The pollution of nitrophenolic compounds generally does not appear in drinking water, because most of these pollutants are caused by the illegal discharge of industrial wastewater. But in many cases there are exceptions, so the test personnel must also be able to master the determination method of such compounds. Today we are going to talk about the operation steps of using gas chromatography to detect nitrophenols in water.
When the sampling volume is 1000 ml and the constant volume of the sample is 1.0 ml, this method can be used for 12 kinds of 2-nitrophenol, 3-methyl-2-nitrophenol, 4-methyl-2-nitrophenol, etc. The detection limit of nitrophenolic compounds is 0.2 ug/L-2 ug/L, and the lower limit of determination is 0.8 ug/L-8 ug/L, so it can be applied to drinking water, surface water, industrial wastewater and other water bodies measurement.This method is to extract nitrophenolic compounds by liquid-liquid extraction or solid-phase extraction under acidic conditions (pH value is 1-2) after the water sample is purified by acid-base distribution, and the extract is dehydrated, concentrated, After constant volume, it was separated by gas chromatography and detected by mass spectrometry. According to retention time, mass-to-charge ratio and abundance ratio of fragment ions, qualitative detection was carried out by internal standard method.
Detection reagent
1. Dichloromethane: pesticide residue grade.
2. Acetone: pesticide residue grade.
3. Methanol: pesticide residue grade.
4. Hydrochloric acid: ρ=1.18 g/ml.
5. Sodium hydroxide.
6. Anhydrous sodium sulfate
Bake at 400 °C for 4 h in a muffle furnace, cool to room temperature in a desiccator, and store in a sealed reagent bottle.
7. Sodium Chloride
Bake at 400 °C for 4 h in a muffle furnace, cool to room temperature in a desiccator, and store in a sealed reagent bottle.
8. Hydrochloric acid solution: 1+1
9. Hydrochloric acid solution: c=0.02 mol/L.
Measure 1.8 ml of hydrochloric acid, slowly add it to water, transfer it to a 1000 ml volumetric flask, and dilute to the mark. Ready to use.
10. Sodium hydroxide solution: c=5.0 mol/L.
Weigh 20.0 g of sodium hydroxide (5), dissolve in water, transfer to a 100 ml volumetric flask, and dilute to the mark. Ready to use.
11. Standard material: purity ≥99%.
2-nitrophenol, 3-methyl-2-nitrophenol, 4-methyl-2-nitrophenol, 5-methyl-2-nitrophenol, 2,5-dinitrophenol, 3- Nitrophenol, 2,4-dinitrophenol, 4-nitrophenol, 2,6-dinitrophenol, 3-methyl-4-nitrophenol, 6-methyl-2,4-dinitro phenol and 2,6-dimethyl-4-nitrophenol.
12. Standard stock solution: ρ=1000 mg/L.
Weigh 50 mg (accurate to 0.1 mg) of each nitrophenolic compound standard substance (11), dissolve with a small amount of methanol, transfer to a 50 ml brown volumetric flask, dilute with dichloromethane to the mark. Mix well. The standard solution can be stored for half a year at -10°C and protected from light. You can also directly buy commercially available certified standard solutions and store them according to the instructions.
13 Standard solution: ρ=200 mg/L.
Dilute stock standard solutions with dichloromethane. It can be stored for 2 months in the airtight refrigeration at 4°C in the dark.
14 Internal standard stock solution: ρ=2000 mg/L.
Naphthalene-d8 and acenaphthene-d10 should be selected as internal standards for nitrophenolic compounds. Commercially available certified standard solutions should be stored according to the instructions.
15 Internal standard solution: ρ=500 mg/L.
Dilute the internal standard stock solution with dichloromethane.
16 Decafluorotriphenylphosphine (DFTPP) solution: ρ=1000 mg/L. Commercially available certified standard solutions should be stored according to the instructions.
17 Decafluorotriphenylphosphine working solution: ρ=50 mg/L.
The decafluorotriphenylphosphine solution was diluted with dichloromethane.
18 Solid phase extraction column: 500 mg/6 ml, packing is divinylbenzene-N-vinylpyrrolidone, or equivalent solid phase extraction column.
19 Solid phase extraction disk: a commercial disk with a diameter of 47 mm, the medium layer is divinylbenzene-N-vinylpyrrolidone, or an equivalent solid phase extraction disk.
20 Membrane: 0.45um PTFE membrane.
21 Cotton wool.
After soaking with dichloromethane and acetone in turn, dry it for later use.
22 Carrier gas: helium, purity ≥99.999%.
23 Nitrogen: purity ≥99.99%.
Instruments required for testing
1. Gas chromatograph-mass spectrometer: The gas chromatograph has a split/splitless injection port, and the column oven can be programmed to heat up. The mass spectrometer has an electron impact (EI) source of 70 eV.
2. Chromatographic column: capillary column with a length of 30m, an inner diameter of 0.25mm, a film thickness of 0.25um, and a stationary phase of 5%-phenyl-95% methyl polysiloxane. or other equivalent capillary columns.
3. Solid phase extraction device: column solid phase extraction device, disc solid phase extraction device.
4. Concentration device: nitrogen blowing concentrator, rotary evaporator or other equipment with the same performance.
5. Sample bottle: 2L, brown glass bottle with stopper and ground mouth.
6. Triangular funnel: 40mm in diameter.
7. Anhydrous sodium sulfate drying device.
Fill a small amount of absorbent cotton in the lower part of the triangular funnel, and fill the interior with 3 cm-5 cm thick anhydrous sodium sulfate, rinse with 5 ml of acetone (4.2) and 5 ml of dichloromethane (4.1) before use.
8. Micro syringe or pipette: 5ul, 10ul, 50ul, 100ul, 250ul, 1.0 ml.
9. Separation funnel: 2000 ml, with teflon piston.
10. Analytical balance: actual division value d=0.1mg.
11. Injection bottle: 2ml brown bottle.
Sample Collection and Storage
Everyone should collect samples in accordance with the relevant regulations of the country for water sample collection. Do not pre-wash the vial with the sample when collecting the sample. After sample collection, add hydrochloric acid solution to adjust pH≤2. The sample should be filled with the sample bottle and sealed with a cap, and stored in the refrigerator below 4°C and protected from light. The samples should be analyzed as soon as possible after collection. If they cannot be analyzed in time, they should be extracted within 7 days. The extract should be stored in a refrigerator below 4°C and protected from light, and the analysis should be completed within 20 days.
Prepare test samples
Acid-base distribution and purification
Shake the water sample well, weigh 1000ml, adjust pH≥12 with sodium hydroxide solution, put it in a separatory funnel, add 60ml of dichloromethane, shake and extract for 10min, after standing for stratification, discard the organic phase. Adjust the pH to 1-2 with hydrochloric acid solution and wait for extraction.Water sample extraction method
liquid-liquid extraction
Add 40 g of sodium chloride to the water sample purified by acid-base distribution and shake to dissolve it completely. Add 60 ml of dichloromethane, shake and extract for 10 min. After standing for stratification, collect the organic phase, dehydrate it with an anhydrous sodium sulfate drying device, and collect it in a concentration tube. Repeat the above steps 2 more times and combine the organic phases.Column solid phase extraction
Fix the solid-phase extraction column on the solid-phase extraction device, activate the solid-phase extraction column with 5 ml of dichloromethane, 5 ml of methanol and 10 ml of hydrochloric acid solution in sequence, and keep the head of the column wet. After the water sample after acid-base distribution and purification is enriched through the solid phase extraction cartridge at a rate of 3 ml/min-5 ml/min, vacuum suction is continued until the cartridge is completely dry. Elute with 10 ml of dichloromethane at a rate of 1 ml/min-2 ml/min, and use a concentrator tube to receive the eluate.disk solid phase extraction
Fix the solid-phase extraction disk on the solid-phase extraction device, activate the solid-phase extraction disk with 5 ml of dichloromethane, 5 ml of methanol and 10 ml of hydrochloric acid solution in sequence, and keep the disk wet. After the water sample after acid-base distribution and purification is enriched through the solid phase extraction disc at a rate of 20ml/min-30ml/min, vacuum suction is continued until the disc is completely dry. Elute with 25 ml of dichloromethane and use a concentrator tube to receive the eluate.Extract concentrate
At room temperature, the extract was concentrated to 0.5ml-0.8ml with a nitrogen blowing concentrator, 10uL of internal standard standard solution was added, the volume was adjusted to 1.0ml with dichloromethane, and transferred to a sample bottle for testing.Specific detection steps
Chromatograph reference conditions
Injection port temperature: 220 °C, splitless injection; column flow: 1.0 ml/min; temperature program: 50 °C (hold for 5 min), rise to 250 °C at 8 °C/min (hold for 4 min).Mass Spectrometer Reference Conditions
Ion source temperature: 230°C; transfer line temperature: 260°C; voltage: 70eV. Other conditions refer to the requirements of the instrument manual. Data acquisition method: Selected ion scanning (SIM). Refer to the compound retention time and quantitative ion table for reference conditions such as the peak sequence, retention time, and quantitative ion of the target compound. Solvent delay time: 4 min.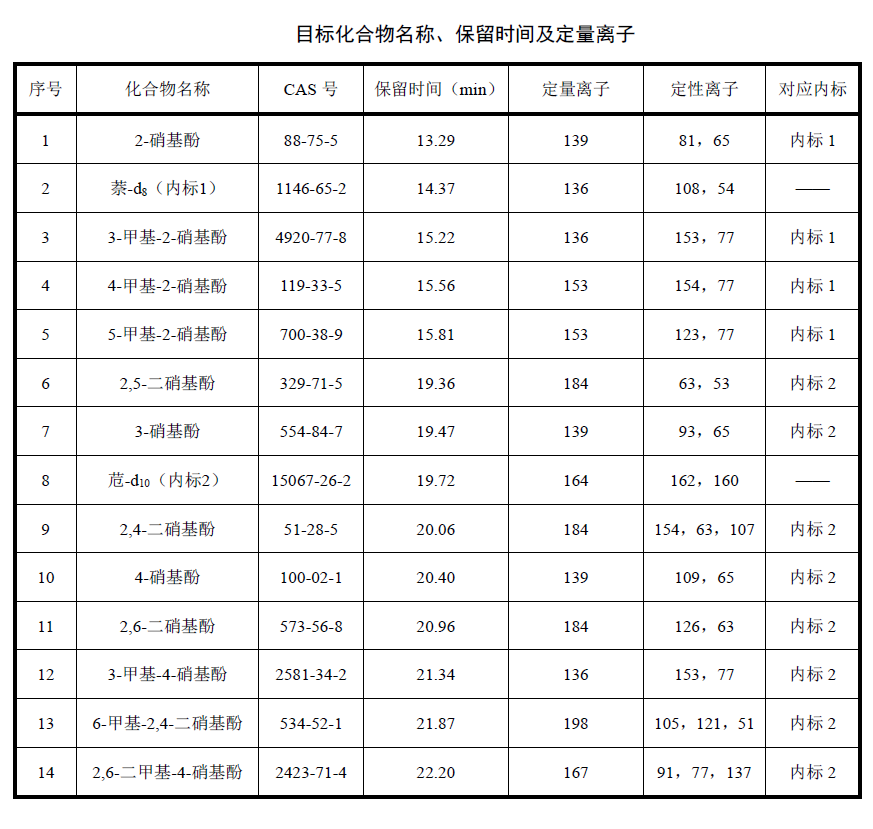
Instrument performance check
An instrument performance check was performed using a liquid-to-liquid gas chromatography-mass spectrometry system using decafluorotriphenylphosphine prior to sample analysis. Injection volume: 1.0uL; data acquisition mode: full scan, scan range: 45amu-500amu. Other analysis conditions refer to instrument analysis conditions. The abundance of the obtained mass ions should meet the requirements of the standard table of key ions and ion abundances.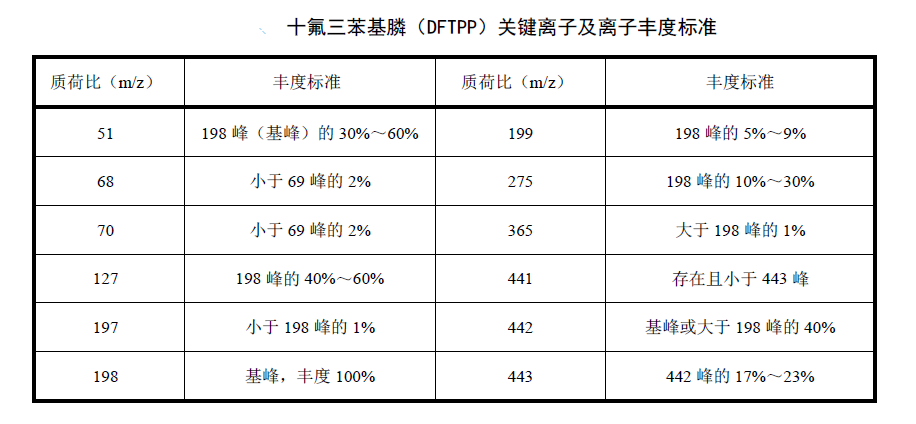
Preparation and determination of standard series
Take an appropriate amount of the standard solution of nitrophenolic compounds into the injection bottle, add 10ul of the standard solution of internal standard, and dilute to 1.0ml with dichloromethane. Prepare standard series with at least 5 concentration points. This is the reference concentration), and the internal standard concentration is 5.0 mg/L.According to the reference analysis conditions of the instrument, the standard series of solutions were injected and analyzed sequentially from low concentration to high concentration. Record the retention time of each target compound and the peak area of the quantitative ion mass spectrum peak.
Calculation of standard curve
Take the mass concentration (mg/L) of the target compound as the abscissa, and the product of the ratio of its corresponding peak area to the peak area of the internal standard and the internal standard concentration as the ordinate to establish a standard curve. The curve correlation coefficient should be ≥ 0.995.Reference Standard GC/MS
Selected ion chromatograms of standard solutions of nitrophenols (20.0 mg/L) under the reference analytical conditions of the instrument.
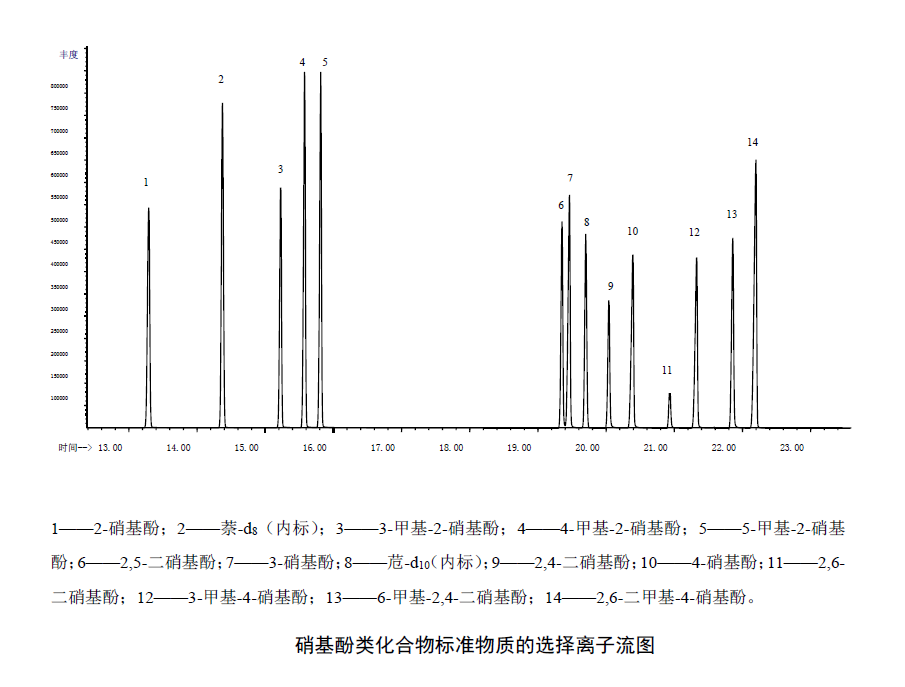
water sample testing
The water sample detection can be carried out according to the same instrument analysis conditions as the standard series of measurement, and the specific steps are carried out according to the preparation operation of the sample.Qualitative Analysis
By comparing the retention time, fragment ion mass-to-charge ratio and abundance of the target compound in the sample with the target compound in the standard series, the target compound is characterized. The standard solution should be analyzed multiple times to obtain the average retention time of the target compound. The average retention time ±3 times the standard deviation is used as the retention time window, and the retention time of the target compound in the sample should be within the range.Compare the relative abundance of qualifier ions and quantification ions of the target compound in the sample with the relative abundance of the target compound at the midpoint of the standard series, and the relative deviation should be within ±30%.
The content of nitrophenolic compounds in the final water can be calculated from the average relative response factor or standard curve.
Operation Precautions
1. The standard substances and organic solvents used in the experiment are toxic and harmful substances. The preparation of reagents and the pretreatment of water samples should be carried out in a fume hood; during operation, protective equipment should be worn as required to avoid contact with skin and clothing.2. The sampling volume can be appropriately adjusted according to the actual water sample conditions.
3. If the color of the organic phase is darker, the extraction times can be appropriately increased to 2-3 times.
4. When using the solid-phase extraction method, if the water sample contains a high concentration of suspended solids, the water sample can be filtered with a filter membrane first, and then the solid-phase extraction is performed.
5. For water samples with complex matrix and high organic content, in order to avoid penetration, two identical solid-phase extraction columns or disks can be used to extract the same water sample of different volumes. When the measurement result of the latter is lower than 20% of the former, it means that the adsorption capacity of the latter has reached saturation, and it is necessary to appropriately reduce the sampling amount or dilute the water sample before solid-phase extraction.



