The halogenated hydrocarbons in the collected surface water samples were adsorbed by solid-phase microextraction fibers, enriched in the headspace, and detected by gas chromatography and electron capture detector (ECD). Qualitative by chromatographic retention time and quantitative by external standard method.

Reagents required for detection
1. Experimental water: double distilled water or laboratory first-grade pure water. Before use, perform a blank check to confirm that there is no interference of the target compound or the concentration of the target compound is below the detection limit of the method.
2. Methanol: chromatographically pure. Before use, perform a blank check to confirm that there is no interference of the target compound or the concentration of the target compound is below the detection limit of the method.
3. Sodium chloride: before use, burn in a muffle furnace at 400°C for 4 hours, cool to room temperature in a desiccator, and transfer to a ground glass bottle for storage.
4. Ascorbic acid.
5. Sodium thiosulfate.
6. Standard solution: 100mg/L-2000mg/L, commercially available certified standard solution with methanol as solvent.
7. Carrier gas: high-purity nitrogen, with a purity greater than 99.999%, deoxidized by deoxidizer and dehydrated by molecular sieve.
Testing equipment
1. Gas chromatograph: with split/splitless inlet, electron capture detector (ECD), temperature programmable.
2. Chromatographic column: Quartz capillary column, 60m (length) × 0.25mm (inner diameter) × 1.4 μm (film thickness), the stationary phase is 6% cyanopropylbenzene-94% dimethylsiloxane, or others Efficient capillary column.
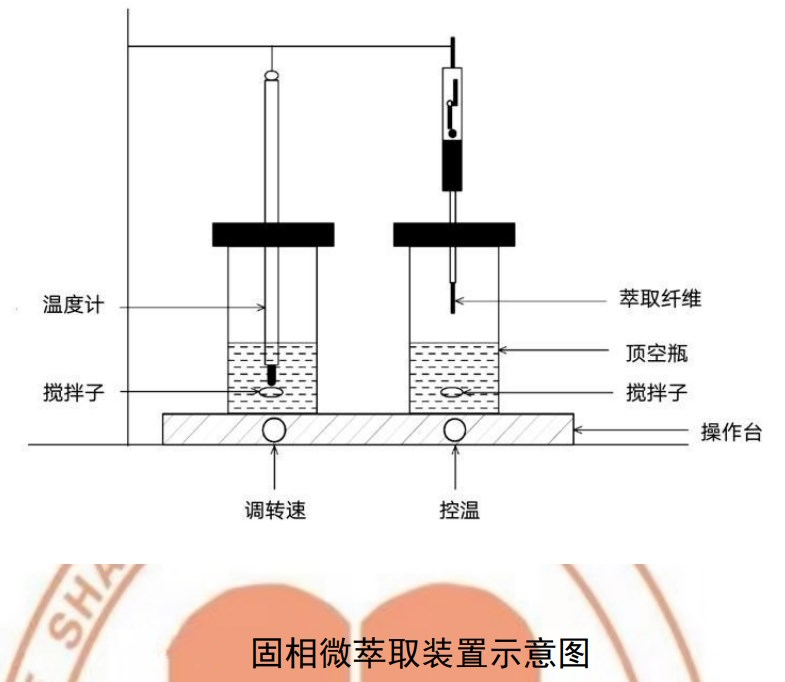
3. Solid phase microextraction device:
SPE bench; SPE handle; SPE fiber (SPME): Divinylbenzene/Carboxen/Dimethicone), or other equivalent extraction fibers. Before the first use, the extracted fibers should be placed in the injection port for aging.
4. Gas chromatograph liner: no glass wool liner.
5. Glass microsyringe: 10uL-250uL.
6. Headspace vial: 15mL or 20mL headspace vial, with sealing gasket (polytetrafluoroethylene/silicon rubber material), sealing cap (screw cap or single-use gland), can also be used with headspace sampler Matching glass headspace vials.
7. Sampling bottle: 40mL brown screw-top glass bottle with a silicone rubber-PTFE liner screw cap.
8. Other commonly used laboratory equipment.
water sample collection
The collection of surface water samples and groundwater samples shall be carried out in accordance with relevant regulations. When collecting water samples, do not wash with water samples, and the water samples should overflow in the water sample bottle without leaving space. When sampling, try to avoid or reduce the exposure of water samples to the air. All water samples were collected in parallel, sealed and labelled immediately after sampling.
water sample preservation
After the water samples were collected, without adding any preservatives, they were immediately placed in a refrigerator for transportation at a temperature below 4°C, and the water sample analysis was completed within 24 hours. If the water sample contains residual chlorine, add 0.3g-0.5g ascorbic acid or sodium thiosulfate to the sampling bottle.
Detection steps
Instrument Reference Conditions
Headspace/Solid Phase Microextraction Reference Conditions:Equilibrium temperature: 30°C; Equilibrium time: 10min; Extraction time: 30min; Stirring speed: 500r/min.
Reference conditions for chromatographic analysis:
Heating program: 45°C (hold for 3 min), raise the temperature at 8°C/min to 90°C (hold for 4 min), and then heat up to 200°C at 6°C/min. (hold for 5min), and finally raise the temperature to 240℃ at 20℃/min (hold for 18min); injection port analysis temperature: 260℃; analysis time: 5min; injection method: splitless injection; detector temperature: 280℃; Carrier gas: high-purity nitrogen; carrier gas flow rate: 1.0 mL/min; makeup: 30 mL/min.
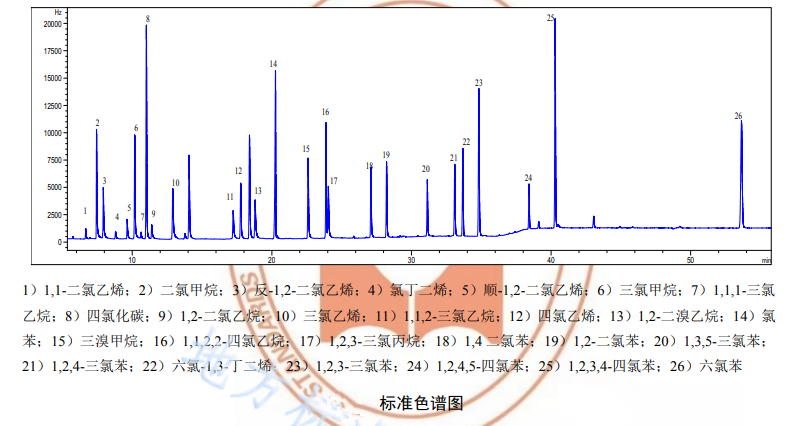
Calibration curve
Weigh 2.5g of NaCl into the headspace bottle, slowly add 10.0mL of experimental water, and then add a certain volume of standard solution to prepare a calibration curve series, and inject samples according to the reference conditions of the instrument for analysis.
Draw the calibration curve with the peak height or peak area as the ordinate and the concentration of the target compound as the abscissa.
Water sample determination
Add 2.5 g of NaCl to the headspace vial, take 10.0 mL of the water sample that has returned to room temperature and slowly add it to the headspace vial, and seal it immediately. Placed in a solid-phase microextraction device, and measured according to the reference conditions of the instrument.When the sample concentration exceeds the calibration curve range, the sample should be diluted to the calibration curve range and then measured.
Qualitative results
According to the retention time of the sample compared with the retention time of each component of the standard material to determine the quality. Before sample analysis, a retention time window t+3S should be established. t is the average value of the retention time of each concentration level standard substance during the initial calibration; S is the standard deviation of the retention time of each standard substance during the initial calibration. During sample analysis, the target compound retention time should be within the retention time window.
Quantitative results
The concentration of halogenated hydrocarbons in the water sample can be calculated according to the relevant formula.
The above content comes from 《DB14/T 1948-2019 Water Quality Determination of Halogenated Hydrocarbons Headspace/Solid Phase Microextraction-Gas Chromatography》



