As a metal element that exists widely in nature, copper is also one of the earliest metals used by mankind. It can be seen in many places; It is clearly stipulated that the content of copper in drinking water cannot exceed 1.0 mg/L. Therefore, copper is a must-test item in the conventional 42 indicators of water plant effluent and pipe network water. Today, I will introduce to you the detection method of heavy metal copper in water.
There are many methods for detecting copper in water. Today we are going to introduce to you the sodium diethyldithiocarbamate extraction spectrophotometric method. The application range of this method is 0.01-2.00mg/L, so it can be applied to various industries. Determination of copper content in water and domestic water. The main principle is that copper reacts with sodium diethyldithiocarbamate in an ammonia solution to form a yellow-brown complex, which can be measured by a spectrophotometer after extraction with carbon tetrachloride.

Instruments and reagents used for testing
1. Spectrophotometer2. Separating funnel with stopper 125mL
3. Nitric acid
4. Carbon tetrachloride
5. Ammonia solution (1+1)
6.Copper sulfate
7. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt-ammonium citrate solution
Weigh 2.0g of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt and 10.0g of ammonium citrate, dissolve in tertiary reagent water and dilute to 100mL, add 4 drops of cresol red solution, use ammonia (1+1) solution to adjust to pH8 ~8.5 (The solution changes from yellow to light purple).
8. Cresyl red indicator 0.4g/L ethanol solution.
9. Sodium diethyldithiocarbamate solution
Weigh 0.2g of sodium diethyldithiocarbamate, dissolve it in tertiary reagent water, and dilute to 100mL, store in a brown bottle in a dark place for two weeks.
10. Ammonia-ammonium chloride buffer solution
Weigh 70g of ammonium chloride, dissolve it in an appropriate amount of tertiary reagent water, add 48mL of ammonia water, and dilute to 1000mL.
11. Starch solution 5g/L solution, prepared before use.
12. Copper standard stock solution (1.00mL contains 0.100mg copper)
Weigh 0.3930 g of copper sulfate pentahydrate and dissolve it in the third-grade reagent water, add 2.0 mL of nitric acid and transfer it into a 100 mL volumetric flask, dilute with the third-grade reagent water to the mark and shake well, and set aside.
13. Copper standard solution (1.00mL contains 0.00500mg copper)
Take 25.0mL of the copper standard stock solution in a 500mL volumetric flask, add 1.0mL of nitric acid, dilute to the mark with tertiary reagent water, shake well, and set aside.
Steps to detect copper content in water
(1) Draw a standard curve
According to the copper standard solution preparation table, accurately draw the copper standard solution into the separatory funnel, add the third grade reagent water to 50mL, add 5.0mL ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt-ammonium citrate solution (I), add 4 drops of cresol Red indicator, use ammonia (1+1) to adjust the solution from red to yellow to light purple (pH=8~8.5), add 5.0mL sodium diethyldithiocarbamate solution, shake well, let stand for 5min, add 10.0 mL of carbon tetrachloride was vigorously shaken for 2 min, and the determination was made within 1 h after standing for layering.After absorbing the water on the inner wall of the neck of the funnel, insert a small group of absorbent cotton, discard the organic phase that originally flowed out, and then move the organic phase into a 10mm absorption pool, at a wavelength of 440nm, using carbon tetrachloride as a reference. Measure the absorbance, subtract the absorbance of the reagent blank from the measured absorbance, and draw a standard curve with the corresponding copper content.
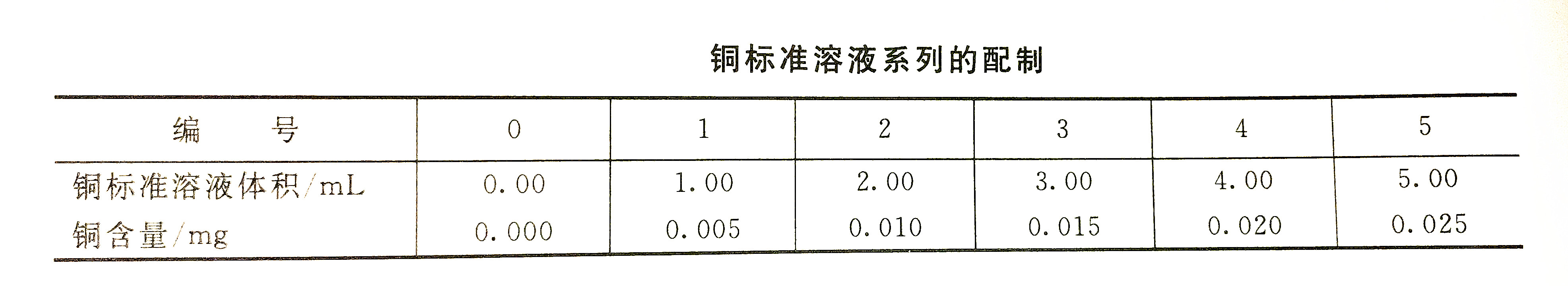
(2) Determination of water samples
Water sample pretreatmentFor water samples containing very little suspended matter and organic matter, 50.0 mL of acidified water samples can be taken in a tall beaker, add 2.0 mL of nitric acid, and cover with a watch glass. Heat it on an electric furnace and boil slightly for 10 minutes, and then cool.
For water samples containing more suspended solids and organic matter, 50.0 mL of acidified water samples can be added to a tall beaker with 5.0 mL of nitric acid and covered with a watch glass. Heat the digestion on an electric furnace or electric hot plate to be nearly dry, slightly cold, rinse the cup wall and watch glass with tertiary reagent water, continue to heat the digestion, steam until nearly dry, after cooling, add about 20 mL of tertiary reagent water, and heat it for 3 minutes. cool down.
Measurement procedure
Transfer the pretreated water sample solution into a separatory funnel and dilute to 50 mL with tertiary reagent water. Follow the steps to draw a standard curve below. Do a blank test at the same time.
After subtracting the absorbance of the blank test from the absorbance of the water sample, find the corresponding copper content from the standard curve. Then calculate the copper content according to the relevant formula.



