Faecal coliform is a very important parameter to know if and to what extent surface water is contaminated with fecal water. Therefore, how to quickly, reliably and accurately detect the content of fecal coliforms is of great significance to the health of water quality.
Today we are going to talk about the operation method for the rapid detection of fecal coliforms in surface water by photometry. β-galactosidase, and decompose the chromogen substrate to release chromogen to make the medium change color, which is measured by continuous spectrophotometry (wavelength: 300nm ~ 600nm), according to the color change of the water sample to be tested and the water faecal coliform According to the principle that the number of groups is related to a certain degree, the concentration of fecal coliform bacteria is obtained.

Interference and elimination during detection
1. Active chlorine has oxidizing properties, which can destroy the enzyme activity in microbial cells and lead to cell death. Sodium thiosulfate solution can be added to eliminate interference when collecting water samples.
2. Heavy metal ions are cytotoxic and can destroy the enzyme activity in microbial cells, leading to cell death. Disodium EDTA solution can be added during water sample collection to eliminate interference.
Reagents required for testing
1. Main components of fecal coliform detection reagent:
- Peptone: 5g;
- Manganese sulfate: 0.005g;
- Magnesium sulfate: 0.001g;
- Zinc sulfate: 0.001g;
- Phosphate: 1.78g;
- Amphotericin B: 0.60g;
- 1000mL of distilled water.
Preparation method: Dissolve the above reagents in distilled water, mix well, adjust pH to 7.2-7.4, 68.95kPa (115°C), autoclave for 20min, and store in aliquots at 4°C in the dark for later use. Commercially available media preparations can also be used.
2. Sodium thiosulfate.
3. Disodium EDTA.
4. Sodium thiosulfate solution: 0.10g/mL,
Weigh 15.7g of sodium thiosulfate, dissolve in an appropriate amount of water, dilute to 100mL, and prepare for immediate use.
5. Disodium EDTA solution: 0.15 g/mL, weigh 15 g of disodium EDTA, dissolve it in an appropriate amount of water, and dilute to 100 mL. The shelf life of this solution is 30 days.
6. Sterile water: take an appropriate amount of pure water, sterilize by high pressure steam at 121℃ for 20min, and set aside.
Instruments required for testing
1. Sampling bottle: 100mL, 250mL, 500mL wide-mouth glass bottle with screw cap or ground stopper.
2. Microbial rapid detector:
- Constant temperature cultivation unit: no less than 2 temperature control systems, the temperature control accuracy is 1°C, and the culture temperature of the sample to be tested can be automatically adjusted (44.5°C ± 1°C);
——Detection unit: no less than 4 independent detection systems, which can realize the simultaneous monitoring of multiple samples;
——Data display and processing unit: Automatically output test results, query and display historical data.
3. High pressure steam sterilizer: 121℃ adjustable, 101.3kpa.
4. Graduated cylinder: 50mL, 100mL.
5. Pipette: 1mL, 10mL.
6. Balance: Sensitive amount 0.01g.
Water sample collection and preservation
Collection method
Point layout and sampling frequency are implemented in accordance with relevant national standards. When sampling with other items, first collect microbial samples separately. The sampling bottle should not be washed with water samples, and the water samples should be collected in sterilized sampling bottles.When collecting surface water samples such as rivers, lakes and reservoirs, hold the bottom of the bottle and directly insert the sampling bottle with a stopper into the water, about 10cm-15cm away from the water surface, with the bottle mouth facing the direction of the water flow, pull out the glass stopper, and pour the water sample into the bottle. Then cap the bottle and remove the sampling bottle from the water. If there is no water flow, hold the bottle horizontally and push forward. The sampling volume is generally about 80% of the sampling bottle capacity. After taking the water sample, quickly tie up the sterile wrapping paper.
When collecting surface water, wastewater samples and water samples at a certain depth, a special sampling device after sterilization can be used for sampling. When stratified sampling is carried out at the same sampling point, it should be carried out from top to bottom to avoid disturbance at different levels.
If the sample containing active chlorine is collected, add sodium thiosulfate solution before sterilizing the sampling bottle to remove the inhibitory effect of active chlorine on bacteria (add 0.1 mL of sodium thiosulfate solution per 125 mL volume); if For samples with high content of heavy metal ions, add disodium EDTA solution before sterilizing the sampling bottle to eliminate interference (add 0.3 mL of disodium EDTA solution per 125 mL volume).
preservation method
After sampling, it should be tested within 2 hours, otherwise, it should be refrigerated below 10 °C but not more than 6 hours. After the laboratory receives the sample, if the test cannot be carried out immediately, the water sample should be refrigerated below 4°C and tested within 2 hours.
Detection steps
inoculate
Inoculate the water sample to be tested in a test bottle containing 5 mL of medium, and dilute the volume to 20 mL. The water sample and medium should be thoroughly mixed.nourish
Turn on the power switch of the instrument, wait for the instrument to stabilize for 30 minutes, place the inoculated detection bottle in the rapid microorganism detector, operate according to the instrument manual, set the detection temperature to 44.5 ℃, click the "Detect" button, 2-18 hours, The instrument automatically cultivates the results.
Blank control experiment
Use sterile water as the water sample to be tested for blank determination according to the operation steps of inoculation and culture. The test result cannot be detected, otherwise the sample determination result is invalid, and the blank and the sample to be tested should be re-measured.
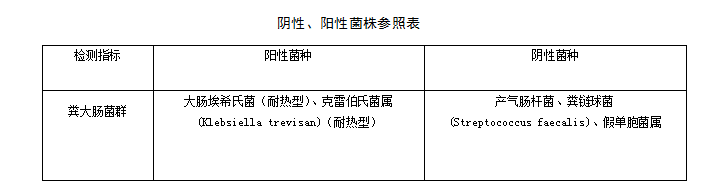
Negative and positive controls
The standard strain is made into a bacterial suspension of 300-3000/mL, and the bacterial suspension is operated according to the requirements of inoculation and culture. The positive strain should show a positive reaction; the negative strain should show a negative reaction. Re-measure.
The negative and positive strains of fecal coliform can refer to the relevant reference table
The above content comes from 《DB37/T 3787-2019 Water Quality Determination of Fecal Coliform Spectrophotometry》



