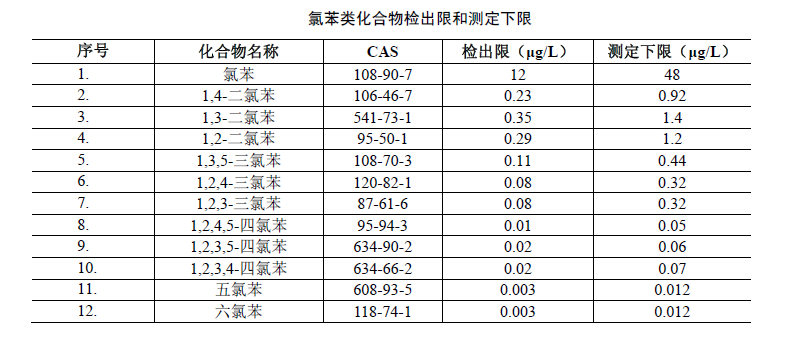
Gas chromatography can detect the content of 12 chlorobenzene compounds in surface water, groundwater, drinking water, seawater, industrial wastewater and domestic sewage. The principle is to use carbon disulfide to extract chlorobenzene compounds in water samples. After purification, concentration and constant volume of the extract, it is analyzed with a gas chromatograph with an electron capture detector (ECD). Legal Quantity.
Reagents used for testing
1. Chlorobenzene compound mixed standard solution:Chlorobenzene 100000ug/ml, 1,4-dichlorobenzene 1000ug/ml, 1,3-dichlorobenzene 1000ug/ml, 1,2-dichlorobenzene 1000ug/ml, 1,3,5-trichlorobenzene 200ug/ml ml, 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene 200ug/ml, 1,2,3-trichlorobenzene 200ug/ml, 1,2,4,5-tetrachlorobenzene 50.0ug/ml, 1,2,3, 5-Tetrachlorobenzene 50.0ug/ml, 1,2,3,4-Tetrachlorobenzene 50.0ug/ml, Pentachlorobenzene 20.0ug/ml, Hexachlorobenzene 20.0ug/ml.
Purchase certified reference materials or standard solutions with different concentrations as needed. After opening, the standard solution should be kept in a sealed container under freezing and dark conditions.
2. Sodium chloride:
Bake at 300 °C for 4 h, cool to room temperature in a desiccator, and store in a ground glass bottle.
3. Anhydrous sodium sulfate
Bake at 300 °C for 4 h, cool to room temperature in a desiccator, and store in a ground glass bottle.
4. Concentrated sulfuric acid: excellent grade pure, 1.84g/ml.
5. Carbon disulfide: chromatographically pure, no interfering peaks are detected by chromatographic detection after 100-fold concentration. Purification can be carried out according to relevant requirements using analytical grade reagents.
6. Methanol: pesticide residue grade.
7. n-hexane: pesticide residue grade.
8. Sodium sulfate solution: 20g/L.
Weigh 20g of anhydrous sodium sulfate, dissolve it in organic-free water and dilute to 1000ml.
9. Carrier gas: nitrogen, purity ≥99.999%.
10. Glass wool
When there is interference, it can be extracted with n-hexane Soxhlet for 4h and stored in a closed container.
Instruments required for testing
1. Gas chromatograph with electron capture detector (ECD).2. Chromatographic column: Quartz capillary column, 30m (length) × 0.25mm (inner diameter) × 0.25um (film thickness), the stationary phase is polyethylene glycol modified with nitroterephthalic acid or other equivalent stationary phases .
3. Separation funnel: 125ml, 2000ml, several.
4. Round bottom flask: 100ml, several.
5. Volumetric flask: 50ml, several.
6. Rotary evaporator.
7. Nitrogen blower.
8. Measuring cylinder: 1000ml.
9. Shaker, 300 times/min.
10. Brown screw bottle: 1ml, with push valve cap.
11. Sample bottle: 2ml.
12. Micro syringe: 10.0ul, 50.0ul.
13. Other commonly used laboratory equipment.
How to deal with water samples
Collect and saveWater samples can be sampled in amber glass bottles, filling the sample bottle with the sample. Seal with caps lined with Teflon silicone pads (or foil pads) to prevent air bubbles. Collected samples should be analyzed as soon as possible. If it cannot be analyzed on the same day, add 1.0 ml of concentrated sulfuric acid to each liter of water sample when sampling, store it at 2-5 °C, and complete the sample analysis within 7 days.
Extraction preparation method
water extraction
Measure 1000ml of water sample with a graduated cylinder, put it in a 2000ml separatory funnel, add 30g of sodium chloride, and extract twice with 20ml and 10ml of carbon disulfide respectively. At the beginning, shake gently by hand, and pay attention to deflation. After the deflation is complete, shake it on the shaker for 5 minutes. After extraction, the layers were left to stand, and the carbon disulfide in the lower layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, collected and incorporated into a 100ml round-bottomed flask, and the anhydrous sodium sulfate layer was rinsed with a small amount of carbon disulfide, and the eluent was also collected in a 100ml round-bottomed flask.
water purification
Seriously polluted surface water, industrial wastewater and domestic sewage are extracted and purified with concentrated sulfuric acid. Use a 125ml separatory funnel to collect the extract, add 5ml of concentrated sulfuric acid and shake gently (to prevent heat generation and pay attention to outgassing), let it stand for stratification and discard the sulfuric acid layer, and repeat the operation until the sulfuric acid layer is colorless. Add 25 ml of sodium sulfate solution, shake to wash off the residual sulfuric acid, stand still for layers, and discard the aqueous phase. The carbon disulfide is dehydrated and dried by anhydrous sodium sulfate, collected in a 100ml round-bottomed flask, and the anhydrous sodium sulfate layer is rinsed with a small amount of carbon disulfide, and the eluent is also collected in a 100ml round-bottomed flask.
Concentrated volume
The extract or purified extract was concentrated to 1.0ml with a rotary evaporator (25°C water bath) and nitrogen blower, and then transferred to a sample bottle. High-concentration samples can be made up to volume in a 50ml volumetric flask and then transferred to sample vials.
Detection steps
Chromatographic analysis reference conditionsInjection volume: 1.0ul.
Vaporization chamber temperature: 220°C.
Detector temperature: 300°C.
Carrier gas flow rate: 1.0 ml/min.
Injection method: splitless injection, split after 0.5min injection, split ratio 60:1.
Heating program: 40°C (4 min hold) then 10°C to 220°C per minute (5 min hold).
Working curve drawing
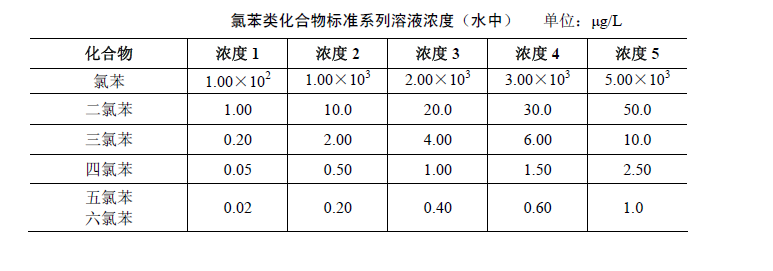
Add 1000ml of pure water to each of 5 2000ml separatory funnels with a measuring cylinder, and then use 10ul, 50ul syringes to add 1.0ul, 10.0ul, 20.0ul, 30.0ul, 50.0ul standard mixed solution and mix well, the concentration of chlorobenzene compounds in water Refer to the concentration of chlorobenzene compound standard series solution. The standard series can be operated according to the water sample extraction preparation steps.Use a gas chromatograph to measure the peak heights or peak areas of standard solutions of chlorobenzene compounds with a series of concentrations, and draw a calibration curve according to the content (ug/L) of various chlorobenzene compounds corresponding to their peak heights or peak areas.
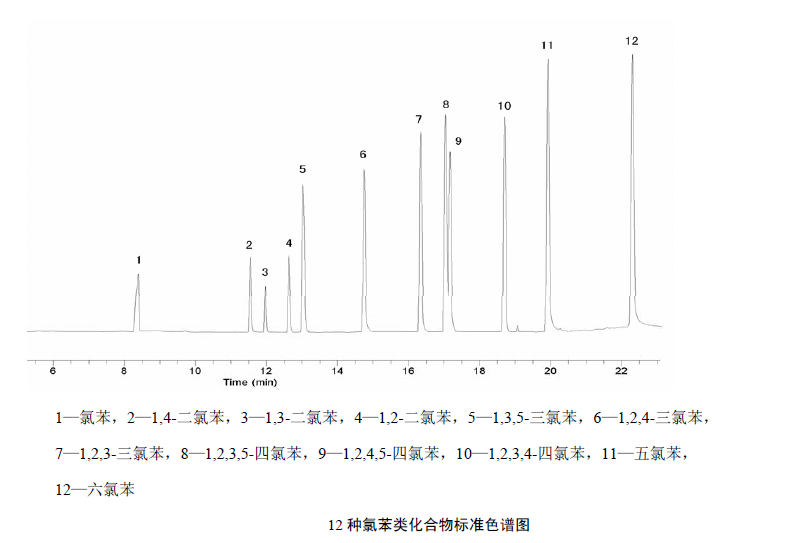
water sample testing
Qualitative analysis can be based on the retention time of each component in the standard chromatogram.In quantitative analysis, the concentration of the analyte in the sample solution can be obtained from the working curve according to the peak area of the analyte.
The concentration of chlorobenzene compounds in water samples can be calculated according to the corresponding formula.
The above content comes from 《HJ 621-2011 Water Quality-Determination of Chlorobenzene Compounds-Gas Chromatography》



