Detection method of sodium ion in water
There are many methods for detecting sodium ions in water, such as atomic absorption spectrophotometry, static method, etc. Among them, the atomic absorption method is suitable for the determination of sodium 5-500mg/L water samples. The main principle is to spray a water sample containing sodium ions into an air-acetylene flame. The sodium ions will be pyrolyzed into ground state atoms. The sodium hollow cathode lamp is used as the light source, and the sodium 330.2nm or 589.0nm is the analysis line to determine the sodium content. The absorbance of the water sample.

Instruments and reagents used to detect sodium ions in water
1. Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer
2. Sodium element hollow cathode lamp
3. Acetylene cylinder
4. Oil-free air compressor
5. Borosilicate glass containers and polyethylene containers need to be soaked in 10% nitric acid solution and then washed with water.
6. Nitric acid.
7.Cesium chloride solution (1L containing 20g cesium) Weigh 25g cesium chloride (cscl) into a 200mL beaker, add 500mL of tertiary reagent water containing 50mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid, dissolve and transfer to a 1L volumetric flask, use three Dilute reagent water to the mark.
8. Sodium ion standard solution
a. Sodium stock solution (1mL containing 1.000mg sodium ions) accurately weigh 2.548g of the reference reagent sodium chloride, which has been baked to constant weight at (140±10)℃, into a 250mL beaker, dissolve it with tertiary reagent water and transfer to a 1000mL capacity In the bottle, dilute to the mark and shake well.
b. Sodium ion standard solution (1mL contains 10ug sodium ion) accurately pipette 10mL sodium ion standard stock solution to a 1000mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark, and shake well. The solution is ready to use.
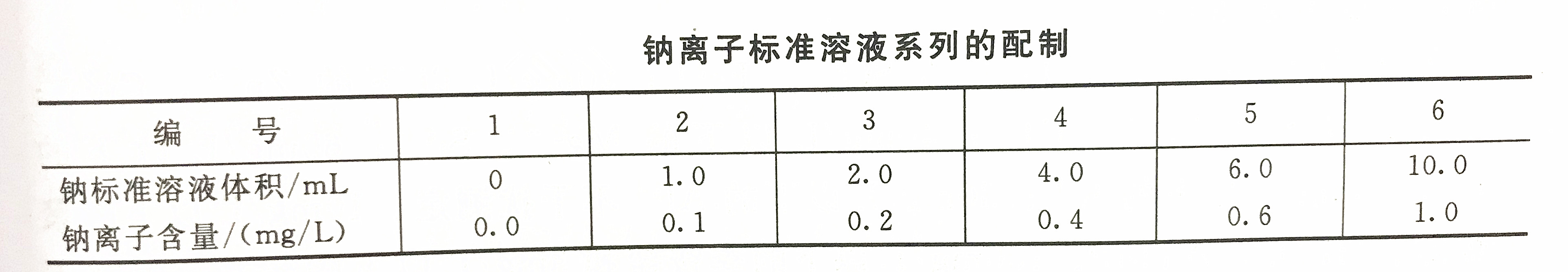
Sodium ion detection steps in water
1. Draw a standard curve
In a 100mL volumetric flask, add 10mL of cesium chloride solution to each, according to the corresponding preparation standard, accurately absorb the sodium ion standard solution and the volumetric flask, and then dilute to the mark with tertiary reagent water and shake well.
Adjust the wavelength of the photometer to 589.0nm, then measure the absorbance one by one from dilute to concentrated, and do a blank experiment at the same time. Draw a standard curve with absorbance as the ordinate and the corresponding sodium content as the abscissa.
2. Preparation of test water samples
Take 500mL of water sample, add concentrated hydrochloric acid to acidify to pH about 1. If there are more suspended solids in the water sample, you can filter it with a 0.45um filter, and store the filtrate in a polyethylene plastic bottle.
3. Measurement of sample
In a 100 mL volumetric flask, add 10.0 mL of cesium chloride solution, pipette 10.0 mL of the sample, and dilute to the mark. According to the same instrument conditions in the standard curve drawing, measure the absorbance and do a blank test at the same time. If the sodium content in the sample is not in the range of 0.1-1.0 mg/L, the volume of the water sample can be adjusted appropriately.
4. Determination of water samples
According to the same instrument conditions in the preparation of the standard curve, zero was adjusted with the third-grade reagent water as the blank, and the absorbance of the water sample was measured. Find out the content of sodium ions in the water sample from the standard curve. If the sodium content in the water sample is greater than 200mg/L, it can be measured after dilution. Then calculate the content of sodium ions in the water based on the measured parameters.





