The volatile organic compounds in water are basically the same as those in air, soil and other media, such as methylene chloride, trichloroethylene and toluene. As early as 2012, my country's environmental protection standards stipulated the determination of relevant volatile organic compounds. Continuous online purge and trap/gas chromatography is used to detect volatile organic compounds in surface water. If the collected water sample is 1.5L, the detection limit is 0.03ug/L-0.34ug/L. The detection principle is to use argon or other inert gas (purging gas) to take out the volatile organic compounds in the sample and adsorb and enrich them on the trapping column, and then rapidly increase the temperature to resolve the volatile organic compounds and release them by argon or other inert gas. The gas (carrier gas) is transmitted to a gas chromatograph (GC), separated by a gas chromatographic column, and then enters a chromatographic detector for detection and analysis. Qualitative by chromatographic retention time, quantitative by external standard method, the content of volatile organic compounds in water samples was determined.
Instruments required for testing
1. Gas chromatograph (the transmission line of the instrument must be made of inert material, and the detection accuracy must be ug/L).
2. Purge and trap device (with water sample temperature sensor, headspace time setting, pipeline purification time, etc., the adsorbent is Tenax GR/silica gel/activated carbon ternary composite adsorbent, or other equivalent adsorbents)
3. Capillary column (HP-1 30m×0.32mm×4.0µm) or other equivalent capillary column.
4. Micro syringe: 100L; graduated pipette: 1ml, 2ml, 5ml and 10ml.
5. Sampling cup: with water inlet, water outlet and overflow, it can quantitatively 1.5L for automatic sample collection.
6. General laboratory instruments and equipment.

Reagents required for testing
1. Methanol (CH3OH): chromatographically pure.
2. 19 kinds of volatile organic compound standard stock solutions: each component concentration ρ=2000mg/L, commercially available certified standard solutions, and stored in accordance with the requirements of the instructions.
3. Volatile organic compound standard intermediate solution: the concentration of each component is ρ=2000µg/L, and the volatile organic compound standard stock solution is diluted with methanol.
4. Purge gas and carrier gas: argon (or other inert gas), purity ≥99.999%.
Check detailed steps
Instrument performance check
After starting up, first check the instrument performance of the instrument system, and run the corresponding inspection according to the instrument manual. In order to ensure the accuracy of the test results, the analysis results should be checked through the built-in check standard sample or the configured standard sample before sample preparation, and the accuracy of the instrument should be determined, and the requirements for the use of the instrument should be met.
Gas Chromatography Reference Conditions
Program temperature: initial temperature 60°C, hold for 1 minute, 4°C/minute to 90°C, then 6°C/minute to 135°C, and finally 20°C/minute to 200°C, hold for 45 seconds, the heating process is 20 minute; valve temperature: 50°C; carrier gas pressure: 620 psi; detector temperature: 80°C. The rest of the parameters are set according to the instrument instruction manual.
Other instruments that meet the requirements can set relevant parameters according to their own characteristics or instructions
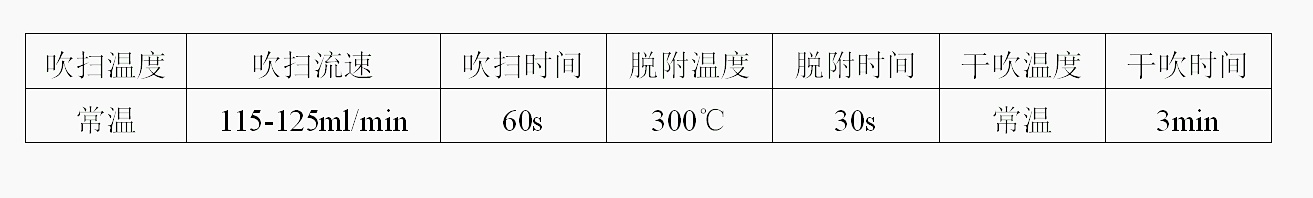
Purge and trap reference conditions
Establishment of calibration curve
The standard solution was diluted step by step to prepare standard series solutions with target compound mass concentrations of 0g/L, 1g/L, 2g/L, 5g/L, 10g/L and 20g/L respectively. The prepared standard series of samples are mixed evenly, and according to the reference conditions of the instrument, the samples are sequentially injected and analyzed from low concentration to high concentration, and the retention time and peak area response value of the standard series of target compounds are recorded. Take the mass concentration of the target compound as the abscissa and the quantitative peak area response value of the target compound as the ordinate to establish a calibration curve.
Test water samples
The collected and processed water samples were measured with the same detection instrument according to the steps of establishing the calibration curve.
The above method comes from 《DB32/T 3945-2020 Water Quality Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds Continuous Online Purge and Trap/Gas Chromatography》



