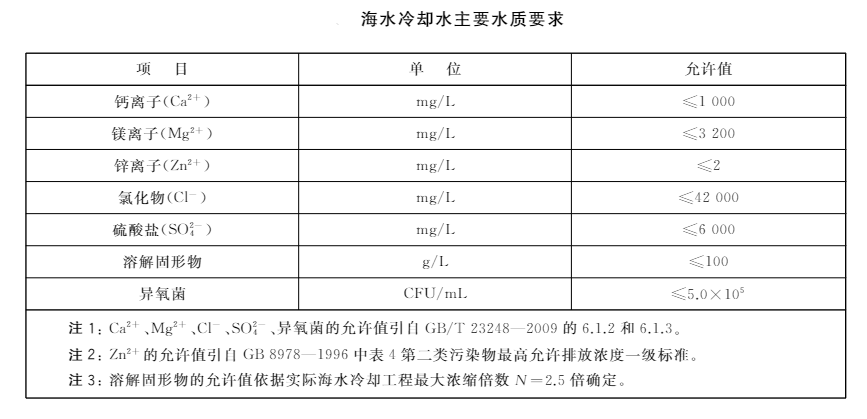
In order to improve the utilization rate of seawater resources, seawater has begun to gradually replace freshwater in some applications in order to promote the optimization of the structure of water resources. Seawater is mostly used for cooling treatment in industry. It can be washed directly or indirectly cooled. Although the use of seawater is very helpful for water saving, it will cause certain pollution to the quality of seawater. Therefore, the country has also formulated relevant standards for the use and discharge of seawater cooling water. Today we will talk about the method of detecting the sulfate content in seawater cooling water.
This method adopts spectrophotometry for detection, and is suitable for seawater cooling water with a sulfate content of 1000mg/L-6000mg/L. The principle is to use barium chloride to react with sulfate in seawater to form a barium sulfate suspension, and then use a spectrophotometer to measure the absorbance of the suspension. The content of sulfate in the water sample is proportional to the absorbance.

Instruments and reagents used for testing
Instruments used
1. Spectrophotometer.
2. Analyze the balance.
3. Electromagnetic stirrer.
4. Timer.
5. Oven.
6. 100mL, 500mL, 1000mL volumetric flasks.
7.5mL, 10mL, graduated pipette.
8.1mL, 2mL single mark pipette.
9. Fiber membrane with a pore size of 0.45um.
Reagents used
1. Barium chloride
2. Hydrochloric acid (36%)
3. Glycerin-acid solution
Measure 50 mL of hydrochloric acid, add 100 mL of water to dissolve, add 250 mL of glycerin to mix, and dilute to 500 mL with laboratory pure water.
4. Sodium chloride solution (5mol/L)
Weigh 292.25g of sodium chloride, add distilled water or laboratory pure water to dissolve, dilute to 1000mL.
5. Sulfate standard solution (based on SO, 1mg/mL)
Dry the premium grade pure anhydrous sodium sulfate at 110℃-130℃ to constant weight, weigh 1.479g with an analytical balance, dissolve it with a small amount of laboratory pure water, transfer it to a 1000mL volumetric flask, and dilute to the mark with laboratory pure water , Shake evenly and set aside.
Seawater cooling water sulfate detection steps
Standard curve drawing
1. Pipette 0mL, 1mL, 2mL, 3mL, 4mL, 5mL, 6mL, 8mL prepared sulfate standard solution, into a set of 100mL volumetric flask, add 5mL glyceric acid solution and 50mL sodium chloride solution, Dilute to 100mL with distilled water and mix well. The content of sulfate in this series of solutions are 0mg, 1mg, 2mg, 3mg, 4mg, 5mg, 6mg, 8mg respectively.
2. Add 0.30g±0.01g barium chloride and a magnetic rotor of the same size to the above solution one by one, shake well and place on an electromagnetic stirrer to stir for 3min (timed by a stopwatch). Stirring should be consistent in each solution preparation.
3. Inject the solution with 0 mg of sulfate content processed according to the above steps into a 2cm cuvette, and adjust the absorbance to 0.00 at a wavelength of 425nm. Measure the absorbance of other suspensions in sequence. Read within 5min after stirring. Draw a standard curve of absorbance and its corresponding sulfate content (mg)
Determination of water samples
1. Use 0.45um filter membrane to filter seawater cooling water samples.
2. Single mark pipette pipette 2mL filtered water sample into a 100mL volumetric flask to prepare a blank sample. Pour this solution into a 2cm cuvette and adjust the absorbance to 0.00 at a wavelength of 425nm. Pipette the same volume of water sample according to the standard curve drawing process. Determine the absorbance. Check the standard curve to calculate the sulfate content in the water sample. When the sulfate content is greater than 4000mg1-, the sampling volume should be 1mL. The relative error of the measurement is within ±1.5%.
References in this article: Seawater cooling water quality requirements and analytical testing methods Part 4: Determination of sulfate (GB/T 33584.4-2017).



