In some microbiology laboratories or places that require aseptic operation, the help of biological indicators is needed to understand the specific effect of sterilization. Usually, sterilization refers to killing all target microorganisms by physical or chemical means, so that they can reach the level of sterility protection. Generally, the most commonly used sterilization methods are chemical reagents, rays, moist heat, dry heat and filtration. Different methods are used for different microorganisms. To verify the effect of these methods, some live microorganisms with sterilization tolerance are needed as indicators for judgment.
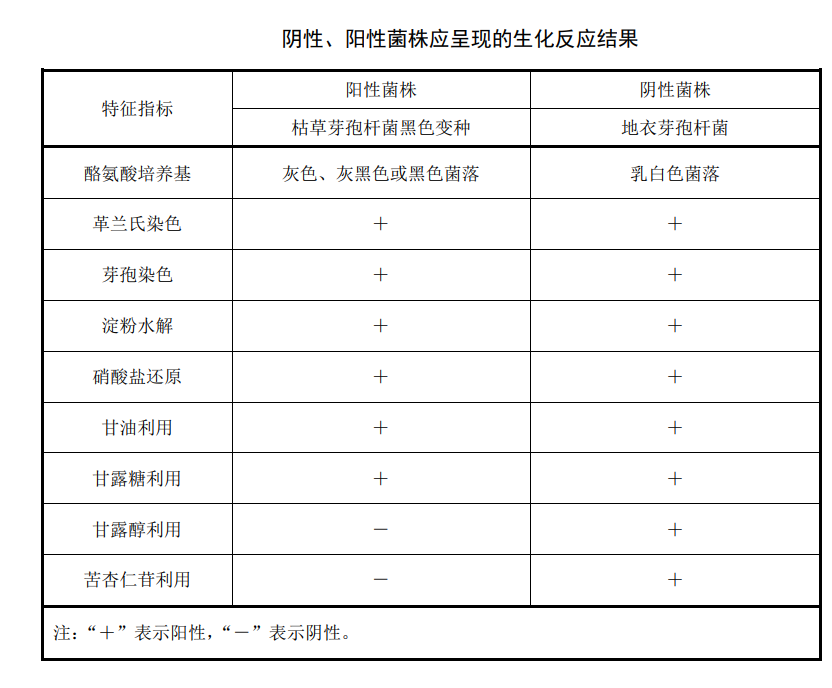
The Bacillus subtilis black variant we are going to talk about today is mainly used in the verification of the disinfection effect of various medical institutions and the pharmaceutical industry. Bacteria and spores are trapped on the filter membrane, then the filter membrane is placed on the tyrosine agar medium, and cultured at 36℃±1℃ for 72h-96h, the tyrosinase produced by Bacillus subtilis var. Can break down and use tyrosine to form melanin, resulting in black characteristic colonies. The characteristic colonies were further identified by biochemical tests after staining and microscopic examination. They could use glycerol and mannose, reduce nitrate and hydrolyzed starch, but could not use amygdalin and mannitol, and were confirmed to be the characteristics of Gram-positive Bacillus. The colony was Bacillus subtilis black variant, and the identification result was positive.
Reagents used for testing
1. Tyrosine agar medium.2. Nutrient agar medium.
3. Starch medium and iodine solution.
4. Nitrate reduction medium and related reagents.
5. Glycerol Fuhong broth medium.
6. Mannose biochemical medium.
7. Mannitol biochemical medium.
8. Amygdalin biochemical medium.
9. Gram stain.
10. Spore staining solution.
11. Negative control bacteria: such as Bacillus licheniformis.
12. Positive control bacteria: Bacillus subtilis black var.
13. Bacillus subtilis var. niger spore suspension
Prepared in accordance with the provisions of the "Disinfection Technical Specifications", the commercially available Bacillus subtilis var. niger spore suspension with a concentration range of 106CFU/ml-109CFU/ml can also be purchased.
14. Sterile filter membrane: cellulose acetate filter membrane with a diameter of 50mm and a pore size of 0.45μm.
Bandage according to the requirements of aseptic operation, sterilize by high pressure steam at 121°C for 20 minutes, and dry it for later use; or put the filter membrane in a beaker, add experimental water, boil and sterilize 3 times, 15min/time, and change after the first 2 times of boiling Wash with water 2-3 times. Commercially available sterile filters can also be used.
15. Paraffin parafilm.
16. Sterile water: Take an appropriate amount of experimental grade pure water, sterilize it by high pressure steam at 121 °C for 20 min, and set aside.
Reagents required for testing
1. Sample bottle: 250ml, 500ml wide-mouth glass bottle with screw cap or ground stopper.2. Constant temperature incubator: 36℃±1℃.
3. Autoclave: 121℃, adjustable.
4. pH meter: accurate to 0.1 pH unit or more. pH precision test paper can also be used.
5. Microscope: objective lens 4× or 5×, 10×, 20×, 40×, oil lens 100×, eyepiece 10× or 15×.
6. Analytical balance: the actual division value is 0.0001g.
7. Petri dish: 90mm in diameter.
8. Filtration device: equipped with sand core filter, cylindrical glass funnel and vacuum pump, the suction filtration pressure is not lower than -50kPa.
9. Inoculation loop: 1mm-3mm in diameter.
10. Tweezers: stainless steel or disposable sterile plastic tweezers.
11. Graduated pipette: 1ml, 10ml. Adjustable pipettes can also be used.
12. Measuring cylinder: 100ml.
13. Erlenmeyer flask: 100ml.
14. Alcohol lamps.
15. Test tube: 10ml.
16. Aseptic operation equipment: sterile room, ultra-clean workbench, biological safety cabinet.
17. General laboratory instruments and equipment.
water sample collection
When evaluating the sterilization effect of using high temperature and high pressure sterilization equipment, take a sample bottle, add Bacillus subtilis var. black spore suspension and 200ml sterile water to make the final concentration of Bacillus subtilis var. black spores in the mixture reach 5×104CFU/ml- 5×105 CFU/ml. After the sterilization treatment, take out the sample bottle and test the water sample for sterilization biological indicator (Bacillus subtilis black var.When evaluating the sterilization effect of other sterilization equipment, take an appropriate amount of Bacillus subtilis var. black spore suspension and add it to the sterilization equipment before sterilization, so that the final concentration of Bacillus subtilis var. black spores in the water sample reaches 5×104CFU/ml-5 ×105CFU/ml. After the sterilization treatment is completed, water samples are collected from the sterilization equipment for the detection of sterilization biological indicators (Bacillus subtilis black var. The sampling volume is generally about 80% of the sample bottle capacity, and the sample bottle should not be washed with the sample. Immediately after sample collection, wrap the vial with sterile wrapping paper.
The samples should be tested within 2 hours after collection, otherwise they should be stored and transported under refrigeration below 10°C, but not more than 6 hours. If the laboratory cannot carry out the test immediately after receiving the sample, the sample should be refrigerated below 4°C and tested within 2 hours.
water sample filtration
Use sterile tweezers to aseptically grasp the sterile filter and place it on the sterilized filter device, and fix the filter device. After fully mixing the sample, take 100 ml of suction filtration, and rinse the inner wall of the filter 2-3 times with sterile water. After the sample is filtered, pump the air for about 5s and turn off the switch. Before filtration, adjust the pH of the sample to 7.0-8.0 according to the requirements of aseptic operation.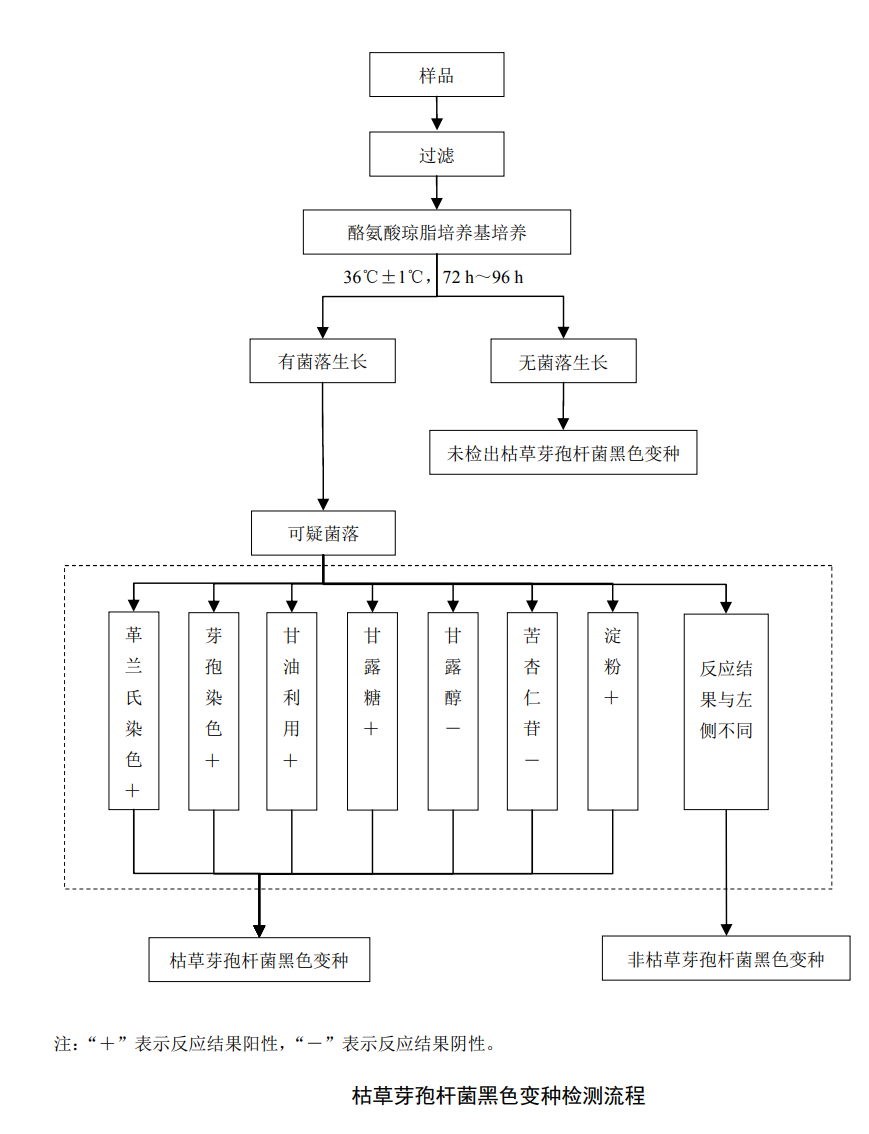
Cultivation process
Use sterilized tweezers to pick up the filter membrane and place it on the tyrosine agar medium, with the bacteria-retaining surface of the filter membrane facing upward, the filter membrane should be completely close to the medium, and there should be no air bubbles between them, and then use paraffin parafilm. Seal the petri dish, invert the petri dish, put it in a constant temperature incubator, and incubate at 36℃±1℃ for 72h-96h.After culturing for 96h, if no colony grows on the medium, the test is terminated; if there is colony growth on the medium, pick the characteristic black colonies on the nutrient agar medium, and cultivate at 36℃±1℃ for 24h, pending identification. At the same time, the tyrosine agar culture dish with the picked colonies was stored at 2°C-5°C for review when necessary.
stain microscopy
Pick black or suspicious colonies and stain them with Gram staining solution and spore staining solution respectively. For Bacillus subtilis black var. gram staining and spore staining microscopic examination, please refer to the relevant microscopic examination diagrams. Bacillus subtilis black var. Lamella-positive bacteria, vegetative cells are rod-shaped, single or arranged in short chains.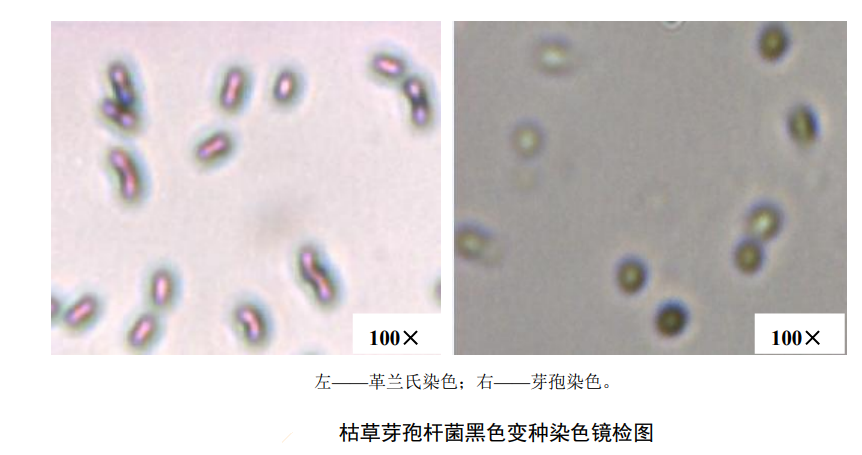
Biochemical experiments
Pick black or suspicious colonies and inoculate them on starch medium, nitrate reduction medium, glycerol red broth medium, mannose biochemical medium, mannitol biochemical medium and amygdalin biochemical medium respectively.Blank control experiment
Use sterile water to operate in accordance with the filtration and culture steps; no colonies should grow on the plate medium after 96 hours of culture, otherwise, the sample identification result will be invalid, and the cause should be re-sampled and tested.Negative and positive controls
The negative control bacteria and positive control bacteria were made into bacterial suspensions with a concentration of 40CFU/L-600CFU/L, and the operations were performed according to the steps of filtration, culture and experiment respectively. The biochemical reaction results presented by the negative and positive control bacteria should be consistent with the results listed in the reference table, otherwise the water sample identification result will be invalid.