The principle of microcoulometric detection of adsorbable organic halogens (AOX) is to acidify the water sample with nitric acid, use activated carbon to adsorb the organic compounds in the acidified water sample, and use the NaNO3-HNO3 mixture to elute the inorganic halide adsorbed on the activated carbon. The activated carbon is pyrolyzed and combusted in an oxygen stream to generate hydrogen halide gas, and the hydrogen halide gas is passed into the micro-coulomb cell, and the amount of halide ions is measured by the micro-coulomb method, and the result is expressed by the mass concentration of chlorine.

Methods of Eliminating Interference in Detection
When the concentration of inorganic chloride in the water sample is greater than 1g/L, or the dissolved organic carbon (DOC) exceeds 10mg/L, it must be diluted and measured. Alcohols, aromatic compounds, and hydroxy acids can cause low results.For water samples containing high chlorides (concentrations of about 1 g/L), the oscillatory adsorption process resulted in higher positive interference than the column adsorption process.
If the water sample contains active chlorine or inorganic bromide and iodide, its adsorption to activated carbon is irreversible, which can lead to a high measurement result of adsorbable organic halogen (AOX). interference.
Organic bromide and organic iodide may be decomposed into elemental bromine and elemental iodine respectively during the combustion process to generate high-valence oxides of bromine and iodine. This part of AOX cannot be measured, which will lead to low measurement results.
Water samples containing living cells (such as microorganisms, algae, etc.) may have high results due to their own chloride content.
For water samples containing suspended solids, the suspended particles may contain substances that contribute to AOX. The pretreatment method of column adsorption may cause pipeline blockage. It is recommended to use the vibration method for activated carbon adsorption.
Reagents needed for testing
1. Activated carbon: use commercially available activated carbon with technical indicators that meet the requirements: iodine value is greater than or equal to 1050; chloride content is less than 0.0015%; as activated carbon for vibration adsorption, the particle size is about 10um-50um; as activated carbon for column adsorption, the particle size is about 50um -100um.2. Nitric acid: 1.42g/ml, 65%.
3. Nitric acid solution: 0.02mol/L.
Measure 1.36ml of nitric acid and make up to 1000ml with water.
4. Hydrochloric acid: 1.19g/ml, 37%.
5. Hydrochloric acid solution: 0.010mol/L.
Measure 0.83ml of hydrochloric acid and dilute to 1000ml with water.
6. Sulfuric acid: 1.84g/ml.
7. Sodium nitrate stock solution: 0.2mol/L.
Weigh 17.00g of sodium nitrate (NaNO3) and dissolve it in water, add 25ml of nitric acid, transfer it into a 1000ml volumetric flask, and dilute to the mark with water. Sodium nitrate stock solution can be stored in amber glass bottles for three months.
8. Sodium nitrate eluent: 0.01mol/L, pH≈1.7.
Take 50ml of sodium nitrate stock solution, transfer it into a 1000ml volumetric flask, and dilute to the mark with water. Sodium nitrate eluent can be stored in amber glass bottles for one month.
9. Sodium sulfite solution: 1mol/L.
Weigh 126g of sodium sulfite (Na2SO3), dissolve it in water, transfer it to a 1000ml volumetric flask, and dilute to the mark with water. This solution can be kept refrigerated at 4°C for one month.
10. p-chlorophenol stock solution: 200ug/ml.
Accurately weigh 72.5mg of p-chlorophenol (C6H5ClO), dissolve it in water, transfer it to a 100ml volumetric flask, and dilute to the mark with water. The p-chlorophenol stock solution is stored in a glass bottle and refrigerated at 4°C for one month.
11. Use solution of p-chlorophenol: 1.00ug/ml.
Take 5.00ml of p-chlorophenol for stock solution, transfer it into a 1000ml volumetric flask, dilute to the mark with water, and prepare it now.
12. 2-Chlorobenzoic acid stock solution: 250ug/ml.
Accurately weigh 110.4mg of 2-chlorobenzoic acid (ClC6H4COOH), dissolve it in water, transfer it to a 100ml volumetric flask, and dilute to the mark with water. The 2-chlorobenzoic acid stock solution is stored in a glass bottle and refrigerated at 4°C for one month.
13. 2-Chlorobenzoic acid using solution: 1.00ug/ml.
Take 4.00ml of 2-chlorobenzoic acid stock solution (, transfer it into a 1000ml volumetric flask, dilute it with water to the mark, and use it now.
14. Calibration Solution
Pipette 1.00ml, 5.00ml, 10.0ml, 20.0ml and 25.0ml of the working solution into a 100ml volumetric flask, and dilute to the mark with water. The concentrations of AOX contained in this calibration solution are: 10.0ug/L, 50.0ug/L, 0.10mg/L, 0.20mg/L and 0.25mg/L. The standard solution series needs to be prepared immediately.
15. Potassium iodide (KI).
16. Starch indicator: 10g/L.
Weigh 1.0g of soluble starch, make a paste with a small amount of water, slowly pour 100ml of warm water, continue to cook until the solution is clear, and use after cooling.
Required instruments and equipment
1. BurnerBurning furnace: The heating temperature is adjustable, at least 950 ℃.
Combustion tube: Quartz combustion tube with a diameter of 2-4cm and a length of about 30cm, both horizontal and vertical furnaces can be used.
2. Detector
A microcoulomb counter capable of detecting 1ugCl- with a relative standard deviation of <10%.
3. Drying tube
For drying gas, the absorption tube is filled with sulfuric acid, and the volume accounts for about 20% of the volume of the tube.
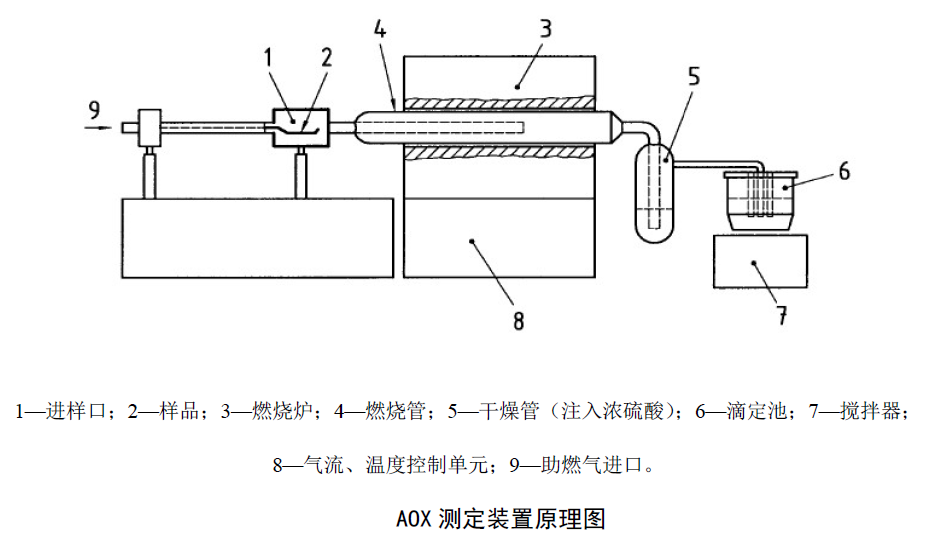
4. Activated carbon adsorption device
1. Oscillation adsorption device
Shaker: A horizontal shaker with a fixed conical flask clamp, the oscillation frequency is 150-250 times/min, and the amplitude is 4-10cm.
Filtration equipment: A filter funnel with a diameter of 25mm and a volume of 150ml can be installed.
Polycarbonate membrane: diameter 25mm, pore size 0.45um.
Erlenmeyer flask: 250ml glass Erlenmeyer flask.
2. Column adsorption device
The inner diameter of the activated carbon column adsorption system is 2-3mm, and the column length is 40-50mm. Each activated carbon adsorption column contains 50 mg of activated carbon, and the activated carbon particles are fixed in a quartz tube with ceramic wool or similar materials at both ends. Two activated carbon adsorption columns are used in vertical series, and the piston pump is connected with the activated carbon adsorption tube with a polytetrafluoroethylene tube.
Water sample collection and preservation
Glass, plastic or polytetrafluoroethylene vessels can be used for sampling, transportation and storage, and glass vessels should be used if the concentration of AOX is expected to be less than 50.0ug/L.
In order to avoid oxidant in the water sample, 10ml of sodium sulfite solution should be added to each liter of water sample immediately after sampling.
If there is free chlorine in the water sample, add 2 ml of nitric acid per liter of water to make the pH < 2. If it cannot be reached, add an appropriate amount. The glass bottle should be filled with water sample without leaving air bubbles.
It should be analyzed as soon as possible after sampling; if storage is required, the water sample should be acidified with nitric acid to make the pH <2, and the water sample can be refrigerated below 4°C for 3 days. If there are microorganisms, acidify the water sample with nitric acid to make the pH < 2, and measure it after 8 hours.
Pretreatment of water samples
The optimal working range of the instrument is about 10.0ug/L-0.300mg/L, try to ensure that the water sample or diluted water sample is within this concentration range; for water samples with chloride ion concentration exceeding 1g/L, use nitric acid For dilution, in the process of water sample dilution, the volume of the original water sample should not be less than 5ml. If the dilution ratio exceeds 10 times, it should be diluted step by step.
After the water sample is placed at room temperature, take 100ml of the mixed water sample or the diluted water sample, and add 5ml of sodium nitrate stock solution.
Oscillation adsorption
Put the water sample in a 250ml conical flask, add 50mg of activated carbon, place the conical flask on a horizontal shaker, the oscillation frequency is based on the slight shaking of the water sample in the conical flask, shake for 1 hour, and pump through a polycarbonate filter. Filter, wash the activated carbon filter cake with about 25ml of sodium nitrate eluent several times to keep the filter cake moist, and avoid long-term contact between the filter cake and the air, which leads to high results. The polycarbonate filter membrane and activated carbon particles after vibration adsorption were transferred to a quartz vessel and fixed with ceramic wool. The adsorption step can also be accomplished using a commercially available complete set of oscillating adsorption pretreatment devices.
Column adsorption
Connect two adsorption columns, each adsorption column is filled with 50mg activated carbon, filter the water sample at a speed of 3ml/min, and then wash with 25ml of sodium nitrate eluent at a speed of 3ml/min, and keep the activated carbon column wet.
If the water contains particulates, make sure the particulates are trapped at the top of the adsorption column. The adsorption step can also be accomplished using a commercially available complete column adsorption pretreatment device.
Detection process
Instrument debugging
1. Adjust the burner temperature to at least 950℃, other parameters refer to the relevant information provided by the instrument manufacturer.2. Connect the combustion pipe and the drying pipe, and inject sulfuric acid into the drying pipe. Be careful to avoid the wrong connection of the absorption tube to cause the concentrated sulfuric acid to be sucked back.
3. Adjust the oxygen flow to about 150ml/min.
Calibration of Coulomb Counters
To check whether the instrument is within the working range before microcoulometric determination, use at least one of the following methods:a) Directly inject 50ul-100ul hydrochloric acid solution (6.6) into the Coulomb cell, and measure its concentration;
b) use the hydrochloric acid solution (6.6) for the determination to obtain a measurement of the charge of the hydrochloric acid sample,
When the equipment is in normal working condition, the test factor should be between 0.97-1.03.
Water sample determination
The prepared sample was pushed into the heating zone in the combustion quartz tube and counted by Coulomb cell titration.
Blank test
Use the same procedure for measuring the sample to determine the reagent blank value.Significant positive deviations may occur if samples with lower AOX values contain more than 1 g/L of chloride ion. In this case, the same concentration of chloride ions can be added to the blank sample for testing, which can effectively compensate for the deviation caused by inorganic chloride.
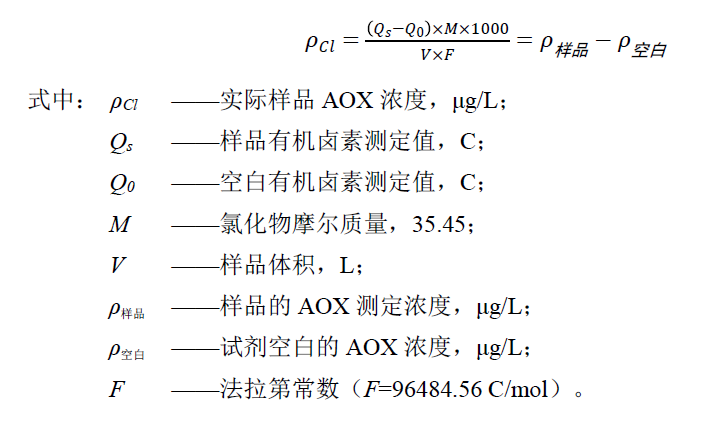
The concentration of AOX in water (ug/L) is calculated according to the formula.