The country has given methods for the detection of sulfide and cyanide in reclaimed water in relevant standards, such as the 2019 standard for the determination of sulfide and cyanide in reclaimed water quality by ion chromatography. The ion chromatography method used in this standard is to enter the water sample into the chromatographic column. With the flow of the eluent, the sulfide and cyanide in the water sample exchange and elute repeatedly with the active exchange groups on the chromatographic column. According to the different retention characteristics of sulfide and cyanide on the chromatographic column, the separation is achieved, and the detection is carried out with an ampere detector. Qualitative by relative retention time of chromatographic peaks, quantitative by peak area or peak height.

Reagents needed for testing
1 Sodium sulfide: stored in a desiccator.
2 Sulfuric acid solution: 1+5.
3 Sodium hydroxide solution: 40g/L.
4 Sodium hydroxide solution: 10g/L.
5 Sodium sulfite solution: 12.6g/L.
6 Standard stock solution of sulfide: p(S)=1000mg/L.
Weigh 0.7500 g of sodium sulfide and dissolve it in 100 mL of sodium hydroxide solution (10 g/L), store in a plastic container, and store in a refrigerator at 4°C. Or use a commercially available standard solution.
7 Standard stock solution of cyanide: 1000mg/L.
Weigh 0.1885 g of sodium cyanide and dissolve it in 100 mL of sodium hydroxide solution (10 g/L), store in a plastic container, and store in a refrigerator at 4°C. Or use a commercially available standard solution.
8 Potassium iodide starch test paper
Weigh 1.5g of soluble starch, stir into a paste with a small amount of water, add 200L of boiling water, mix well. Let cool. Add 0.5g potassium iodide and 0.5g sodium carbonate, dilute with water to 250mL, immerse the filter paper strip, take it out to dry, store in a brown bottle, and keep it tightly sealed.
9 Nitrogen: purity ≥99.99%
Instruments used for testing
1 Ion chromatograph: equipped with eluent pump, guard column, anion analysis column, amperometric detector, and data processing system.
2 All-glass distillation unit.
3 Aqueous filter membrane: the pore size is 0.22um.
Water sample treatment method
1. Water sample collection and preservation method
Water samples need to be collected in accordance with relevant regulations or standards. After the water samples are collected in a brown glass bottle, the pH is adjusted to 9.0-10.0 with sodium hydroxide solution (40g/L) for fixation. The water sample should be filled with the sampling bottle so that there are no air bubbles in the bottle, and it should be sealed immediately. Avoid direct sunlight during transportation.
The collected water samples should be analyzed as soon as possible, otherwise they should be stored at low temperature (0℃-4℃) in the dark, and the determination should be completed within 24 hours.
2. Interference and sample pretreatment
When the water sample contains cobalt (>0.05mg/L), it is necessary to add 1mL of sulfuric acid solution to adjust the pH of the water sample to <2.0, then use an all-glass distillation device for distillation, and then use 10mL of sodium hydroxide solution (10g/L), and finally pass 0.22 um water phase filter after filtration.
If the water sample contains free chlorine and other oxides (>1.0mg/L), it will interfere with the determination of cyanide. The interference can be eliminated by adding sodium sulfite solution before distillation. Two samples of the same volume can be measured and added to one of the samples. 1-3 pieces of potassium iodide-starch test paper, add sulfuric acid solution to acidify, and drop with sodium sulfite solution until the potassium iodide-starch test paper changes from blue to colorless, and record the dosage. Another sample, without adding potassium iodide-starch test paper, only added the sodium sulfite solution of the above amount.
The water sample containing nitrite ions (>50mg/L) will interfere with the determination of cyanide. Sulfamic acid can be added before distillation to eliminate the interference. 1 mg of nitrite needs to be added with 2.5 mg of sulfamic acid.
Detection steps
Ion Chromatography Setup Conditions
Debug the ion chromatograph according to the best conditions provided in the instrument instruction manual, and set the chromatographic conditions as follows:
Chromatographic column: The filler is a chromatographic column of polystyrene/divinylbenzene copolymer with quaternary ammonium group or a gel agglomerated chromatographic column, and other chromatographic columns that can achieve separation effect can also be used;
Eluent: prepared according to the instrument model and the operating conditions of the chromatographic column manual;
Flow rate: 0.8mL/min-1.2mL/min;
Column temperature: 30℃-35℃;
Injection volume: 20uL-25uL;
Detector: Ampere detector.
draw standard curve
Pipette the sulfide standard stock solution or the cyanide standard stock solution and dilute it with sodium hydroxide solution (10g/L) step by step to prepare the sulfide or cyanide mass concentration of 0.5ug/L, 1.0ug/L, 2.0ug/L, respectively. L, 5.0ug/L, and 10.0ug/L calibration solutions were used as low-concentration calibration curves. Prepare calibration solutions with sulfide or cyanide mass concentrations of 10.0ug/L, 20.0ug/L, 50,0ugL, and 100.0ug/L, respectively, as a high-concentration calibration curve. Inject samples from low concentration to high concentration for measurement, take the peak area or peak height as the ordinate, the mass concentration of sulfide or cyanide in the calibration solution as the abscissa, draw the calibration curve and calculate the regression equation.
Determination of water samples
For blank experiment, sodium hydroxide solution (10g/L) can be used as blank solution for blank experiment.
The water sample should be filtered with an aqueous filter with a pore size of 0.22um before testing. After the flow rate and column temperature are stable, inject the test solution under the same chromatographic conditions as the calibration curve. The test solution is quantified by peak area or peak height, and the corresponding concentration of sulfide and cyanide is calculated from the calibration curve or calculated according to the regression equation. The response values of sulfide and cyanide in the test solution should be within the linear range determined by the instrument. An example of a standard chromatogram under specific chromatographic conditions can be found in the following figure.
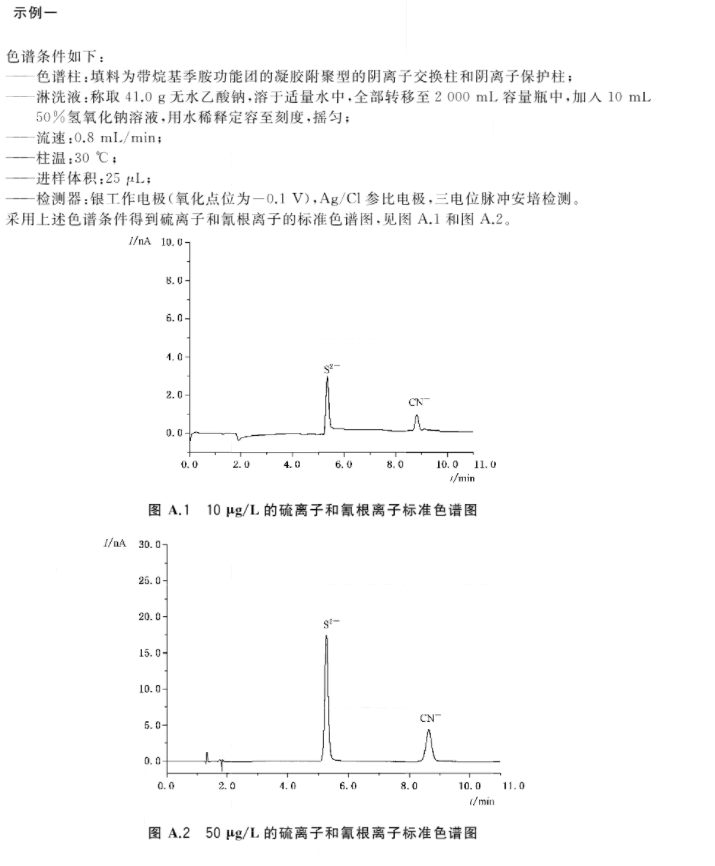
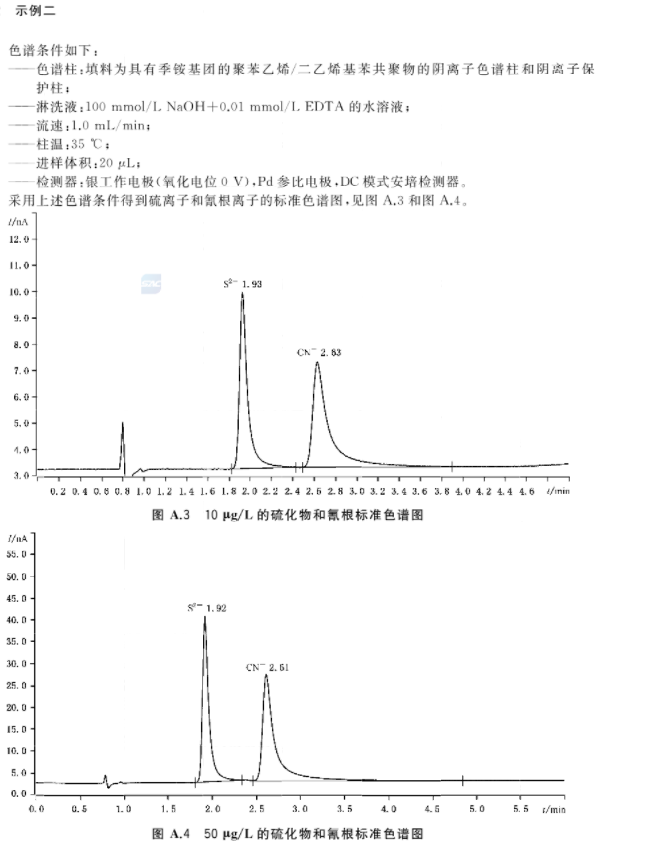
The parameters of sulfide and cyanide in the final water sample can be calculated according to the relevant formula.
The above content comes from 《GB/T 37907-2019 Quality of Reclaimed Water-Determination of Sulfide and Cyanide-Ion Chromatography》



