At present, if you want to know whether surface waters such as rivers, lakes, and reservoirs are eutrophic, you can judge by detecting the content of nutrients such as phosphorus and nitrogen in the water, or by observing the reproduction of algae in the water. But what we are going to talk about today is to determine whether the water body is eutrophic by detecting chlorophyll a in the water. We all know that the most important manifestation of water eutrophication is the proliferation of algae in water, and all algae contain chlorophyll a. Therefore, the amount of algae in the water can be judged by the content of chlorophyll a in the water body.
The principle of the method is to filter a certain amount of samples with a filter membrane to retain algae, grind and break algal cells, extract chlorophyll with acetone solution, and measure the absorbance of the extract at wavelengths of 750nm, 664nm, 647nm and 630nm after centrifugation, and calculate the chlorophyll in water according to the formula. the concentration of a.

Reagents and instruments required for testing
Experimental reagents
1 Acetone.
2 Magnesium carbonate.
3 Acetone solution: 9+1.
Add 100 ml of experimental water to 900 ml of acetone.
4 Magnesium carbonate suspension.
Weigh 1.0g of magnesium carbonate, add 100ml of experimental water, and stir to form a suspension (shake well before use).
5 Glass fiber membrane: diameter 47mm, pore size is 0.45um-0.7um.
laboratory apparatus
1 Sampling bottle: 1L or 500ml brown glass bottle with ground stopper.
2 Filter device: equipped with vacuum pump and glass sand filter device.
3 Grinding device: glass mortar or other tissue grinder.
4 Centrifuge: The relative centrifugal force can reach 1000×g (speed 3000r/min~4000r/min).
5 Glass graduated centrifuge tube: 15ml, the screw cap material does not react with acetone.
6 Visible spectrophotometer: with 10mm quartz cuvette.
7 Syringe filter: 0.45um PTFE organic phase needle filter.
8 General laboratory instruments and equipment.
Water sample collection and preservation
The collection of water samples generally uses plexiglass water collectors or other appropriate samplers to collect water samples 0.5m below the water surface. Lakes and reservoirs can be stratified or mixed as needed, and the sampling volume is 1L or 500ml. If the water sample contains sedimentary solids (such as sediment, etc.),
Shake the water sample well, pour it into a 2L graduated cylinder, let it stand in the dark for 30 minutes, take a water sample 5cm below the water surface, and transfer it to a sampling bottle. Add 1 ml of magnesium carbonate suspension to each liter of water sample to prevent acidification from causing pigment dissolution.
Water samples should be stored and transported at 0°C-4°C in the dark after collection, and transported to the testing laboratory for filtration within 24 hours (if the water sample cannot be delivered to the testing laboratory within 24 hours, it should be filtered on site, and the filter membrane should be transported refrigerated in the dark), The water sample filter was stored at -20°C in the dark, and the analysis was completed within 14 days.
Prepare water samples
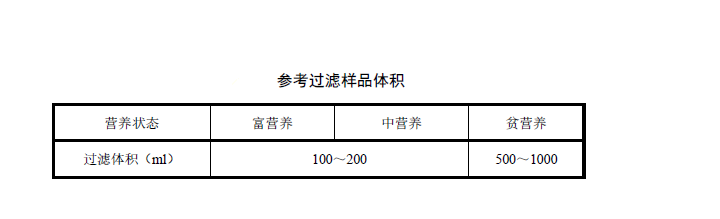
Install the glass fiber filter on the filter unit. Determine the sampling volume according to the nutritional state of the water body. For details, refer to the volume of the filtered water sample. Measure a certain volume of the mixed water sample with a measuring cylinder, filter it, and finally rinse the filter wall with a small amount of distilled water. The negative pressure during filtration should not exceed 50kPa. The suction filtration is ended when the water sample has just completely passed through the filter membrane. The filter membrane is taken out with tweezers, the side with the water sample is folded in half, and the filter membrane is dried with filter paper.
grind
Place the sample filter in the grinding device, add 3ml-4ml of acetone solution, and grind to a paste. Add 3ml-4ml of acetone solution, continue grinding, and repeat 1-2 times to ensure sufficient grinding for more than 5min. The completely broken cell extract was transferred to a glass graduated centrifuge tube, the mortar and grinding pestle were rinsed with acetone solution, and transferred to a centrifuge tube together, and the volume was adjusted to 10ml.
Soak extraction
After fully vibrating and mixing the grinding extract in the centrifuge tube, wrap it in aluminum foil, and place it at 4°C in the dark for more than 2 hours, but not more than 24 hours. Shake upside down 2-3 times during soaking.
Centrifugal
Put the centrifuge tube into the centrifuge and centrifuge at a relative centrifugal force of 1000×g (3000 r/min ~ 4000 r/min) for 10 min. Then filter the supernatant with a needle filter to obtain an acetone extract (sample) of chlorophyll a for testing.
Detection steps
Water sample determination
The sample was moved to a cuvette, and the acetone solution was used as the reference solution to measure the absorbance at wavelengths of 750 nm, 664 nm, 647 nm, and 630 nm. The absorbance at the wavelength of 750nm should be less than 0.005, otherwise it needs to be filtered again with a needle filter and then measured.
The mass concentration of chlorophyll a in the final water sample can be calculated according to the corresponding formula.
The above content comes from 《HJ 897-2017 Water Quality Determination of Chlorophyll a Spectrophotometry》



