At present, whether it is drinking water, surface water or sewage, ammonia nitrogen can roughly determine the change of water quality. Before we introduced Kjeldahl method, Nessler method, etc., today we will introduce another method - salicylic acid spectrophotometry Law.
The principle of using salicylic acid to detect ammonia nitrogen in water In the presence of alkaline medium (pH=11.7) and sodium nitroferricyanide, ammonia and ammonium ions in water react with salicylate and hypochlorite ions to form blue compounds , and the absorbance was measured with a spectrophotometer at 697 nm.

Interference and cancellation
This method is used for interfering substances and limits that may be encountered in the analysis of water samples. For details, please refer to the table of the influence of coexisting ions and their elimination.
Serious interferences from aniline and ethanolamine are uncommon and are usually caused by primary amines. Chloramines, excessive acidity, alkalinity, and substances that reduce hypochlorite ions can also interfere.
If the color of the water sample is too dark, the salt content is too high, the potassium tartrate salt has insufficient masking ability for metal ions in the water sample, or if there are high concentrations of calcium, magnesium and chloride in the water sample, pre-distillation is required.
Reagents required for testing
1. Ammonia-free water, prepared by one of the following methods in an ammonia-free environment.
ion exchange method
Distilled water was passed through a column of strongly acidic cation exchange resin (hydrogen form), and the effluent was collected in a glass bottle with a ground glass stopper. Add 10 g of the same resin per liter of effluent to facilitate preservation.
Distillation
In 1000ml of distilled water, add 0.10ml of sulfuric acid, redistillate in an all-glass still, discard the first 50ml of distillate, and then collect about 800ml of distillate in a glass bottle with a ground glass stopper. Add 10g of strong acid cation exchange resin (hydrogen form) per liter of distillate.
water purifier method
1.Prepared immediately before use with a commercially available water purifier.
2. Ethanol, 0.79 g/ml.
3. Sulfuric acid, 1.84 g/ml.
4. Light Magnesium Oxide
Free of carbonates, the magnesia is heated at 500°C to remove carbonates.
5. Sulfuric acid absorption solution, 0.01mol/L.
Measure 7.0ml of sulfuric acid into water and dilute to 250ml. Take 10ml before use and dilute to 500ml.
6. Sodium hydroxide solution 2mol/L.
Dissolve 8g of sodium hydroxide in water and dilute to 100ml.
7. Color developer (salicylic acid-potassium sodium tartrate solution)
Weigh 50g of salicylic acid, add about 100ml of water, then add 160ml of sodium hydroxide solution, stir to dissolve it completely; then weigh 50g of potassium sodium tartrate, dissolve in water, combine with the above solution and transfer to a 1000ml volumetric flask, add water to dilute to the marking line. Stored in amber glass bottles with rubber stoppers, this solution is stable for 1 month.
8. Sodium hypochlorite
Commercial reagents can be purchased or prepared by yourself.
Sodium hypochlorite stored in plastic bottles should be calibrated for available chlorine concentration and free alkali concentration (calculated as NaOH) before use.
9. Sodium hypochlorite working solution, 3.5g/L, c (free base)=0.75mol/L.
Take the calibrated sodium hypochlorite, dilute it with water and sodium hydroxide solution into a sodium hypochlorite working solution with an effective chlorine concentration of 3.5g/L and a free alkali concentration of 0.75mol/L (calculated as NaOH), and store it in a brown dropping bottle. This reagent is stable 1 month.
10. Sodium nitroferricyanide solution, 10g/L.
Weigh 0.1g of sodium nitroferricyanide into a 10ml colorimetric tube with a stopper, and add water to the mark. This reagent is stable for 1 month.
11. Cleaning solution
Dissolve 100 g of potassium hydroxide in 100 ml of water, add 900 ml of ethanol after cooling the solution, and store it in a polyethylene bottle.
12. Bromthymol blue indicator (bromthymolblue), 0.5g/L.
Dissolve 0.05 g of bromothymol blue in 50 ml of water, add 10 ml of ethanol, and dilute to 100 ml with water.
13. Ammonia nitrogen standard stock solution, 1000ug/ml.
Weigh 3.8190g of ammonium chloride (excellent grade, dry at 100-105℃ for 2h), dissolve it in water, transfer it into a 1000ml volumetric flask, and dilute to the mark. This solution is stable for 1 month.
14. Ammonia nitrogen standard intermediate solution, 100ug/ml.
Pipette 10.00ml of ammonia nitrogen standard stock solution into a 100ml volumetric flask and dilute to the mark. This solution is stable for 1 week.
15. Ammonia nitrogen standard solution, 1ug/ml.
Pipette 10.00ml of ammonia nitrogen standard intermediate solution into a 1000ml volumetric flask and dilute to the mark. Ready to use.
Equipment used for testing
1. Visible spectrophotometer: 10-30 mm cuvette.
2. Dropping bottle: The dropper drops the volume of liquid, 20 drops are equivalent to 1 ml.
3. Ammonia nitrogen distillation device: It is composed of 500 ml Keck flask, nitrogen ball, straight condenser tube and conduit. The end of the condenser tube can be connected to a dropper of appropriate length, so that the tip of the outlet is immersed under the liquid surface of the absorption liquid. Distillation flasks can also be used.
4. Glassware commonly used in laboratories: All glassware should be carefully cleaned with cleaning solution and then rinsed with water.
Water sample collection and preservation
Water samples are collected in polyethylene or glass bottles and analyzed as soon as possible. For preservation, add sulfuric acid to acidify the water sample to pH<2, and it can be stored for 7d at 2-5℃.
Pre-distillation of water samples
Transfer 50ml of sulfuric acid absorption solution into the receiving bottle, and ensure that the outlet of the condenser tube is below the liquid level of the sulfuric acid solution. Divide 250ml of water sample (if the ammonia nitrogen content is high, it can be taken less appropriately, add water to 250ml), transfer it into the flask, add a few drops of bromothymol blue indicator, if necessary, adjust the pH to 6.0 with sodium hydroxide solution or sulfuric acid solution (the indicator is yellow) -7.4 (the indicator is blue), add 0.25g of light magnesium oxide and a few glass beads, and immediately connect the nitrogen ball and the condenser tube. Heat the distillation to make the distillate rate about 10ml/min. When the distillate reaches 200ml, stop the distillation and add water to make the volume to 250ml.
Detection steps
Calibration curve
When measuring with a 10mm cuvette, you can refer to the figure below to prepare a standard series.
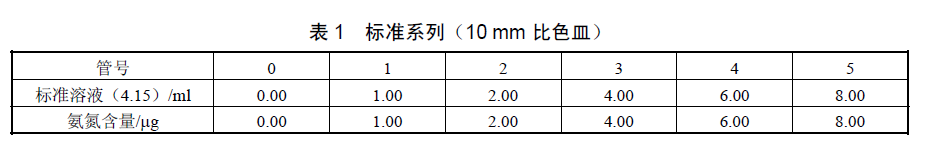
When measuring with a 30-code cuvette, the standard series can be prepared according to the following figure
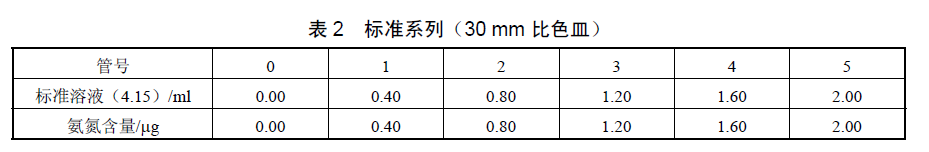
According to the above two charts, take six 10ml colorimetric tubes, respectively add the above ammonia nitrogen standard solution, dilute to 8.00ml with water, and measure the absorbance according to the water sample detection steps. Take the absorbance after subtracting the blank as the ordinate, and draw the calibration curve with its corresponding ammonia nitrogen content (ug) as the abscissa.
Water quality determination
Take 8.00ml of water sample or pre-distilled sample (when the concentration of ammonia nitrogen in the water sample is higher than 1.0mg/L, it can be properly diluted and sampled) in a 10ml colorimetric tube. Add 1.00ml of developer and 2 drops of sodium nitroferricyanide and mix well. Add 2 drops of sodium hypochlorite solution and mix well, add water to dilute to the mark, and mix well.
After 60min of color development, at the wavelength of 697nm, use a 10mm or 30mm cuvette to measure the absorbance with water as a reference.
Blank test
The water samples were replaced with water, and the pretreatment and measurement were carried out in the same steps as the sample analysis.
Finally, the concentration of ammonia nitrogen in the water sample was obtained according to the formula.



