Indication error
During normal operation of the instrument, three standard solutions with concentration values of about 40 mg/L, 100 mg/L and 160 mg/L of chemical oxygen demand (CODCr) are measured respectively. Each solution is measured n (n=6) times continuously. The relative error between the average value of n (n=6) times measured value and the mass concentration value of the standard solution. Calculate each indication error Re according to formula (1).

Where: Re -- indication error,%;
X -- average value of n measurements of each concentration, mg/L;
P -- Mass concentration value of chemical oxygen demand (CODCr) standard solution, mg/L.
Lower limit of quantification
During the normal operation of the instrument, continuously measure n (n=7) times of the standard solution with the concentration value of chemical oxygen demand (CODCr) of about 15 mg/L, calculate the indication error Re of n (n=7) times of measured values according to formula (1), calculate the standard deviation S of n (n=7) times of measured values according to formula (2), and calculate the lower limit of quantification LOQ of the instrument according to formula (3).
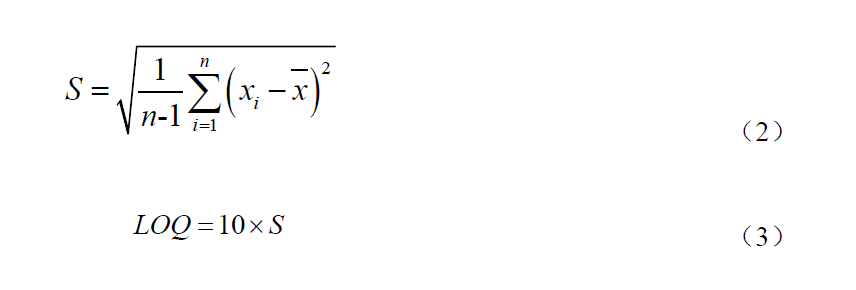
Where: S -- standard deviation of n times measured value, mg/L;
N -- number of measurements;
X i -- the ith measured value, mg/L;
X -- the average value of the measured value of the standard solution, mg/L.
LOQ -- lower limit of quantification, mg/L.
Repeatability
During the normal operation of the instrument, respectively measure the standard solutions with the concentration values of about 40 mg/L and 160 mg/L of chemical oxygen demand (CODCr). For each standard solution, measure n (n=6) times continuously. Calculate the relative standard deviation Sr of n (n=6) times of measured values for each concentration according to formula (4), and take the maximum value of the two times of relative standard deviation as the test result of instrument repeatability.
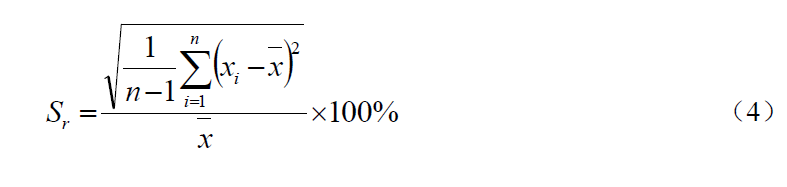
Where: Sr -- repeatability,%;
X -- average value of n measurements, mg/L;
X i - the ith measurement value, mg/L;
N -- number of measurements.
24h low concentration drift
During the normal operation of the instrument, measure the standard solution with the concentration of chemical oxygen demand (CODCr) of about 30 mg/L, once every hour, and continuously measure for 24 hours. Use the initial value (the average value of the first three measurements) Z0 in this time to calculate the deviation between Zi and Z0, and take the maximum deviation as the detection result of 24h low concentration drift. See Formula (5) for calculation method.
Where: ZD -- 24h low concentration drift, mg/L;
Zi -- the ith measurement value, mg/L;
Z0 -- the average value of the first three measurements, mg/L.
24h high concentration drift
During the normal operation of the instrument, measure the standard solution with the concentration of chemical oxygen demand (CODCr) of about 160 mg/L, once every hour, and continuously measure for 24 hours. Using the initial value (the average of the first three measurements) R0 in this time, calculate the percentage of the average absolute deviation value of Ri and R0 relative to the upper limit of the detection range as 24h high concentration drift RD. See Formula (6) for calculation method.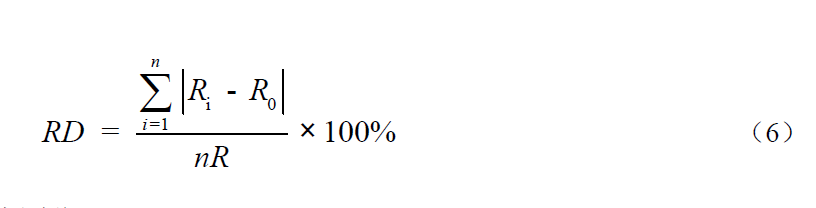
Where: RD -- 24h high concentration drift,%;
Ri - the ith measured value, mg/L;
R0 -- the average of the first three measurements, mg/L;
R -- upper limit of detection range, mg/L;
N -- Number of measurements
memory effect
During the normal operation of the instrument, after the instrument continuously measures the standard solution with the chemical oxygen demand (CODCr) concentration value of about 160 mg/L for three times (the measurement results will not be examined), the instrument successively measures the standard solution with the concentration values of about 40 mg/L and 160 mg/L for seven times respectively. The difference between the first measurement value of the standard solution with two concentrations and the average value of the last six measurements is the memory effect T, and the calculation method is shown in Formula (7), The absolute value is the judgment value of memory effect.
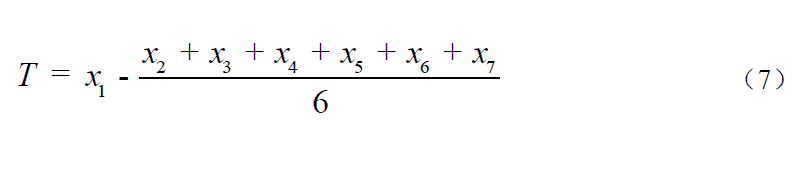
Where: T -- memory effect, mg/L;
Xi -- The ith measurement value, mg/L.
Voltage influence test
During the normal operation of the instrument, the standard solution with the chemical oxygen demand (CODCr) concentration of about 160 mg/L is used, and the instrument is tested three times under the initial voltage of 220 V; Adjust the voltage to 242 V and measure the same standard solution for three times; Adjust the voltage to 198 V again, measure the same standard solution for three times, take the average value of the three measurements at 220 V as Vs, and calculate the relative error of the average value Vi of the three measurements at 242 V and 198 V relative to Vs according to Formula (8) Δ 5. The higher absolute value shall be taken as the judgment value of voltage influence test.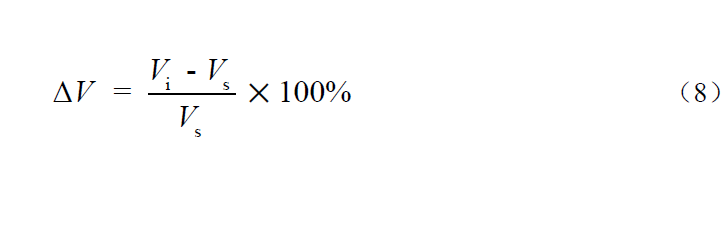
Where: Δ V - voltage influence,%;
Vi -- Average value of three measurements under certain voltage, mg/L;
Vs - average value of three measurements under 220V, mg/L.
Chloride ion influence test
During the normal operation of the instrument, the standard solution with the concentration of about 40 mg/L, 100 mg/L and 160 mg/L of chemical oxygen demand (CODCr) without chlorine ion and the standard solution with chlorine ion( ρ (Cl -)=2000 mg/L) Standard solution with chemical oxygen demand (CODCr) concentration of about 40 mg/L, 100 mg/L and 160 mg/L. Under three concentration levels, first measure the standard solution without chloride ions for three times, take the average value of the three data as the reference value Ds, and then measure the standard solution containing chloride ions for three times, take the average value of the three data as Di, and calculate the effect of chloride ions at different concentration levels according to Formula (9) Δ D. Take the maximum absolute value as the judgment value of the chloride ion influence test.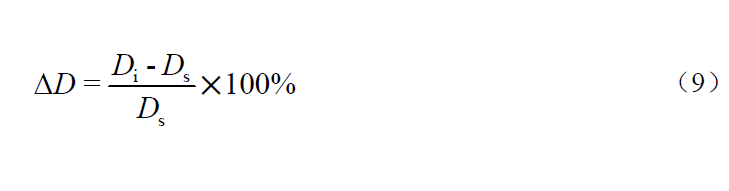
Where: Δ D - chloride ion effect,%;
Di -- Average value of three measurements of standard solution containing chloride ion, mg/L;
Ds -- measured value of standard solution without chloride ion, mg/L.



