Hydrazine is easily oxidized under alkaline conditions, especially oxidants such as chlorine, bromine, and iodine will reduce the test results. In addition, turbid water samples and water samples with pigments will also interfere with the measurement results, and the aromatic amines in the water samples will also interfere with the hydrazine detection results. You must pay attention to it when operating.

Instruments and reagents used for hydrazine testing
1. Spectrophotometer2. Colorimetric tube 50mL
3. Potassium dichromate
4.2mol/L sulfuric acid solution
5.1% starch indicator
Weigh 1.0g of soluble starch in an agate mortar, add 5mL of secondary reagent water to grind into a paste, slowly pour into 90mL of boiling secondary reagent water, continue to boil for 1-2min, and dilute to 100mL after cooling. The reagent life is two weeks.
6. Potassium iodide
7. Iodine
8. Arsenic trioxide
9.1% phenolphthalein indicator (ethanol solution)
10.15% sodium hydroxide solution
11. Hydrochloric acid solution (1+99)
12.Sodium bicarbonate
13. Sodium hydroxide solution (c=2mol/L)
14. Sodium thiosulfate standard solution (c=0.1000mol/L)
a. Preparation
Weigh 26g sodium thiosulfate or 16g anhydrous sodium thiosulfate, dissolve it in 1L secondary reagent water, slowly boil for 10min, then add 0.2g anhydrous sodium carbonate, shake well and store the solution in a ground plug In the brown reagent bottle, let it stand for two weeks and filter it for later use.
b. Calibration
Weigh 0.1500g of benchmark potassium dichromate baked to constant weight at 120°C. Place in an iodine flask, add 25mL of secondary reagent water to dissolve, add 2g of potassium iodide and 20mL of 2mol/L sulfuric acid solution and mix well. Place in a dark place for 10 minutes. Add 150 mL of secondary reagent water and titrate with sodium thiosulfate standard solution. When the solution is light yellow, add 1 mL of 1% starch indicator, and continue titration until the solution turns from blue to bright green. At the same time, do a reagent blank test.
15. Iodine standard solution
a. Preparation
Weigh 13g of iodine tablets and 35g of potassium iodide, dissolve in 100mL of secondary reagent water and dilute to 1000mL, and store in a brown bottle.
b. Calibration
Accurately weigh 0.18g of arsenic trioxide that has been dried to a constant weight in a sulfuric acid dryer, put it into a 250mL iodine measuring flask, and add 6mL of sodium hydroxide (1mol/L) solution to dissolve it. Then add 50mL secondary reagent water, 2 drops of phenolphthalein indicator, neutralize with sulfuric acid solution, then add 3g sodium bicarbonate and 3mL starch indicator, use iodine standard stock solution to drop to light blue, and do a blank self-test at the same time.
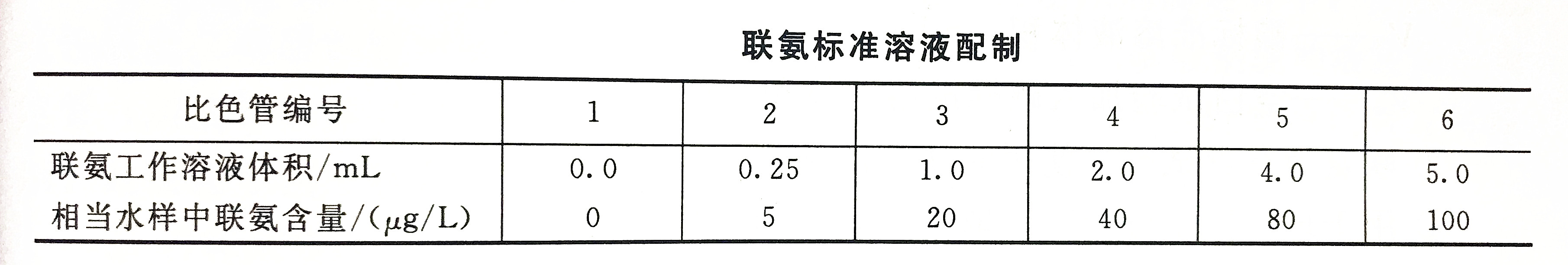
16. Hydrazine standard solution
a. Preparation
Weigh 0.410g hydrazine sulfate or 0.328g hydrazine hydrochloride, dissolve it in 500mL secondary reagent water to which 74mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid has been added, transfer it into a 1L volumetric flask, dilute to the mark with secondary reagent water (this solution is hydrazine Stock solution).
b. Calibration
Measure 20.0mL stock solution, dilute to 100mL with secondary reagent water, titrate with 2mol/L sodium hydroxide solution to the end of phenolphthalein, record the volume A (mL) of sodium hydroxide solution consumed.
Take another 20.0mL stock solution, inject it into a 250mL conical flask with a ground stopper, dilute to 100mL with secondary reagent water, add (A+2)mL2mol/L sodium hydroxide solution, and use a brown burette to accurately add 10mL0.1mol /L iodine standard solution, mix well, and store in the dark for 3 minutes.
Add 2.5mL of 1mol/L sulfuric acid solution and titrate the excess iodine with 0.1mol/L sodium thiosulfate standard solution. When approaching the end point (titration until the solution is light yellow), add 1mL 1% starch indicator, continue titration until the blue disappears, record the consumption of sodium thiosulfate standard solution, and conduct a blank test at the same time.
17. p-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde-sulfuric acid solution
Measure 100 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid and slowly add it to a beaker with 300 mL of secondary reagent water under constant stirring. After cooling, add 15 g of p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde, and transfer it to a 500 mL volumetric flask after it is completely dissolved. Use secondary reagent water. Dilute to the mark and store in a brown bottle in a dark place.
18. Hydrazine working solution
According to the concentration of the stock solution, take an appropriate amount of stock solution and dilute 100 times with hydrochloric acid solution (1+99).