Purge and trap gas chromatography mainly uses nitrogen or other inert gas to purge the sample at a certain flow rate, and the purged gas passes through a trap tube equipped with an appropriate adsorbent for enrichment; after the purge procedure is completed Then, rapidly heat the trap tube and backflush with nitrogen to desorb the acrylonitrile and acrolein adsorbed in the trap tube and enter the gas chromatograph, where they are separated by a capillary column and detected by a hydrogen flame ionization detector. Retention time qualitative, chromatographic peak area (peak height) quantitative.

Reagents and instruments used for testing
1. Acrylonitrile and acrolein standard products: commercially available certified standard products, generally using water as solvent; or directly purchase chromatographically pure standard products.
2. Acrylonitrile standard solution 100mg/L
3. Acrylonitrile standard stock solution
Weigh 100 mg of acrylonitrile (chromatographically pure, accurate to 0.1 mg) into a 10 ml volumetric flask containing part of laboratory first-grade pure water, dilute to volume with laboratory first-grade pure water, and mix well. The concentration of this stock solution was 10000 mg/L.
4. Acrylonitrile standard solution
Take 100.0ul of acrylonitrile standard stock solution in a 10mL volumetric flask containing part of laboratory first-grade pure water, dilute to volume with laboratory first-grade pure water, and mix well. The concentration of the standard solution is 100 mg/L.
5. Acrolein standard solution 100mg/L
Standard stock solution of acrolein: Weigh 100mg of acrolein (chromatographically pure, accurate to 0.1mg) into a 10ml volumetric flask containing some laboratory first-grade pure water, dilute to volume with laboratory first-grade pure water, and mix well. The concentration of this stock solution was 10000 mg/L.
6. Standard use liquid of acrolein
Take 100.0ul of acrolein standard stock solution in a 10mL volumetric flask containing part of laboratory first-grade pure water, dilute to volume with laboratory first-grade pure water, and mix well. The concentration of the standard solution is 100 mg/L.
7. High-purity nitrogen, purity 99.999%.
8. Hydrogen, purity 99.99%.
9. Air
10. Gas chromatograph
With temperature program function and hydrogen flame ionization detector (FID), chromatography data processing workstation or integrator matched with the instrument.
11. Chromatographic column: polar capillary column, 60m×0.53mm×1.0um, or a chromatographic column with similar performance. The performance of the chromatographic column should be such that the resolution between the components is greater than 1.5 under the given conditions.
12. Micro syringe: 10ul, 100ul, 1000ul.
13. Purge and trap instrument
Brown VOC matching glass tube, 40mL, or similar performance tube. Capture tube containing Tenax, or similar performance capture tube, aeration tube, 5mL or 25mL.
14. Volumetric flask, 10 mL.
Sample handling and storage
Apply 10% (V/V) hydrochloric acid at the sampling site to adjust the pH value of the water sample to 4-5, and then pour it into a 40mL brown VOC tube. The water sample should fill the entire VOC tube without leaving air bubbles and cover it. seal. The collected water samples were immediately stored at 4°C away from light, and the analysis was completed within 1 day.
Water sample testing steps
Reference chromatographic analysis conditions:
1. Column temperature: the initial temperature was 40°C, raised to 80°C at a rate of 5°C per minute and held for 8 minutes, and then raised to 190°C at a rate of 50°C per minute and held for 7 minutes.
Since the boiling point of acrolein is low at 52.5°C, it is reasonable to choose 40°C as the initial temperature after experiments with different initial temperatures. Considering the complexity of the analysis speed of the sample and the actual composition of the sample in the temperature program, the resolution is greater than 1.5, and the interference of other components on acrolein and acrylonitrile is also considered. The final rise to 190°C is to completely elute and burn off the residue in the column.
2. Detector: temperature 250℃.
3. Injection port: splitless injection, temperature 200℃.
4. Gas flow: N2: 8.1mL/min, H2: 30mL/min, AIR: 300mL/min.
Purge conditions:
1. Sample purge temperature: 50°C.
Selection of purging temperature: Increasing the purging temperature is equivalent to increasing the vapor pressure, so the purging efficiency will also increase. When purging components with high water solubility, the purging temperature has a greater effect on the purging efficiency. However, the amount of water vapor brought out by the high temperature increases, which is not conducive to the next step of adsorption. Since the boiling point of acrolein is 52.5°C, 50°C was chosen as the purge temperature.
2. Purge time: 20min.
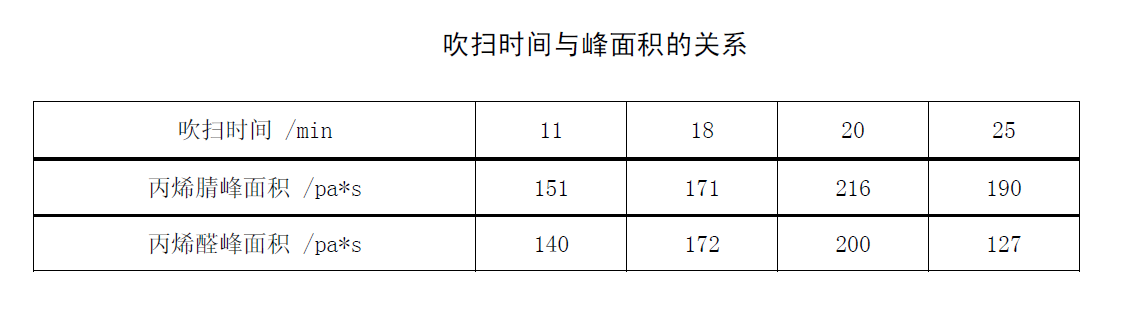
The volume of the purge gas is equal to the product of the flow rate of the purge gas and the purge time. The appropriate purge efficiency is usually selected by controlling the gas volume. The larger the total gas volume, the higher the purging efficiency. However, the total volume is too large, which is unfavorable for subsequent capture, and will blow off the substances captured in the adsorbent. Therefore, it is generally controlled between 400-500ML. When the purging flow rate is constant, 4 groups of acrylonitrile and acrolein with the same concentration are subjected to purging tests at different times, and the results refer to the relationship table between purging time and peak area.
3. Desorption temperature and time: desorption temperature 190℃, desorption time 0.5min.
A reasonable desorption temperature is the key to the analysis of purge and trap gas chromatography, which affects the accuracy and repeatability of the entire analytical method. A higher desorption temperature can better send volatile substances into the gas chromatographic column and obtain narrow chromatographic peaks, generally between 190-200 °C.
Steps for drawing the calibration curve
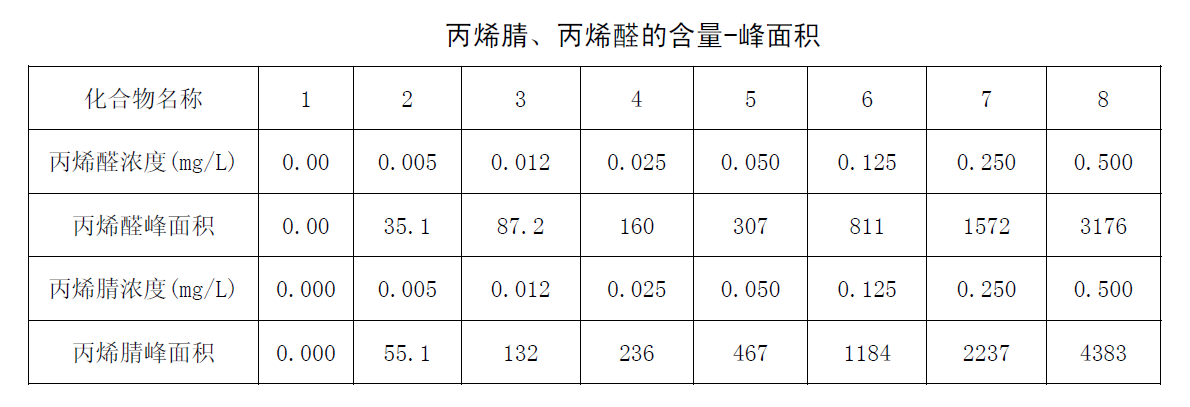
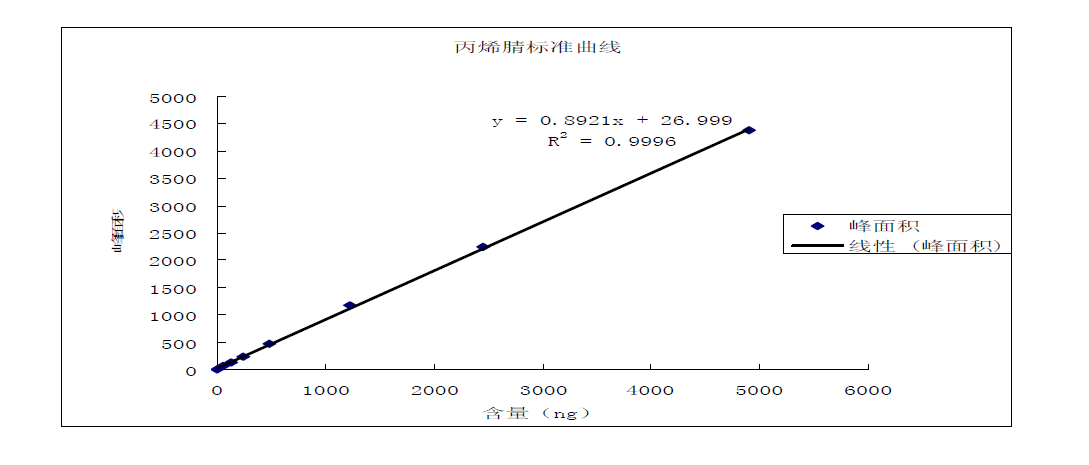
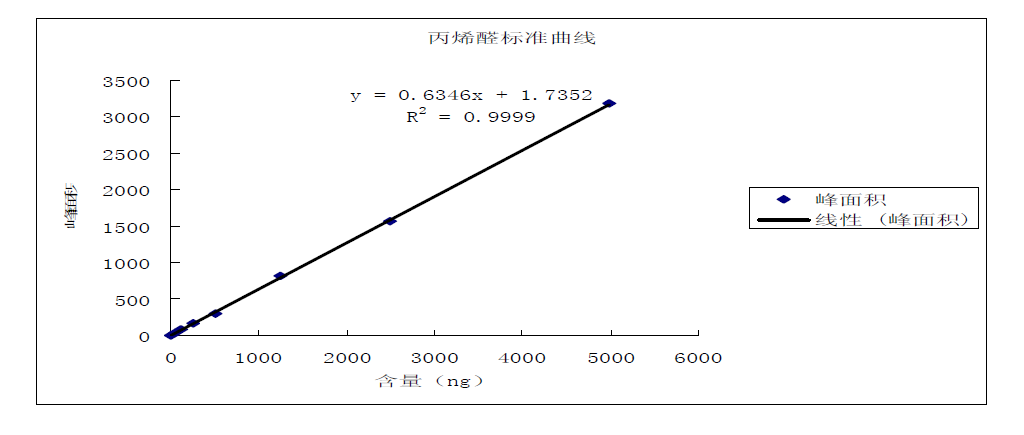
Take 8 VOC tubes with 40ml distilled water (pH4-5) added, and add acrylonitrile and acrolein standard solution in turn; the standard concentrations are 0.000mg/L, 0.005mg/L, 0.012mg/L, 0.025mg/L, 0.050 mg/L, 0.125mg/L, 0.250mg/L, 0.500mg/L, shake well. Accurately take 5.0mL to the aeration tube for purging, and then analyze by gas chromatography. Take the peak area (peak height) as the ordinate and the concentration of acrylonitrile and acrolein as the abscissa to draw the working curve. The specific determination results are shown in the acrylonitrile, acrolein content-peak area, acrolein calibration curve and acrylonitrile calibration curve graphs.
Test water samples
Before each test, the chromatographic system must be calibrated. After the calibration is completed and there is no problem with the instrument, draw the same conditions according to the calibration curve, and take 5mL of the treated water sample to the aeration tube for testing. Finally, according to the measured peak areas (peak heights) of acrylonitrile and acrolein in the water sample, the concentrations of acrylonitrile and acrolein were directly calculated through the calibration curve.



