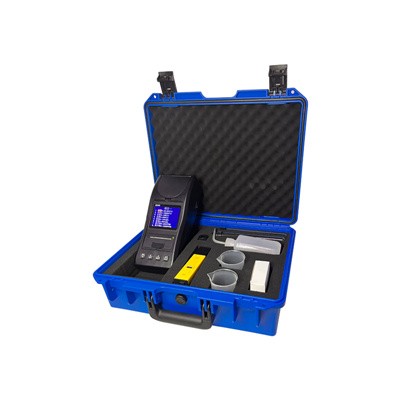

MOdel:GA-DCS030
BRAND:Guanao
- presentation
- parameters
- feature





GA-DCS030 Portable multi-parameter water quality tester can be used to test 30 parameters. Easy and fast to operate, just added reagents after zero calibration , and then to complete the measurement by reading. It can be widely used in city water supply, sewage treatment factory,pure water,beverage factory, food factory, environmental protection departments, industrial water, and epidemic prevention departments, urban water supply,the environment, health care, chemical, pharmaceutical, aquaculture, biotechnology, fermentation process, textile, petrochemical, water treatment and other areas for fast test and laboratory standard test of water quality.
GA-DCS030 Portable multi-parameter water quality tester is a single fixed wavelength spectrophotometer, which adopt the principle of spectrophotometry to measure the parameters. In the instrument, the linear curves of the concentration of different parameters and the absorbance were established, and the concentration of the water samples was obtained through the identification of the color.
Detection method and working principle of guanao portable 30 parameter water quality detector:
1. Turbidity detection method in water: turbidity test is divided into two methods: one is scattering turbidity measurement, the other is transmission turbidity measurement. 1、 The turbidimeter emits light through a section of the sample and detects how much light is scattered by particles in the water at 90 ° to the incident light. This method is called scattering method. 2、 Transmission turbidity measurement principle: through the monochromatic light emitted by the instrument, the light beam passes through the water sample and encounters the scattered light generated by the tiny particles in the water and attenuates. The transmitted light intensity and light intensity attenuation rate are calculated to measure the water sample turbidity (high turbidity). Through the Ordovician turbidity detection, two methods are adopted at the same time, the results are more accurate.
2. Method of color detection in water: platinum cobalt standard colorimetric method.
3. Detection methods of ammonia nitrogen in water: Nessler's colorimetry, phenol hypochlorite (or salicylic acid hypochlorite) colorimetry and electrode method. Nessler's reagent colorimetric method has the characteristics of simple operation and sensitivity. The interferences of metal ions such as calcium, magnesium and iron, sulfide, aldehyde and ketone, color and turbidity in water should be pretreated. Phenol hypochlorite colorimetry has the advantages of sensitivity and stability. The interference and elimination method are the same as those of Nessler's Reagent Colorimetry. Electrode method usually does not need pretreatment of water sample and has the advantages of wide measurement range. When the content of ammonia nitrogen is high, distillation acid titration can be used. Ordovician turbidity detection is carried out in two ways at the same time, the results are more accurate.
4. Detection method of suspended solids in water: transmission turbidity measurement, multi parameter water quality detection instrument through the emission of monochromatic light, the light beam passing through the water sample, meeting the scattered light of small particles in the water and attenuates, calculating the transmitted light intensity and light intensity attenuation rate, so as to measure the turbidity (high turbidity) of water sample. The instrument is intelligent and automatic, and the parameters can be read directly.
5. Detection method of DPD residual chlorine in water: after DPD (n, n-diethyl-p-phenylenediamine) reagent reacts with residual chlorine in water (free residual chlorine), the solution turns red. After the water sample reacts with special DPD residual chlorine reagent, the remaining chlorine value is calculated by spectrophotometry. The instrument is intelligent and automatic, and the parameters can be read directly.
6. Detection method of DPD total chlorine in water: after DPD (n, n-diethyl-p-phenylenediamine) reagent reacts with residual chlorine in water, the solution turns red. After the water sample reacts with special DPD residual chlorine reagent, the total chlorine value is calculated by spectrophotometry. The instrument is intelligent and automatic, and the parameters can be read directly.
7. DPD compound residual chlorine in water method: the content of total chlorine in water the content of residual chlorine is the chemical residual chlorine. The instrument is intelligent and automatic, and the parameters can be read directly.
8. Detection method of phosphate in water: chemical reagent is used in the water sample to be detected. After reaction, it is measured by spectrophotometry, and the concentration value can be read directly.
9. Detection method of nitrate nitrogen in water: chemical reagent is mixed into the water sample to be detected. After reaction, it is measured by spectrophotometry, and the concentration value can be read directly.
10. Detection method of nitrite nitrogen in water: chemical reagent is mixed into the water sample to be detected. After reaction, it is measured by spectrophotometry, and the concentration value can be read directly.
11. Detection method of sulfate in water: chemical reagent is used in the water sample to be detected. After reaction, it is measured by spectrophotometry, and the concentration value can be read directly.
12. Detection method of dissolved oxygen in water: chemical reagent is used to dissolve into the water sample to be detected. After reaction, it is measured by spectrophotometry, and the concentration value can be read directly.
13. Detection method of ozone in water: the water sample containing ozone is mixed with acid indigo blue reagent, and the blue color will be decolorized by ozone. The degree of decolorization was determined by absorbance at 610nm. Compared with the blank sample, the reduction value was proportional to the ozone concentration. The instrument is intelligent and automatic, and the parameters can be read directly.
14. Determination of nickel content in water (dimethylglyoxime spectrophotometry) method: in ammonia solution, in the presence of oxidant iodine, nickel reacts with dimethylglyoxime to form a wine red soluble complex with the composition ratio of 1:4. The complex has two absorption peaks at 440 nm and 530 nm. In order to eliminate the interference of ferric citrate, the detection can be carried out at 530 nm wavelength with lower sensitivity. The instrument is intelligent and automatic, and the parameters can be read directly.
15. Detection principle of iron content in water: phenanthroline spectrophotometry. The instrument is intelligent and automatic, and the parameters can be read directly.
16. Determination method of manganese content in water: after the sample is extracted by water or acid, in sulfuric acid phosphoric acid medium, the divalent manganese in the test solution is oxidized into purple red permanganate ion with periodate, and the absorbance is measured at the wavelength of 526nm. The instrument is intelligent and automatic, and the parameters can be read directly.
17. Detection principle of copper content in water: after digestion of water samples, copper ions and sodium diethyldithiocarbamate form a brown yellow complex in alkaline solution, which is dissolved in carbon tetrachloride, and is quantitatively determined compared with standard series. The instrument is intelligent and automatic, and the parameters can be read directly.
18. Determination of chromium content in water: ①. Determination of hexavalent chromium: in acidic solution, hexavalent chromium reacts with diphenylcarbazide to form purple red product, which can be determined by visual colorimetry or spectrophotometry. ② Determination of total chromium: trivalent chromium in water sample is oxidized to hexavalent chromium by potassium permanganate, excess potassium permanganate is decomposed by sodium nitrite, excess sodium nitrite is decomposed by urea, the obtained clear solution is colored with diphenylcarbazide, and the content is determined. The instrument is intelligent and automatic, and the parameters can be read directly.
19. Determination of zinc content in water: in the solution of pH = 8.5 ~ 9.5, zinc reagent reacts with Zn2 + to form a blue coordination compound. The coordination compound has the maximum absorption at 620nm, so it can be determined by spectrophotometry. The instrument is intelligent and automatic, and the parameters can be read directly.
20. PH value detection method: the glass electrode method is used to determine the pH value of water samples. The saturated calomel electrode is used as the reference electrode, and the glass electrode is used as the indicator electrode. The working battery is composed of the water sample to be measured, and the pH value is directly read by the pH meter. The glass electrode method is accurate and fast, and is less affected by color, turbidity, colloidal substances, oxidant, reducing agent and salinity.
21. Detection method of TDS in water: the concentration of total dissolved substances in water, unit mg / L (mg / L), mainly reflects the concentration of Ca2 + Mg2 + Na + K + plasma in water, which has a good corresponding relationship with the hardness and conductivity of water. The smaller the TDS value, the lower the concentration of Ca2 + Mg2 + Na + K + plasma in water, the smaller the conductivity. The instrument is intelligent and automatic, and the parameters can be read directly.
22. Water temperature detection method: direct detection by thermometer.
- Features:
1.Microcomputer system configuration, touch-type keyboard, LCD backlit display, clearly displaying date, time, measurement value and measurement unit.
2. photoelectric colorimetric principle, Easy and fast to operate, just added reagents after zero calibration , and then to complete the measurement by reading.
3.High strength longlife lamp, lamp stability
4. Built-in Thermal Printer, printing out measurement results and measure time clearly
5. light source automatically switching according to users’requirements , repeatability error:≤±2%
6. Equipped with a high-power battery, it can be used in field measurement and can work for 8 hours continuously.
7.The instrument has a calibration curve in the full range, with power protection, calibration data will not be lost
8.Power supply:220V,50HZ,size(mm):475×335×175;weight(kg):6.0



