
Instruments and reagents required for internal electrolysis
1. High temperature furnace
2. Silver-zinc primary batterya. Preparation of sintered silver particles (porous silver particles)
Weigh 50g of silver powder or precipitated silver, spread it flat in a 100mL porcelain evaporating dish or a dish, and flatten the surface. The thickness of the silver powder is about 5mm. Put the porcelain evaporating dish into a high temperature furnace at 620℃, sinter it for about 30 minutes, take it out and let it cool, take out the silver block with a tool, and cut it into a silver bar with a width of 10mm and a length of 20mm. Put the silver bar back into the original evaporating dish, then burn it in a high-temperature furnace at 800°C for 30 minutes, take it out and cool it and cut it into porous silver particles with a particle size of 3 to 5 mm.
b. Preparation of silver-zinc reduction burette (silver-zinc reduction battery)
Take a 50mL acid burette, pad about 10mm thick glass fiber on the bottom, fill the burette with secondary reagent water and remove the air bubbles on the tip of the tube. Take a few zinc particles with a particle size of 5-10mm (usually 7 particles are needed), and fill the porous silver particles and zinc particles at the ratio of one zinc particle per 4mL porous silver particles, and the volume of the silver zinc reducing agent is about Up to 30mL, the top is covered with 4mL porous silver particles. Vibrate from time to time during the filling process so that the silver particles and zinc particles are in full contact without leaving air bubbles.
The service life of silver-zinc reducing agent is generally not more than 3 months. After a long time of use, the color of the silver particles becomes dark. At this time, you can pour out the silver-zinc mixture, remove the zinc particles, heat with hydrochloric acid (1+1) to dissolve the impurities, then wash off the hydrochloric acid, and then place the porous silver particles in the porcelain The evaporating dish is first dried on an electric stove, and then placed in a high-temperature furnace at 800°C for 30 minutes, so that the silver-white metallic luster can be restored.
3. Electric heating constant temperature water bath
4. Special Dissolved Oxygen Measurement Bottles The actual volume is required to be about 300mL, colorless and transparent, the volume of each bottle is the same, and the stopper is a universal ground stopper.
5. Water-sealed bucket (15-25L in volume)
6. Sulfuric acid solution (1+3)
7. Ammonia solution (1+90)
8. Hydrochloric acid solution (1+1)
9. Acidic indigo sodium disulfonate stock solution
a. Preparation
Weigh 0.8~0.9g sodium indigo disulfonate (relative molecular weight 466.36) into a 50mL beaker, add 1mL secondary reagent water to make it wet, add 7mL concentrated sulfuric acid, and heat on a water bath at about 80°C for 30 minutes. Stir from time to time to mix well. Then add a small amount of secondary reagent water, after all the sodium indigo disulfonate is dissolved, transfer it to a 500mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark, and calibrate after mixing. If there is insoluble matter, it needs to be filtered before calibration.
b. Calibration
Take 10mL of acidic indigo sodium disulfonate solution and pour it into a 100mL conical flask, add 10mL of secondary reagent water and 10mL of sulfuric acid solution (1+3), and titrate with 0.01mol/L potassium permanganate standard solution until it is just yellow. .
According to the calibration results, dilute the acidic indigo sodium disulfonate solution with secondary reagent water into a solution of p=40ug/mL. The life of this reagent is about 1 month. If there is sediment during use, it should be reconfigured.
10. Acidic indigo sodium disulfonate standard solution
Accurately draw 50mL of acidic indigo sodium disulfonate stock solution (1mL is equivalent to 40ug O2), pour it into a 100mL volumetric flask, and dilute to the mark with secondary reagent water. The titer of this solution is 20g/mL.
11. Ammonia-ammonium sulfate buffer solution
Weigh 20g of ammonium sulfate, add about 200mL of secondary reagent water, dissolve it, transfer it into a 1L volumetric flask, add 60mL of concentrated ammonia water, dilute to the mark with secondary reagent water, shake well for later use.
12. Ammonia indigo sodium disulfonate solution
Mix the ammonia-ammonium sulfate buffer solution and the acid sodium indigo disulfonate stock solution in equal volumes according to the required amount. Since the ammoniated indigo sodium disulfonate solution is unstable, the solution must be prepared during use.
13. Reduced indigo sodium disulfonate solution
Drain the water in the upper part of the silver-zinc reduction burette, inject a small amount of ammonia indigo sodium disulfonate solution to wash the silver-zinc burette, drain the washing liquid, and then fill the burette with the ammonia indigo sodium disulfonate solution. The blue turns to bright yellow, drain the blue solution from the tip of the burette, and it can be used. If you are in a hurry, you can clamp the silver-zinc burette between your palms and gently rub it, or hold the silver-zinc burette in your hand and shake it up and down to speed up the reduction of the sodium indigo disulfonate. This solution should be prepared before use. After the solution originally stored in the burette is discarded, a new solution is added for preparation, and the use period is 4h.
14. Picric acid solution
Weigh 0.74g picric acid that has been dried to a constant mass (accurate to 2mg) in a desiccator, dissolve it in secondary reagent water, and dilute to 1L. The yellow chromaticity of this solution is equivalent to the chromaticity of a reduced indigo sodium disulfonate solution with a concentration of 20ug/mL.
15. Standard solution of potassium permanganate.
Dissolved oxygen standard color preparation table
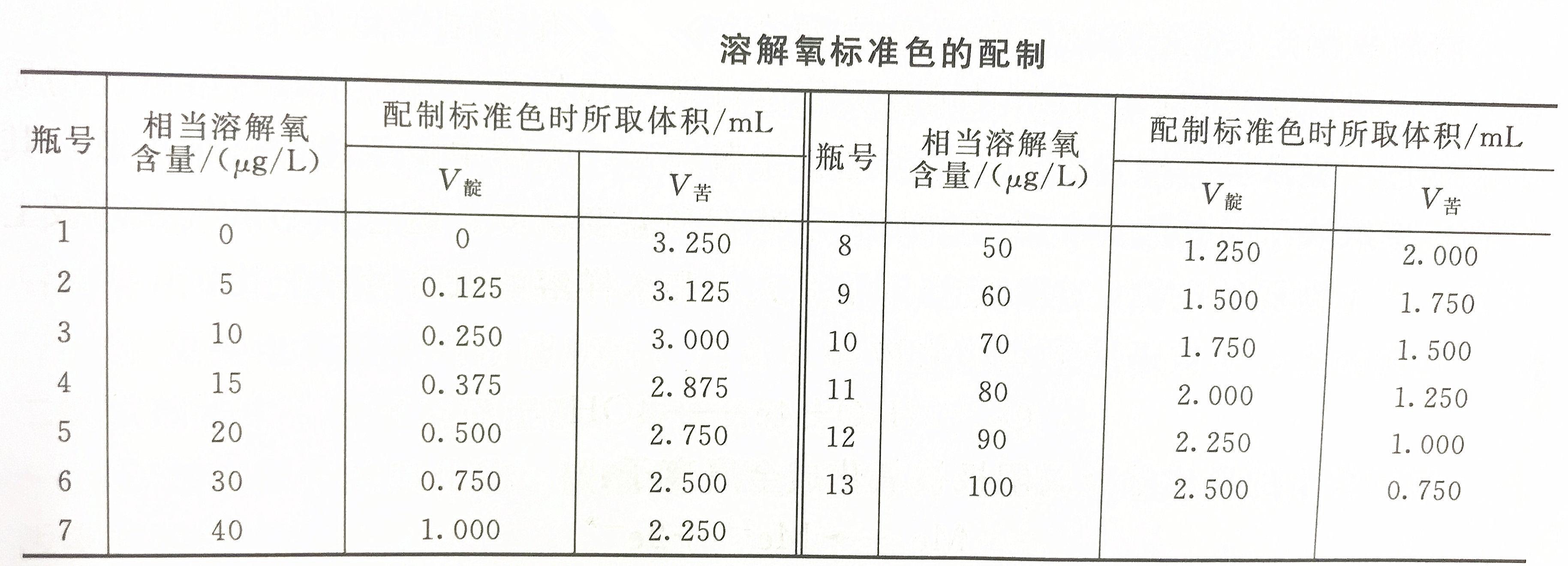
1. Prepare dissolved oxygen standard color
Since the standard dissolved oxygen is not easy to obtain, the method for preparing the dissolved oxygen standard color is prepared according to the "false color principle". That is to say, add acidic indigo sodium disulfonate and unreacted sodium indigo disulfonate according to the amount of hypothetical reduced indigo sodium disulfonate (yellow) and dissolved oxygen to form oxidized sodium indigo disulfonate (blue). (Yellow) Use the corresponding picric acid instead to prepare the dissolved oxygen standard color.Pour the prepared dissolved oxygen standard color solution into the dedicated dissolved oxygen bottle, seal it with wax after filling, and discard the excess solution. The validity period of this solution is 5 days.



