The methyl tert-butyl ether in the water is purged with high-purity helium (or nitrogen) and then adsorbed in the trapping tube. The trapping tube is rapidly heated and backflushed with high-purity helium (or nitrogen), and then desorbed by heat. The components were separated by gas chromatography and detected by mass spectrometry. Qualitative by comparison with the retention time of the standard substance and the relative abundance of key ions, and quantified by the internal standard method.

Reagents required for testing
1. Methanol: chromatographically pure.2. Standard stock solution of methyl tert-butyl ether: 2000 mg/L, dissolved in methanol.
Commercially available certified standard solution, stored in accordance with the instructions.
3. Methyl tert-butyl ether standard solution: 20.0 mg/L.
Dilute the methyl tert-butyl ether standard stock solution with methanol to prepare, transfer to a brown reagent bottle with a teflon liner screw cap, and store it for one month at 0-4°C in the dark.
4. Internal standard stock solution: fluorobenzene, 2000 mg/L, dissolved in methanol.
Commercially available certified standard solutions should be selected and stored in accordance with the instructions.
5. Internal standard standard solution: 10.0mg/L, dissolved in methanol.
Dilute the internal standard stock solution with methanol to prepare, transfer to a brown reagent bottle with a teflon-lined screw cap, and store at 0-4°C in the dark for one month.
6. 4-Bromofluorobenzene (BFB), 25ug/ml, commercially available certified standard solution.
7. Helium, purity ≥99.999%.
8. Nitrogen, purity ≥99.999%.
Instruments used for testing
1. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometer: The chromatographic part has a split/splitless injection port, and the temperature can be programmed. The mass spectrometer part has an electron impact (EI) ionization source, and has functions such as manual/automatic tuning, data acquisition, quantitative analysis and spectral library retrieval.2. Purge and trap device: with 5ml purge tube. The trap tube uses 1/3 Tenax, 1/3 silica gel, 1/3 activated carbon mixed adsorbent or other equivalent adsorbents.
3. Chromatographic column: Quartz capillary column, 60m×0.32mm, film thickness 1.8um, stationary phase is 6% nitrile propylphenyl/94% dimethylpolysiloxane, or other equivalent capillary column.
4. Vials: 40ml amber wide-mouth glass vials with teflon-lined screw caps.
5. Air tight syringe: 10ul, 25ul, 50ul, 250ul.
6. General laboratory instruments and equipment.
Collection and preservation of water samples
The water sample is slowly introduced into the water sample bottle along the wall until the bottle is full, the escape of methyl tert-butyl ether due to agitation should be minimized, and the introduction of air bubbles into the sampling bottle should be avoided. Water samples were refrigerated and transported at about 4°C after collection. Analysis should be carried out as soon as possible after returning to the laboratory, otherwise it should be refrigerated at 1-4 ℃, and the analysis should be completed within 14 days.Water sample testing process
Instrument testing reference conditions
Purge and trap reference conditionsSampling volume: 5ml; Purge temperature: 40°C; Purge flow rate: 40ml/min; Purge time: 11min; Desorption temperature: 180°C; Desorption time: 2min; Baking temperature: 180°C; Baking time: 10min; other parameters are set according to the instruction manual.
Gas Chromatography Analysis Reference Conditions
Program temperature: 45°C for 2.0min, rise to 120°C at 10°C/min, then rise to 200°C at 20°C/min, hold for 1.0min; inlet temperature 200°C; carrier gas flow: 2.0ml/min; Injection method: split injection (split ratio 10:1).Mass Spectrometry Reference Conditions
Electron bombardment source: EI source; ionization energy: 70 eV; ion source temperature: 230 °C; transmission line temperature: 250 °C; solvent delay time: 5.0 min; scanning mode: full scan; selected ion scan (SIM). Target scan ions: 73, 55, 57; quantitative ions: 73; internal standard scan ions: 96, 70, 50; quantitative ions: 96.Instrument performance check
Before analyzing a sample, a gas chromatograph-mass spectrometer must undergo an instrument performance check. Draw 2ul of 4-bromofluorobenzene and inject directly through the gas chromatography injection port or use a volumetric flask to prepare an aqueous solution of 4-bromofluorobenzene with a concentration of 25.0ug/L, then inject the sample through the purge and trap device, and use the gas chromatography- The mass spectrometer is used for analysis, and the analysis conditions refer to the relevant calibration standards. The obtained 4-bromofluorobenzene key ion abundance should meet the requirements in Table 1, otherwise the parameters of the mass spectrometer should be adjusted or the ion source should be cleaned.Establishment of calibration curve
Pipette a certain amount of methyl tertiary butyl ether standard solution and quickly add it to a 50ml volumetric flask containing experimental water, make up to the mark, and prepare the concentration series as 1.0ug/L, 5.0ug/L, 10.0ug/L , 20.0ug/L and 50.0ug/L standard. Use a 5ml air-tight syringe to draw 5.0ml of the standard solution, add 5.0ul of the internal standard standard solution, measure from low concentration to high concentration in accordance with the relevant instrument detection reference conditions, and record the standard series of targets and the retention time of the internal standard , Quantitative ion response value.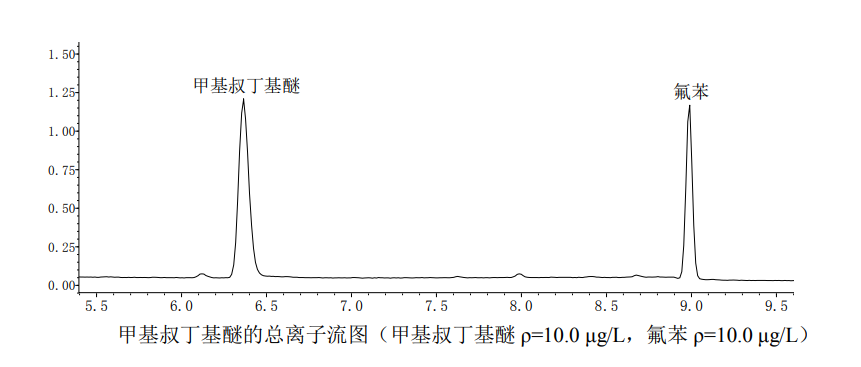
Detection steps
After the water sample returned to room temperature, use an airtight syringe to draw 5.0ml of water sample, and add 5.0ul of internal standard standard solution to the water sample to make the internal standard concentration in the water sample 10.0ug/L. Quickly inject it into the purge tube, and use the corresponding calibration curve to measure according to the reference conditions of the instrument. Purge and trap instruments with autosamplers can be operated by referring to the instrument instructions.Qualitative analysis can be used to identify the target by comparing the retention time, mass spectrum, mass-to-charge ratio of fragment ions and their abundance of the target in the water sample with the target in the standard series. The standard solution should be analyzed multiple times to obtain the average retention time of the target. The average retention time ± 3 times the standard deviation is used as the retention time window, and the retention time of the target in the water sample should be within the range.
When the quantitative analysis can be calculated by using the average relative response factor, the mass concentration ρx of methyl tert-butyl ether in the water sample is calculated according to the formula.



