The analytical method of conductivity water quality detector is to put the measured solution in a conductivity cell composed of two platinum electrodes with a fixed area and a fixed distance, and determine the content of the measured substance by measuring the conductivity of the solution.
In the actual water quality detection, the conductivity analysis method has simple device and convenient operation, but poor selectivity, and is not suitable for the determination of complex solution systems. Therefore, it is often used to determine the purity of water and the salt of natural water in water quality analysis. Its detection principle is also very simple. Let's explain it to you.
Basic principle of conductivity detector
Electrolyte solution has conductivity, so the resistance of electrolyte obeys Ohm's law at a certain temperature. It can be calculated according to the following figure:
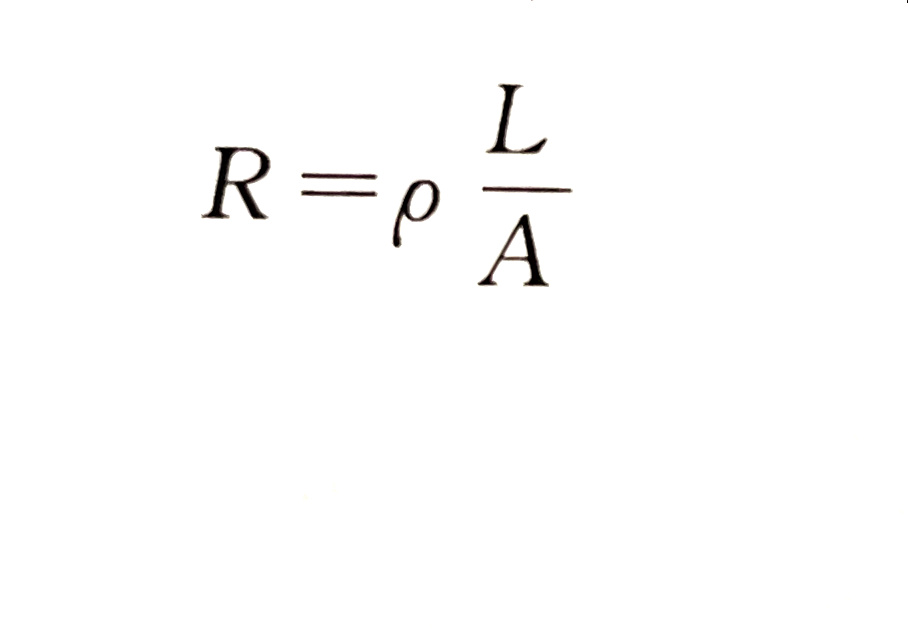
Where R - resistance, Ω;
P - resistivity, Ω · cm;
L - length of electrolyte conductor, cm;
A - sectional area of electrolyte conductor, cm2
The reciprocal of resistance is called conductivity. It represents the conductivity of the solution, usually represented by the symbol S.
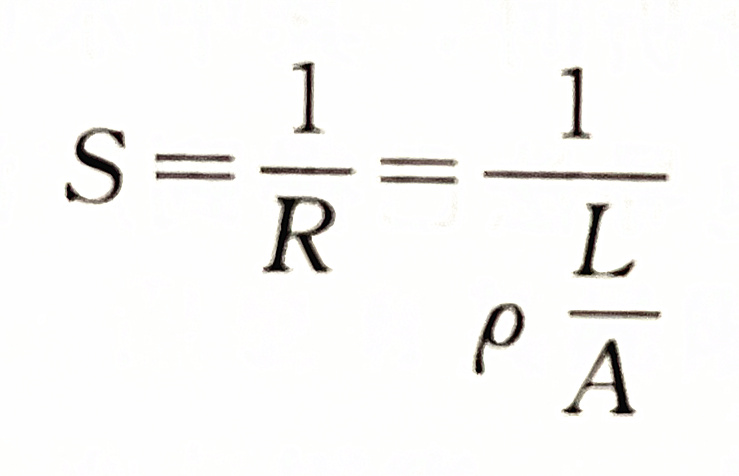
The unit of conductivity is Siemens, referred to as "West", which is represented by the symbol S (i.e. Ω - 1). In water quality analysis, uS is commonly used, 1S=106 μ S。
To measure the conductivity of the electrolyte solution, insert two electrodes into the solution to form a conductivity cell. The conductivity of the solution can be measured by measuring the resistance between the two electrodes. For a conductivity cell, the distance (L) between two electrodes and the electrode area (A) are fixed, so L/A is a constant, expressed in Q, called the conductivity cell constant.
The reciprocal of resistivity is called conductivity.
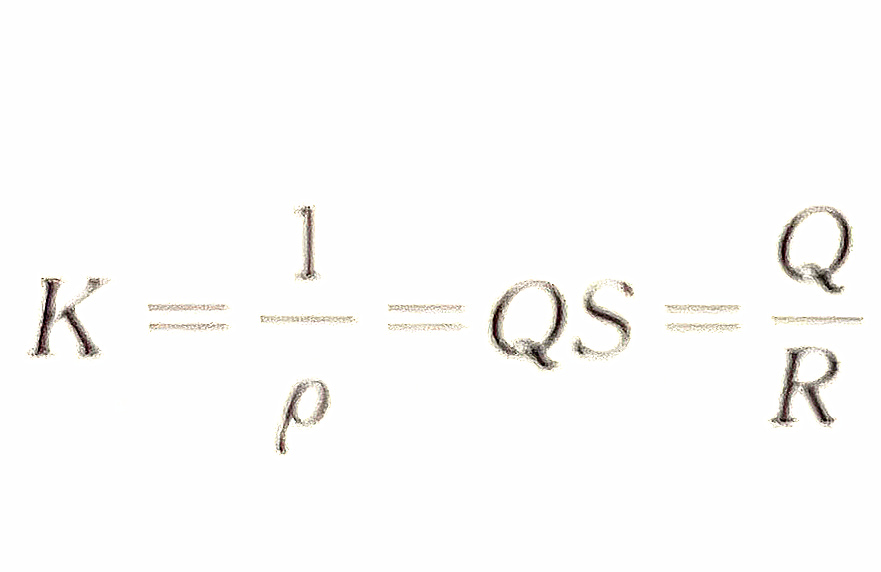
When the conductivity cell constant is known and the resistance is measured, the conductivity can be calculated.
Application of conductivity water quality detector
Determine the purity of water qualityIn order to prove the quality of high purity water, the conductivity method is the most suitable method. At 25 ℃, the theoretical conductivity of absolute pure water is 0.055uS/cm. Generally, the purity of distilled water, deionized water or ultrapure water is measured by the conductivity. The conductivity of ultra-pure water is 0.01~0.1 μ S/cm, 0.5~2 for distilled water μ S/cm, deionized water is 1 μ S/cm, etc.
Judge water quality
The pollution of natural water and industrial wastewater can be preliminarily judged by the measurement of conductivity. For example, the conductivity of drinking water is 50-1500 uS/cm, that of clean river water is 100 uS/cm, and that of natural water is 50-500 μ S/cm, mineralized water is 500~1000 μ S/cm or higher, 30000 for seawater μ S/cm, 10000 for some industrial wastewater μ Above S/cm.



