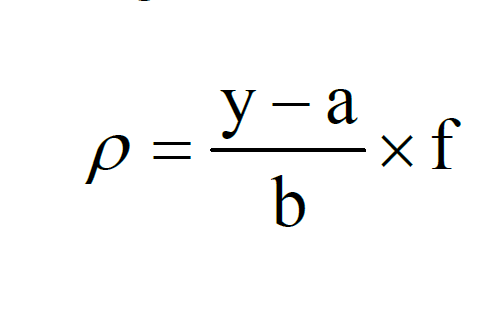After the water sample is distilled online, hydrogen cyanide will be released, which will be converted into cyanogen monochloride by reacting with chloramine-T, and then react with isonicotinic acid and 1,3-dimethylbarbituric acid to form a red substance. We measured its absorbance at a wavelength of 600 nm. Finally, the content of cyanide in the tested water sample is obtained through the relevant calculation formula.

Methods of Eliminating Interference During Detection
The presence of oxidative substances such as active chlorine in the water sample will interfere with the detection. You can add sodium sulfite solution before distillation to eliminate the interference; the presence of nitrite ions in the water sample will also interfere with the detection. You can add sulfamic acid before distillation to eliminate the interference ; If there is sulfide in the water sample to interfere with the detection, solid powder such as cadmium carbonate or lead carbonate can be added before distillation to eliminate the interference; if the concentration of carbonate or bicarbonate in the water sample is too high, it must be used with hydrogen Dilute the sodium solution 5-10 times. Carbonates/bicarbonates are unstable in acidic solutions and tend to generate carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide will interfere with the air bubbles of the distillate and interfere with the measurement, which can be eliminated by dilution, but when the concentration of carbon dioxide is higher than 1000mg/L, it will interfere with the detection, and it must be diluted before operation. Thiocyanate produces less than 1% positive interference.
Detection reagent
1. Sodium hydroxide.2. Hydrochloric acid: 1.19g/ml.
3. Potassium cyanide.
4. Sodium chloride: benchmark grade.
Dry at 600 °C for 1 h, cool in a desiccator, and wait for use.
5. Potassium chromate.
6. Chloramine-T.
7. Citric acid.
8. Potassium hydrogen phthalate.
9. 1,3-Dimethylbarbituric acid.
10. Zinc sulfate.
11. Isonicotinic acid.
12. Brij35 (Laureth, 30%).
13. Silver nitrate.
14. Try Yinling (p-dimethylaminobenzylidene rhodamine).
15. Sodium hypochlorite).
16. Sodium hydroxide solution 2.5mol/L.
Weigh 100g of sodium hydroxide and dissolve it in an appropriate amount of water. After dissolving, transfer it to a 1000ml volumetric flask, add water to the mark, and mix well.
17. Sodium hydroxide solution 0.5mol/L.
Weigh 20g of sodium hydroxide and dissolve it in an appropriate amount of water. After dissolving, transfer it to a 1000ml volumetric flask, add water to the mark, and mix well. Store in the refrigerator below 4°C for 7 days.
18. Sodium hydroxide solution 0.10mol/L
Weigh 4.0g of sodium hydroxide and dissolve it in an appropriate amount of water. After dissolving, transfer it to a 1000ml volumetric flask, add water to the mark, and mix well. Store in the refrigerator below 4°C for 7 days.
19. Sodium hydroxide 0.01mol/L
Weigh 0.4g of sodium hydroxide and dissolve it in an appropriate amount of water. After dissolving, transfer it to a 1000ml volumetric flask, add water to the mark, and mix well. Store in the refrigerator below 4°C for 7 days.
20. Hydrochloric acid solution 1.0mol/L
Measure 88ml of hydrochloric acid into a 1000ml volumetric flask, add water to the mark, and mix well. Store in the refrigerator below 4°C for 7 days.
21. pH5.2 buffer solution
Weigh 2.3g of sodium hydroxide and dissolve it in 500ml of distilled water, add 20.5g of potassium hydrogen phthalate and add distilled water to about 975ml, mix well, adjust the pH value to 5.2 with hydrochloric acid solution and sodium hydroxide solution, add water to make up the volume To 1000ml, add 1ml Brij35 reagent, mix well. The solution can be stored for 3 months at 4°C in the dark.
22. Chloramine-T solution 2.0g/L
Weigh 2.0g of chloramine-T and dissolve it in 1000ml of water, and mix well. It is prepared and filtered for temporary use.
23. Color developer
Weigh 7.0g of sodium hydroxide and dissolve it in 500ml of distilled water, add 16.8g of 1,3-dimethylbarbituric acid and 13.6g of isonicotinic acid, add distilled water to about 975ml, mix well, use hydrochloric acid solution and hydroxide Adjust the pH value of sodium solution to 5.2, add water to make up to 1000ml, vigorously shake or stir at 30°C for 1 hour, and prepare it immediately for use.
24. Distilling the solution
Weigh 2.0g of citric acid and dissolve it in 700ml of distilled water, add 120ml of sodium hydroxide, mix well, adjust the pH value to 3.8 with hydrochloric acid solution and sodium hydroxide solution, and add water to make up to 1000ml. Store in the refrigerator below 4°C for 7 days.
25. Zinc sulfate solution 10.0g/L
Weigh 10.0g of zinc sulfate and dissolve it in 700ml of distilled water, add water to make up to 1000ml.
26. Sampler flush
Weigh 0.4g of sodium hydroxide and dissolve it in an appropriate amount of water, transfer it to a 1000mL volumetric flask after dissolving, and add water to the mark. Store in the refrigerator below 4°C for 7 days.
27. Sodium chloride standard solution 0.0100mol/L.
Weigh 0.2922g of sodium chloride and dissolve it in an appropriate amount of water. After dissolving, transfer it to a 500mL volumetric flask, add water to the mark, and mix well.
28. Silver nitrate standard solution 0.0100mol/L.
Weigh 0.850g of silver nitrate and dissolve it in water. After dissolving, add water to dilute to 500mL. The solution was stored in a brown bottle and was calibrated with a standard solution of sodium chloride before use.
Calibration method: Measure 10.00mL of sodium chloride standard solution into a 150mL conical flask, and add 50mL of water. Add 3-5 drops of potassium chromate indicator solution to the conical flask, under constant shaking, add the standard solution of silver nitrate to be calibrated from the burette until the solution changes from yellow to light brick red, and record the amount of silver nitrate standard solution. At the same time, use 10.00mL water instead of sodium chloride standard solution for blank test.
29. Cyanide standard stock solution 100mg/L (calculated in CN).
Weigh 0.4g of sodium hydroxide and dissolve it in about 800mL of water, then add 0.25g of potassium cyanide, and after it is completely dissolved, add water to make up to 1000mL, and mix well. This solution is stored in a brown bottle and needs to be calibrated weekly. Or buy certified reference materials.
Calibration method of the configured cyanide standard stock solution: Measure 10.00mL of the cyanide standard stock solution in a conical flask, add 50ml of water and 1ml of sodium hydroxide solution, add 0.2ml of the silver test indicator solution, and titrate with the silver nitrate standard solution , until the solution changes from yellow to orange-red, record the amount of silver nitrate standard solution. At the same time, use 10ml of water instead of cyanide standard stock solution for blank test, and record the amount of silver nitrate standard solution.
30. Cyanide standard solution 10.0mg/L
Measure 10.00ml of cyanide standard stock solution, dilute to 100ml with 0.01mol/L sodium hydroxide solution. Store in the refrigerator below 4°C for 7 days.
31. Silver spirit indicator solution
Weigh 0.02 g of test silver spirit and dissolve it in 100 ml of acetone. The solution is stored in a brown bottle in a dark place for 1 month.
32. Potassium chromate indicator solution
Weigh 10.0 g of potassium chromate, dissolve it in a small amount of water, and add silver nitrate solution dropwise until an orange-red precipitate is formed. After standing overnight, filter and dilute to 100 ml with water.
33. Nitrogen purity ≥99.9%.
testing equipment
1. Continuous flow analyzer: including automatic sampler, chemical reaction module (pretreatment channel, injection pump, reaction channel and flow detection cell, optical path is generally 50mm), peristaltic pump, data processing system.2. Analytical balance: Sensitivity 0.0001g.
3. Ultrasonic instrument: frequency 20-40kHz.
4. Sampling bottle: polyethylene bottle.
Detection steps
How to collect water samples
When collecting water samples, add 2ml of 10mol/L sodium hydroxide solution per liter of sample to make the pH of the sample ≥12, and then store it at 4°C in the dark. The collected samples were measured within 24 h as much as possible. When there is no sulfide, the maximum storage time is 14 days.debug instrument
After the instrument is turned on as required, replace all reagents with pure water to test the tightness of the analysis flow path and the smoothness of the liquid flow. After waiting for 30 minutes for the baseline to stabilize, the system starts pumping the reagent again, and then waits for the baseline to stabilize again before performing the detection operation.Calibrate Instruments
Preparation of standard series
Pipette 0ml, 0.20ml, 0.40ml, 0.60ml, 0.80ml and 1.00ml of standard cyanide solution from a set of 100ml volumetric flasks, dilute with sodium hydroxide solution to the marked line and mix well to prepare 6 concentrations The standard series of points, the cyanide mass concentration (in CN) are: 0mg/L, 0.020mg/L, 0.040mg/L, 0.060mg/L, 0.080mg/L, 0.100mg/L.Create a calibration curve
Measure an appropriate amount of standard series solutions and place them in the sample cup respectively, sample and analyze from low concentration to high concentration, and obtain the signal value (peak height or peak area) of different concentrations of cyanide. Taking the signal value (peak height or peak area) as the ordinate and the corresponding cyanide mass concentration (in CN, mg/L) as the abscissa, draw a calibration curve.water sample testing
Firstly, according to the same instrument measurement conditions as the calibration curve, take an appropriate amount of treated water sample for detection, then record the signal value, and calculate the concentration of cyanide in the water sample through the corresponding formula.