Most of the benzene series are found in the atmosphere, so the detection of this substance is mostly found in the air standards, but the content of benzene series in industrial wastewater is also very large, so the content of benzene series in the water quality test of reclaimed water resources is also clear Provisions. Today we will talk about the detailed steps for detecting benzene series in reclaimed water. This method is suitable for the detection of benzene series in reclaimed water from 0.5ug/L to 100ug/L, and it is also suitable for the detection of benzene series in surface water, industrial water and domestic water within this range.

Detection principle of benzene series in water
The benzene series in the water sample are purged with high-purity nitrogen and adsorbed in the trapping tube. The trapping tube is heated and blown back with high-purity nitrogen. After the thermally desorbed components are separated by gas chromatography, they are separated by hydrogen Flame ionization detector is used for detection, qualitatively based on retention time, and external standard method is used to quantify the peak height or peak area to calculate the content of each component.
Reagents and equipment required for testing
Reagents used for detection of benzene series in water
1. Laboratory first-grade pure water
2. Chromatographic grade methanol
3. Ascorbic acid
4. Hydrochloric acid solution: 1+1
5. Standard stock solution of benzene series
100ug/mL-1000ug/L methanol solution, store in the dark. If the standard stock solution needs to be stored after opening, it should be stored in a frozen and sealed manner at -10°C~-20°C, and return to room temperature during use and test. If the response value or the type of benzene series is abnormal, you must not continue to use it.
6. Benzene series standard solution
Take an appropriate amount of benzene series standard solution diluted with methanol to 1.0ug/mL, this solution is now prepared.
7. Helium or nitrogen with purity ≥99.999%
8. Hydrogen with purity ≥99.999%
9. Ordinary compressed air
Equipment used for testing
1. Gas chromatograph: equipped with hydrogen flame ionization detector.
2. Purging and catching device: Packing 1/3 carbon fiber, 1/3 silica gel and 1/3 activated carbon uniformly mixed packing or other equivalent adsorbents.
3. Chromatographic column: Quartz capillary column, 30m (length) × 320um (inner diameter) × 0.50um (film thickness), the stationary phase is polyethylene glycol, and other equivalent capillary columns can also be used.
4. Sampling bottle: brown glass bottle, equipped with screw cap (with PTFE coated gasket), 40mL or other specifications.
5. Air-tight syringe: 5mL.
6. Micro syringe: 10uL, 100uL, 500u1.
Water sample collection and storage
1 Wash the equipment required for water sample collection with laboratory pure water in accordance with relevant standards. Avoid shaking and washing during collection, and refrigerate immediately after sample collection. All samples are collected in parallel with double samples, and each batch of samples should be accompanied by a full procedure blank. Try to avoid water samples from leaking in the air when sampling.
2 After the water sample is collected, the residual chlorine content should be determined first. If there is no residual chlorine, add an appropriate amount of hydrochloric acid solution to make the pH ≤ 2.0, and store it below 4°C for no more than 14 days; if the collected water sample contains residual chlorine, When the residual chlorine content is ≤5.0mg/L, add about 25mg ascorbic acid per 40mL sample, and then add an appropriate amount of hydrochloric acid solution to make the pH ≤2.0, and store at below 4℃ for no more than 14 days; if the residual chlorine content is 5.0mg/L, To increase by 5.0mg/L, you need to add 25mg more ascorbic acid to every 40mL sample, and then add an appropriate amount of hydrochloric acid solution to make the pH ≤ 2.0, and store it below 4°C, and the time should not exceed 14 days;
It should be noted that the water quality samples should be stored to avoid organic interference to prevent cross-contamination.
Chromatographic reference conditions and purge collection conditions
According to relevant standards, we recommend the following chromatographic conditions, or you can choose chromatographic conditions according to the chromatographic instrument manual, so that the resolution of the measured component is greater than or equal to 1.5.
a. Column temperature
The temperature is programmed, and the temperature is kept at 40°C for 6 minutes, and the temperature rises to 100°C at a temperature rise rate of 5°C/min. Keep it for 2 minutes, and then increase to 200°C at a temperature rise rate of 5°C/min.
b. Inlet temperature: 200℃
c. Detector temperature: 280℃
d. Carrier gas flow: 2.5mL/min
e. Split ratio: 10:1
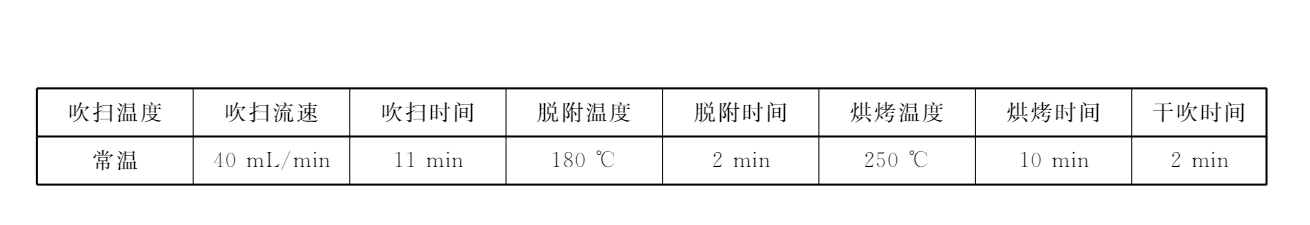
The purge collection conditions can be set by referring to the instrument's instruction manual or the figure below.
Draw calibration curve
1. Draw a low concentration calibration curve
Pipette 0uL, 50uL, 100uL, 200uL, 500uL benzene series standard solutions into a series of 100mL volumetric flasks, dilute to the mark with water, and shake gently. The concentration of this series of calibration solutions are 0ug/L, 0.5ug/L, 1.0ug/L, 2.0ug/L, 5.0ug/L. In the order from low concentration to high concentration, 5.0 mL of calibration solution was injected into the gas chromatograph for detection. Take the mass concentration of the calibration solution as the abscissa, and the measured peak height or peak area as the ordinate, draw the calibration curve and calculate the regression equation
2. Draw a high concentration calibration curve
Pipette 0.00mL, 0.50, 1.00mL, 2.00mL, 5.00mL, 10.00mL benzene series standard solution into a series of 100mL volumetric flasks, dilute to the mark with laboratory ultrapure water, and then gently shake it evenly. The concentrations of the calibration solutions are 0.0ug/L, 5.0ug/L, 10.0ug/L, 20.0ug/L, 50.0ug/L, <100.0ug/L. In the order from low concentration to high concentration, 5.0mL calibration solution was injected into the gas chromatograph for detection. Using the mass concentration of the calibration solution as the abscissa and the measured peak height or area as the ordinate, draw the calibration curve and calculate the regression equation.

Detection steps
Do two detection experiments in parallel, place the blank of the whole procedure and the sample solution collected at room temperature and then inject them into the gas chromatograph in sequence. The purge and trap system without autosampler uses an air-tight syringe to draw 5.0 mL of sample from the sampling bottle and inject it into the purge tube for purge and trap. The purge and trap system with autosampler puts the sample bottle directly into the sample tank of the autosampler, sets the sampling volume to 5.0mL, and then performs purge and trap. Record the peak height or peak area of each measured component chromatographic peak, check it from the calibration curve or calculate the content of each measured component from the regression equation. At the same time, a blank test was performed with laboratory ultrapure water as a blank. When the content of the tested component in the sample exceeds 100ug/L, it must be diluted before testing.
The above method is derived from "GB/T 39298-2020 Reclaimed Water Quality Determination of Benzene Series Gas Chromatography"



