Nitrosamines are one of the common substances when drinking water is industrially contaminated. Especially nitrosodimethylamine, there are high concentrations of nitrosodimethylamine in many industrial pollution events in natural water bodies. In addition, water plants and sewage treatment plants use chloramines and ozone to treat influent water. by-products.
There are many detection methods for nitrosamine compounds in water. Today we will talk about the operation process of gas chromatography. Gas chromatography mainly uses dichloromethane to extract nitrosamine compounds in the sample, then dehydrates and concentrates it, and then purifies it with a Florisil column or a basic alumina column to constant volume. Finally, after separation by capillary column, the concentration of hydrogen flame ionization detector was determined.

Reagents used for testing
1. Dichloromethane: pesticide residue grade.2. Methanol: pesticide residue grade.
3. Acetone: pesticide residue grade.
4. Pentane: pesticide residue grade.
5. Diethyl ether: pesticide residue grade.
6. Sodium thiosulfate: excellent grade pure.
7. Anhydrous sodium sulfate: excellent grade pure.
Before use, it should be burned in a muffle furnace at 450 ℃ for 4 hours, after cooling, put it in a ground glass bottle, seal it, and store it in a desiccator.
8. Sodium chloride: excellent grade pure.
Before use, it should be burned in a muffle furnace at 350 ℃ for 4 hours. After cooling, it should be put into a ground glass bottle and sealed, and stored in a desiccator.
9. Sulfuric acid: 1.84g/ml, excellent grade.
10. Sulfuric acid solution: 1+4 (v/v).
Prepared with sulfuric acid.
11. Sodium hydroxide: excellent grade pure.
12. Sodium hydroxide solution: 2mol/L.
Weigh 8.0 g of sodium hydroxide and dissolve it in an appropriate amount of water. After cooling to room temperature, dilute to 100 ml and mix well. Transfer to a plastic reagent bottle for preservation.
13. Florisil: 60-100 mesh.
Burn in a muffle furnace at 650 °C for 5 h, and store in a brown glass container with a glass stopper or a screw cap lined with aluminum foil after cooling. Before use, take an appropriate amount of calcined Florisil, activate it in a glass container lined with aluminum foil screw cap at 130 °C for 16 hours, add 2 ml of water, shake well and mix for 10 minutes, and let it stand for at least 2 hours before use.
14. Basic alumina: 100-200 mesh.
Weigh 100.0g of alumina into a 500ml brown glass container with a glass stopper or a screw cap lined with aluminum foil, add 2ml of water, shake well and mix for 10min, let stand for at least 2h before use.
15. Mixed standard stock solution: 2000mg/L.
Weigh 0.200g (accurate to 0.0001g) of N-nitrosodimethylamine, N-nitrosodiethylamine, N-nitrosodi-n-propylamine and N-nitrosodiphenylamine, respectively, and dissolve them in an appropriate amount of diphenylamine. Methyl chloride, transfer the full amount into a 10ml volumetric flask, dilute the volume to the mark with dichloromethane, mix well, refrigerate below 4°C, protect from light and seal for 6 months. Commercially available certified standard solutions can also be purchased directly.
16. Mixed standard solution: 200mg/L.
Accurately pipette 1.00ml of the mixed standard stock solution into a 10ml volumetric flask, dilute the volume to the mark with dichloromethane, mix well, refrigerate below 4°C, protect from light and seal for 2 months.
17. Glass wool: commercially available silanized glass wool.
18. Nitrogen: purity ≥99.999%.
19. Hydrogen: purity ≥99.99%.
20. Supporting gas: oil-free compressed air, purified by 5Å molecular sieve.
Instruments needed for testing
1. Gas chromatograph: with hydrogen flame ionization detector (FID), with split/splitless injection port, and the oven temperature can be programmed.2. Column Ⅰ: Quartz capillary column, column length 30 m × inner diameter 0.25 mm, film thickness 0.25 µm, the stationary phase is 5% diphenyl-95% dimethylpolysiloxane, or other equivalent columns .
3. Column Ⅱ: Quartz capillary column, column length 30 m × inner diameter 0.25 mm, film thickness 0.25 µm, the stationary phase is 35% diphenyl-65% dimethylpolysiloxane, or other equivalent columns .
4. Concentration device: rotary evaporator (or concentration device with the same function) and nitrogen blowing concentrator.
5. Chromatography column I: about 400 mm long × 22 mm inner diameter, used for the purification method of Florisil silica column.
6. Chromatography column II: about 300 mm long × 10 mm inner diameter, used for purification by basic alumina column.
7. Separation funnel: 500 ml, with PTFE stopper.
8. General laboratory instruments and equipment.
Water sample collection and storage requirements
When collecting, use a hard ground glass bottle or a screw-top glass bottle with a teflon material cover pad. The water sample should be filled with the sample bottle and sealed with a cap. It should be refrigerated below 4°C, protected from light, and transported. The samples should be extracted within 7 days after sampling. If the samples cannot be determined in time after extraction, they should be refrigerated below 4°C, protected from light and sealed, and the analysis and determination should be completed within 30 days.Preparation of water samples
Extraction and concentration
1. Measure 250ml of the sample into a 500ml separatory funnel, adjust the pH of the sample to 6-9 with sulfuric acid solution or sodium hydroxide solution, add 50ml of dichloromethane, shake and extract for 2min, let stand for 10min, and the two phases are layered. The organic phase was collected and the extraction was repeated 2-3 times. Combine the organic phases in a conical flask, add anhydrous sodium sulfate, dehydrate and dry.2. For samples that do not need purification, use a concentrating device to concentrate the extract to 1ml (V1) for testing. For samples that need to be purified, use a concentrating device to concentrate the extract to 5ml and wait for purification.
Purified water samples
For surface water, industrial wastewater and domestic sewage with complex composition, use Florisil column or alkaline alumina column for purification after extraction.Flory Silica Column Purification
Put about 0.5cm thick glass wool at the bottom of the column I, and then put 22.0g of activated Florisil, tap the column to make the contents sink down, and put the upper end of the Florisil on the bottom of the column I. Add about 0.5 cm thick anhydrous sodium sulfate. The column was rinsed with 40 ml of ether/pentane (15+85, v/v), the eluent was discarded, and 5 ml of the concentrated extract was added just before the anhydrous sodium sulfate layer was exposed to air.
The first elution was performed with 90ml ether/pentane (15+85, v/v), followed by the second elution with 100ml acetone/ether (5+95, v/v), and the two elutions were collected and combined liquid. Concentrate the collected eluate to 1.0ml (V1) using a concentrating device for testing.
Basic alumina column purification
Put about 0.5cm thick glass wool at the bottom of the column II, and then put 12.0g of the prepared basic alumina, tap the column to make the contents sink down, add about 12.0g to the top of the basic alumina layer 1cm thick anhydrous sodium sulfate. The column was rinsed with 10 ml of ether/pentane (3+7, v/v), the eluent was discarded, and 5 ml of the concentrated extract was added just before the anhydrous sodium sulfate layer was exposed to air.The first elution was performed with 10 ml ether/pentane (3+7, v/v), followed by the second elution with 60 ml ether/pentane (1+1, v/v), and the two washes were collected and combined. Deliquoring. Concentrate the collected eluate to 1.0ml (V1) using a concentrating device for testing.
Preparation of blank samples
Measure 250ml of the same batch of experimental water instead of the sample, and prepare a blank sample according to the same steps as the sample preparation.Specific detection steps
Instrument Reference Conditions
The optimal working conditions of different models of gas chromatographs are different, and the operation should be carried out in accordance with the instrument manual. Commonly used instrument reference conditions are as follows:Injection port temperature: 250°C.
Injection method: split injection with a split ratio of 5:1.
Column oven temperature: the initial temperature was 50 °C, maintained for 2.5 min, and then increased to 220 °C at a rate of 30 °C/min, and maintained for 4 min.
Column flow: nitrogen 1.2 ml/min.
Injection volume: 1.0ul.
Detector temperature: 300°C; gas: hydrogen flow 30ml/min; auxiliary gas: air flow 400ml/min.
Plotting the calibration curve
Take six 5ml volumetric flasks, add appropriate amount of dichloromethane respectively, add 25.0ul, 50.0ul, 100.0ul, 150.0ul, 200.0ul, 250.0ul mixed standard solution, dilute to volume with dichloromethane, shake well, and prepare Mixed standard series with mass concentrations of 4 nitrosamine compounds of 1.00mg/L, 2.00mg/L, 4.00mg/L, 6.00mg/L, 8.00mg/L and 10.0mg/L, respectively. According to the reference conditions of the instrument, the determination is performed sequentially from low concentration to high concentration. Take the mass concentration (mg/L) of nitrosamine compounds as the abscissa, and the peak area or peak height as the ordinate, and draw a calibration curve.
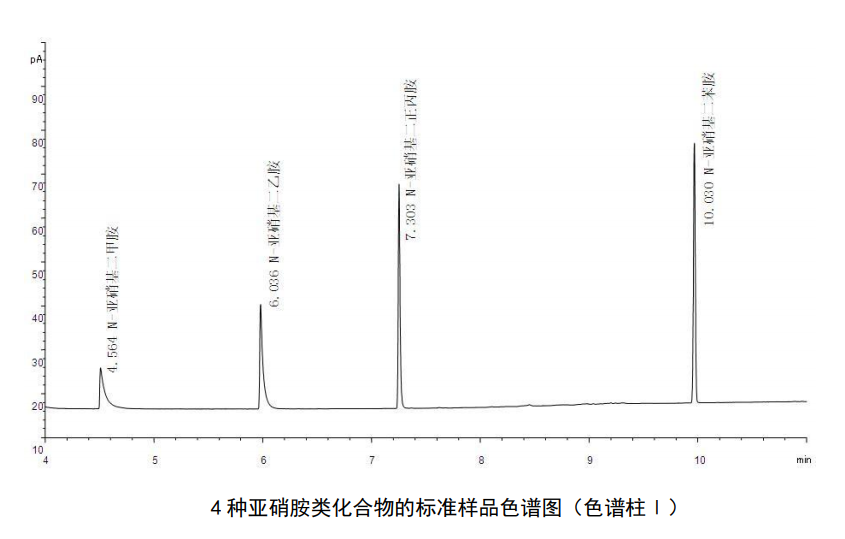
water sample testing
Accurately pipette 1.00ul of the prepared sample, and measure it according to the same instrument reference conditions and steps as for drawing the calibration curve. The quantitative analysis uses the external standard standard curve method, and the mass concentration of the target compound in the water sample can be calculated according to the formula.
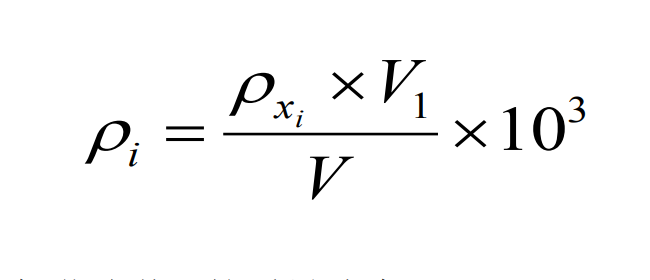
This method is derived from 《Water Quality - Determination of Nitrosamine Compounds - Gas Chromatography》



