We have introduced to you that you can use atomic absorption spectrometry to detect the heavy metal lead content in water. The advantage of this method is that the preparation of reagents is simple and the operation steps are simple, but the shortcomings are also obvious, that is, the detection environment and equipment are certain. In addition, the acetylene gas used in the detection is also very dangerous. So today we will introduce to you another method to detect the heavy metal lead content in water-dithizone spectrophotometry.
This method is often applied to the detection of trace lead in surface water, reclaimed water and other water, and the detection range is 0.01mg/L-0.3mg/L.

Detection principle
In the ammoniated citrate-cyanide reducing medium with pH=8.5-9.5, the lead in the water sample can form a reddish chelate with dithizone that can be extracted by chloroform or carbon tetrachloride. The absorbance value of the chelate measured by a spectrophotometer is equivalent to the lead content in the water.
Instruments and reagents used for testing
1. Spectrophotometer
2. Commonly used glassware in the laboratory
3. Trichloromethane
4. Premium grade pure perchloric acid
5. Nitric acid solution (20%)
Dilute 200 mL of nitric acid with laboratory ultrapure water to 1000 mL.
6. Nitric acid solution (0.2%)
Dilute 2mL of nitric acid with laboratory ultrapure water to 1000mL.
7. Hydrochloric acid solution (0.5mol/L)
Take 42mL of hydrochloric acid and dilute to 1000mL with laboratory ultrapure water.
8. Ammonia
9. Ammonia solution (1+9)
Take 10mL ammonia water and 90mL laboratory ultrapure water.
10. Ammonia solution (1+100)
Take 10mL ammonia water and 100mL laboratory ultrapure water.
11. Citrate-potassium cyanide reducing solution
Dissolve 400g of diammonium hydrogen citrate, 20g of anhydrous sodium sulfite, 10g of hydroxylamine hydrochloride and 40g of potassium cyanide (be careful!) The solution is very toxic, so do not use mouth to suck)
12. Sodium sulfite solution
Dissolve 5g of anhydrous sodium sulfite in 100mL laboratory ultrapure water.
13. Iodine solution (0.05mol/L)
Dissolve 20g potassium iodide in 25mL laboratory ultrapure water, add 6.35g sublimated iodine, and then dilute to 500mL with laboratory ultrapure water.
14. Lead standard stock solution
Weigh 0.1599g lead nitrate (purity ≥99.8%), dissolve it in about 200mL laboratory ultrapure water, add 10mL nitric acid, quantitatively transfer it into a 1000mL volumetric flask, and finally dilute it with laboratory ultrapure water to the mark (or reduce the purity of 0.1000 ≥9.9% metallic lead) was dissolved in 20mL (1+1) nitric acid, and then diluted to 1000mL with laboratory ultrapure water.
15. Lead standard use solution
Take 20.00mL lead standard stock solution and place it in a 1000mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark with laboratory ultrapure water, and shake well.
16. Dithizone stock solution
Weigh 100mg of pure dithizone, dissolve it in 1000mL of chloroform, store it in a brown bottle, and place it in the refrigerator for later use.
The exact concentration of this solution can be determined according to the following method: take a certain amount of the above dithizone-chloroform solution, put it in a 50mL volumetric flask, dilute with chloroform to make the concentration less than 0.001%. Then place this solution in a 10mm cuvette, measure its absorbance at a wavelength of 606nm, divide this absorbance by the molar absorption coefficient of 40.6L/(mol·cm) to obtain the exact concentration of dithizone.
17. Dithizone working solution
Take 100mL dithizone stock solution and place it in a 250mL volumetric flask and dilute to the mark with chloroform.
18. Special solution for dithizone
Dissolve 250mg of dithizone in 150mL of chloroform. This solution does not need to be purified and is dedicated to extraction and purification of the test solution.
Water quality testing steps
Water sample pretreatment
Under normal circumstances, the collected water samples need to be digested, unless it is proved that the current water sample does not need to be digested, for example, groundwater without suspended solids and clean surface water can be directly measured, otherwise the following two types must be used The situation is preprocessed.
1. Relatively turbid surface water
Add 1mL nitric acid to each 100mL water sample, place it on a hot plate for 10 minutes, and then filter it with quick filter paper after cooling. The filter paper is washed several times with 0.2% nitric acid solution, and then diluted with this acid to a certain volume for determination.
2. Surface water or wastewater containing more suspended matter and organic matter
Add 5mL nitric acid per 100mL water sample, heat it on a hot plate, digest to about 10mL, cool it a little, add 5mL nitric acid and 2mL perchloric acid to continue heating and digestion, and steam until nearly dry. After cooling, use 0.2% nitric acid solution to warm the residue. After cooling, filter with quick filter paper. The filter paper is washed several times with 0.2% nitric acid. After the filtrate is diluted with this acid to a constant volume, it is used for determination. Two blank tests are performed in parallel for each batch of samples analyzed.
Accurately measure an appropriate amount of sample with a lead content of no more than 30ug and put it into a 250mL separatory funnel, make up to 100mL with laboratory ultrapure water, add 3 drops of 0.1% thymol blue indicator, and use 6mol/L sodium hydroxide solution Or adjust the 6mol/L hydrochloric acid solution to just appear a stable yellow, the pH value of the solution at this time is 2.8, ready for determination.
Water quality sample determination
1. Color extraction
Add 10 mL of 20% nitric acid and 50 mL of citrate-potassium cyanide reducing solution to the sample (with lead content not exceeding 30ug and maximum volume not exceeding 100 mL) placed in a 250 mL separatory funnel, plug tightly, shake well and cool to At room temperature, after adding 10mL of dithizone working solution, stoppered and airtight, shake the separatory funnel vigorously for 30s, and place for layering.
2. Spectroscopic detection
Insert a small group of lead-free absorbent cotton into the neck of the separatory funnel, then release the lower organic phase, discard the 1-2mL chloroform layer, and then pour it into a 10mm cuvette. Take chloroform as the ratio, measure the absorbance of the extract at 510nm, subtract the absorbance of the blank test, and find the lead content from the calibration curve
3. Blank test
Take the laboratory ultrapure water instead of the sample, and the dosage of other reagents is the same, and the treatment is carried out according to the above steps.
Calibration curve drawing
Take a set of lead standard use solutions according to the lead standard solution preparation table, and pour them into a 250mL separatory funnel, add an appropriate amount of laboratory ultrapure water to 100mL, and then follow the water sample detection steps to determine the absorbance value.
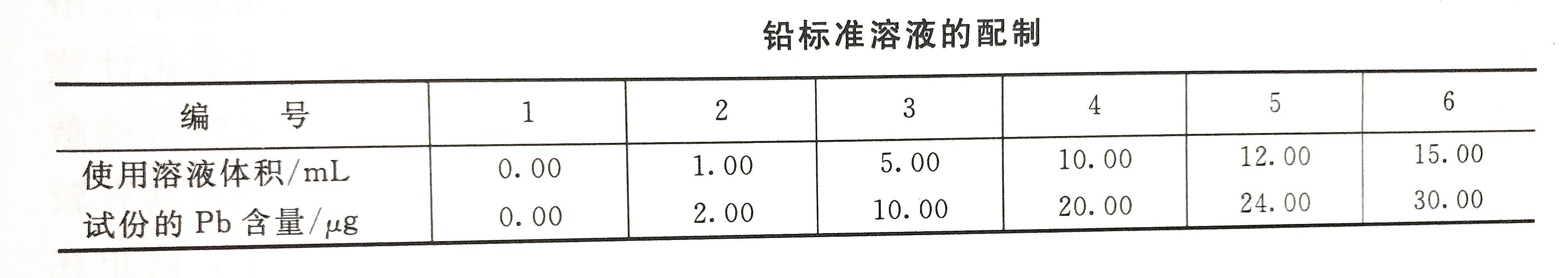
According to the above-mentioned measured parameters, the accurate content parameters of heavy metal lead in water can be obtained according to the corresponding formula.



