Water quality heavy metal pollution mainly refers to substances such as lead, zinc, nickel, chromium, mercury, etc. At present, a large part of the existing water pollution is heavy metal pollution. They are mainly caused by the illegal discharge of industrial waste water and mining wastewater entering surface water or groundwater. It mainly exists in the form of particles, has high activity, can participate in various chemical reactions, and has different chemical stability and toxicity. As the water environment changes, its shape will change immediately, but the toxicity will not be lost with structural changes.
Therefore, if you want to understand the detailed parameters of heavy metals in water, you must master the basic operations of water sample digestion and correctly prepare standard solutions. Today we will talk about the detection methods of heavy metals zinc and lead in water.

Detection principle
The water sample is sprayed into the air-acetylene flame, and the zinc (lead) ground state atomic vapor generated in the flame absorbs the characteristic spectrum of 213.8nm (283.3mm) wavelength emitted by the zinc (lead) element hollow cathode lamp. After deducting the blank absorbance from the measured absorbance of the water sample, the zinc (lead) content is checked from the standard curve.
Instruments and reagents used for testing
1. Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer
2. Zinc element hollow cathode lamp, lead element hollow cathode lamp
3. Acetylene cylinder or acetylene generator, air compressor
4. Nitric acid: top grade pure; hydrochloric acid: top grade pure; perchloric acid: top grade pure;
5. Standard stock solution of zinc and lead
Accurately weigh 0.5000 g of spectrally pure metal zinc and lead after the oxide film has been removed and dried after washing with dilute acid, and dissolve it with 50 mL (1+1) hydrochloric acid. If necessary, heat until the dissolution is complete, transfer it into a 500 mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to Marking line, this solution contains 1.00mg/mL zinc and 1.00mg/mL lead
6. Zinc standard liquid
Draw an appropriate amount of zinc standard stock solution, dilute it with 2% nitric acid into a solution containing 10ug/mL zinc, and prepare it when it is used.
7. Lead standard liquid
Draw an appropriate amount of lead standard stock solution, dilute it with 2% nitric acid into a solution containing lead of 100ug/mL, and prepare it when it is used.
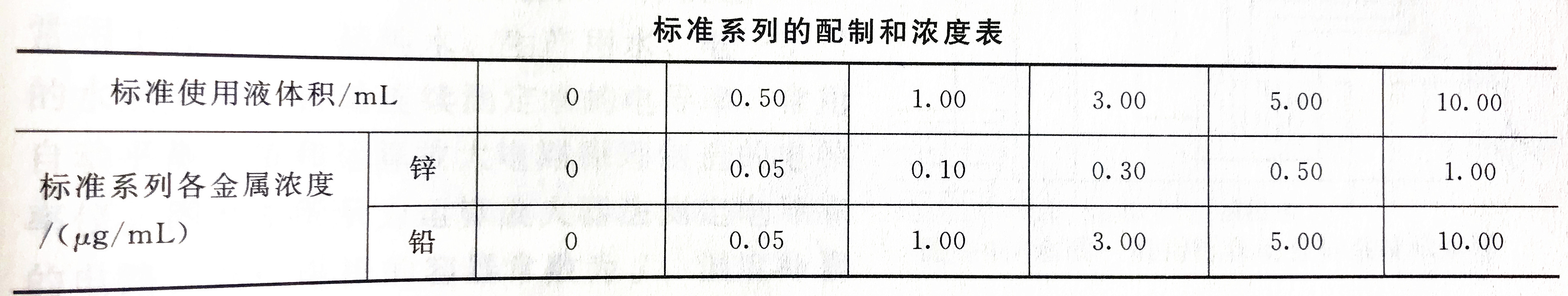
Detection steps
1. Sample pretreatment
Take 100mL of water sample into a 200mL beaker, add 5mL of nitric acid, and heat and digest on an electric hot plate (do not boil). Steam to about 10mL, add 5mL nitric acid and 2mL perchloric acid, continue to digest until about 1mL. If the digestion is not complete, add 5mL of nitric acid and 2mL of perchloric acid, and steam again to about 1mL. Remove and cool, add water to dissolve the residue, and dilute to 100 mL with water.
Take 100mL of 0.2% nitric acid, operate according to the same procedure as above, and use this as a blank sample.
2. Drawing of standard curve
Accurately draw 0mL, 0.50mL, 1.00mL, 3.00mL, 5.00mL, 10.00mL zinc and lead standard use solution, respectively put them into the corresponding 100mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark with 0.2% nitric acid, and mix. Then, the absorbance was measured according to the steps of sample determination, and the absorbance of each standard after blank calibration was plotted against the corresponding concentration, and a standard curve was drawn.
3. Determination of water samples
Take an appropriate amount of the treated water sample, acidify it with nitric acid to pH 1, filter it in a 100mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark with deionized water, mix well, and determine the absorbance value of the water sample according to the procedure of drawing the standard curve, after subtracting the blank absorbance , Find the corresponding zinc and lead concentrations of the water sample from the standard curve.



